10 Essential Insights on Malware Security Risks for Defense Contractors
Explore essential insights on malware security risks for defense contractors to enhance cybersecurity.

Introduction
Malware security risks have become a pressing concern for defense contractors, especially as cyber threats grow more sophisticated and widespread. Alarmingly, only 1% of U.S. security suppliers feel fully prepared for the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC). This statistic underscores the urgent need for effective risk management. As organizations navigate the complexities of various malware types and delivery methods, a critical question emerges: how can defense contractors protect sensitive information while ensuring compliance and operational integrity in an ever-evolving threat landscape?
This article explores essential insights and strategies to help defense firms navigate the multifaceted world of malware security. By understanding these challenges, contractors can bolster their defenses and contribute to safeguarding national security. Are you ready to take action and enhance your organization's cybersecurity posture?
CMMC Info Hub: Comprehensive Guidance on Malware Security Risks for Defense Contractors
CMMC Info Hub serves as a vital resource for military suppliers, providing comprehensive guidance on malware security risks posed by harmful software. It features organized articles and practical approaches that demystify the complexities of software threats, empowering organizations to bolster their security posture. Alarmingly, recent findings indicate that only 1% of U.S. security suppliers feel fully prepared for the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC). This underscores the pressing need for effective threat risk management. With the emergence of AI-driven threats, cyber attacks have become increasingly covert and adaptable, necessitating a proactive cybersecurity strategy.
To combat these evolving threats, defense firms must prioritize robust security strategies to address malware security risks. Statistics reveal that fewer than 50% of surveyed contractors have implemented essential security controls, and only 29% utilize secure backup technologies. This significant gap in preparedness poses a risk to sensitive information and national security.
Effectively managing malware security risks associated with malicious software involves integrating security criteria into supplier agreements—a practice currently adopted by only 22% of CMMC organizations. By fostering a culture of measurement discipline and governance, organizations can enhance their resilience against cyber threats. CMMC Info Hub transforms uncertainty into clarity, equipping businesses to confront these challenges and ensuring they are ready to meet compliance requirements while effectively managing security threats. As a proactive measure, security firms should assess their existing protective strategies and identify areas for improvement to strengthen their overall cybersecurity posture.

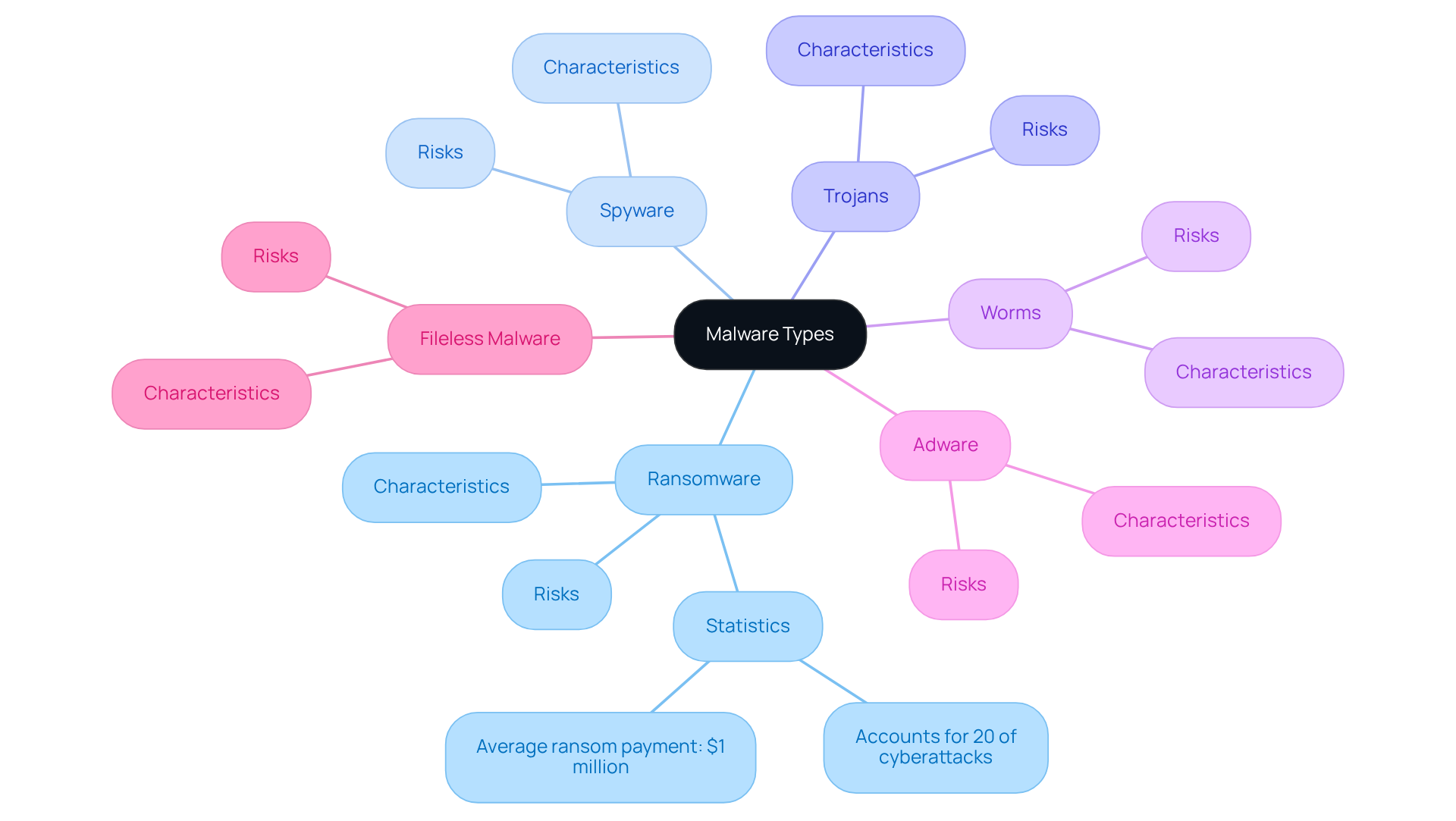
Malware Types: Key Variants Every Defense Contractor Must Recognize
Defense contractors must remain vigilant about several key malware variants that pose significant risks to their operations:
-
Ransomware: This type of malware encrypts files and demands payment for decryption. Ransomware accounts for approximately 20% of all cyberattacks, and in 2025, the average ransom payment reached nearly $1 million. This highlights the financial stakes involved. Notably, multi-extortion ransomware has become the norm, combining data encryption with threats to leak sensitive information, which adds pressure on victims.
-
Spyware: Designed to monitor user activity, spyware collects sensitive information without the user's consent. The prevalence of malware security risks among defense contractors necessitates robust detection and prevention measures, as it can lead to significant data breaches.
-
Trojans: Often disguised as legitimate software, Trojans create backdoors for attackers, allowing them to infiltrate systems undetected. This kind of malicious software is especially hazardous, enabling additional attacks once within the network.
-
Worms: Self-replicating software that spreads across networks, worms can quickly compromise multiple systems, making them a significant threat to organizational integrity.
-
Adware: While primarily known for displaying unwanted advertisements, adware can lead to more severe infections and may serve as a gateway for other types of malware.
-
Fileless Malware: This emerging threat operates in memory and uses legitimate tools, making it difficult to detect. Its rise in 2025 underscores the need for defense contractors to adapt their detection strategies.
Identifying these categories is crucial for formulating effective strategies to address malware security risks. As cybersecurity expert Micheal Small emphasizes, "The adversaries are agile. Their tactics are evolving. And so must we."
To protect sensitive information from these evolving threats, contractors must apply robust cyber hygiene practices and embrace a Zero Trust strategy. Are you prepared to take action against these risks?
Impact of Malware: Consequences for Defense Operations and Security
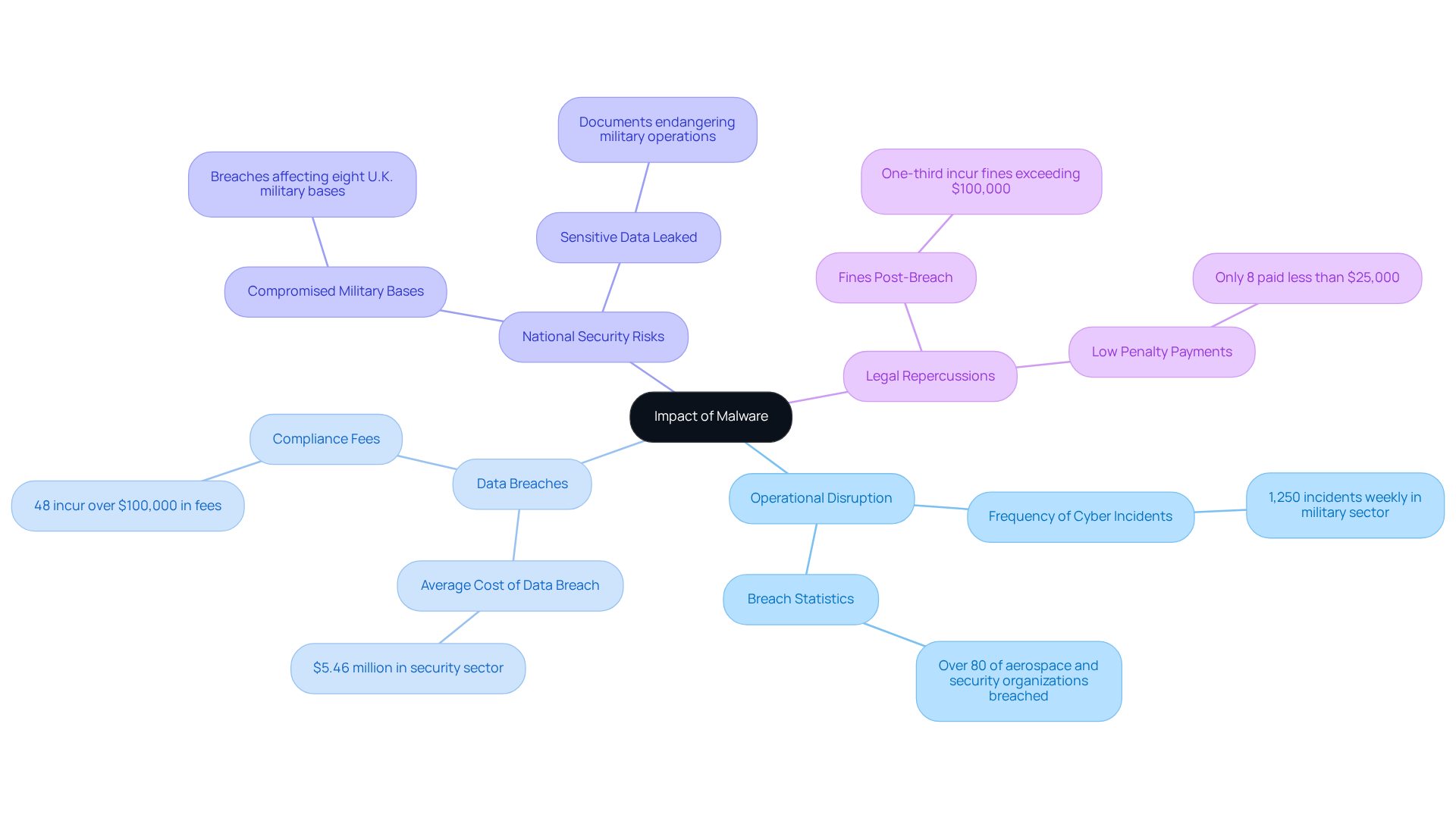
Malware attacks pose severe threats to defense operations, leading to a range of detrimental consequences:
-
Operational Disruption: Malware can incapacitate essential operations, causing project delays and jeopardizing contract fulfillment. In 2025, the military sector reported an alarming 1,250 cyber incidents weekly, underscoring the frequency of such disruptions. Significantly, over 80% of aerospace and security organizations have encountered a breach in the past 12 months, emphasizing the widespread nature of these threats.
-
Data Breaches: The theft of sensitive information can result in substantial financial losses and reputational harm. The average expense of a data breach in the security sector reached roughly $5.46 million, and 48% of companies penalized after a data breach incur over $100,000 in compliance fees, highlighting the financial stakes involved.
-
National Security Risks: Compromised systems can jeopardize national security by revealing vital security information to adversaries. Recent breaches affecting eight U.K. military bases, including RAF Lakenheath, have raised significant concerns about the implications for military operations and personnel safety. The leaked data included sensitive documents about RAF bases, potentially endangering military operations and personnel security.
-
Legal Repercussions: Organizations may face legal actions and regulatory penalties for inadequate protection of sensitive data. In 2025, over one-third of organizations incurred fines following data breaches, with many facing costs exceeding $100,000. Furthermore, only 8% of fined organizations paid less than $25,000, emphasizing the significant financial impact of legal repercussions.
The consequences of malware security risks go beyond immediate operational effects, jeopardizing the integrity of national security and the legal position of contractors. As the landscape of online threats changes, it is essential for organizations to implement strong protective measures to guard against malware security risks.
Malware Delivery Methods: How Threats Enter Defense Networks
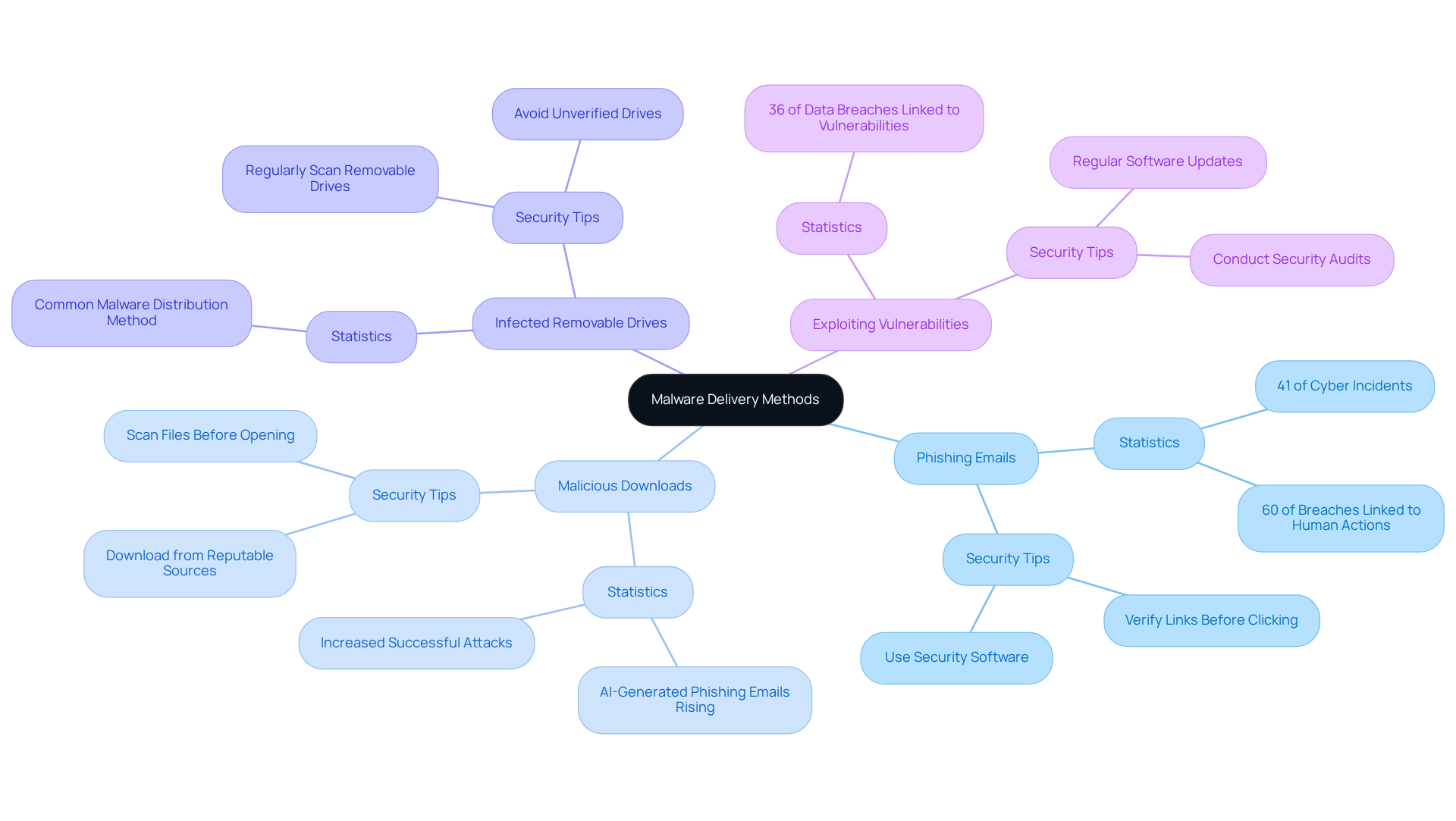
Malware can infiltrate defense networks through various delivery methods, each posing significant malware security risks to cybersecurity. Understanding these methods is crucial for security firms to implement effective protective strategies and mitigate the security risks associated with malware. Here are some key methods:
-
Phishing Emails: These deceptive emails are designed to trick users into clicking malicious links or downloading infected attachments. Phishing remains a major attack vector, responsible for 41% of all cyber incidents, often serving as the initial step in deploying harmful software. Are you cautious enough about emails from unknown sources? Always verify links before clicking.
-
Malicious Downloads: Software or files downloaded from untrusted sources can harbor concealed threats. With the rise of AI-generated phishing emails in 2025, these downloads have become increasingly convincing, contributing to malware security risks and a surge in successful attacks. Ensure that your downloads come from reputable sites, and consider using security software to scan files before opening them.
-
Infected Removable Drives: USB drives or external devices can unknowingly transport harmful software from one system to another. This method exploits the convenience of portable storage, making it a common means for malware distribution. To safeguard your systems against malware security risks, avoid using unverified removable drives and regularly scan them for threats.
-
Exploiting Vulnerabilities: Attackers often exploit software vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to systems. In 2025, vulnerabilities contributing to malware security risks were linked to 36% of all data breaches, highlighting the importance of regular software updates and patch management. Are your systems up-to-date? Conduct regular security audits to ensure all software is current.
Be wary of external links in emails and websites, as they can lead to untrusted sources that may compromise your systems. As information security architect Mohammed Khalil states, "True readiness in this new era requires a fundamental shift in mindset." Taking proactive measures today can significantly enhance your cybersecurity posture.
Legal Implications: Regulatory Consequences of Malware Incidents
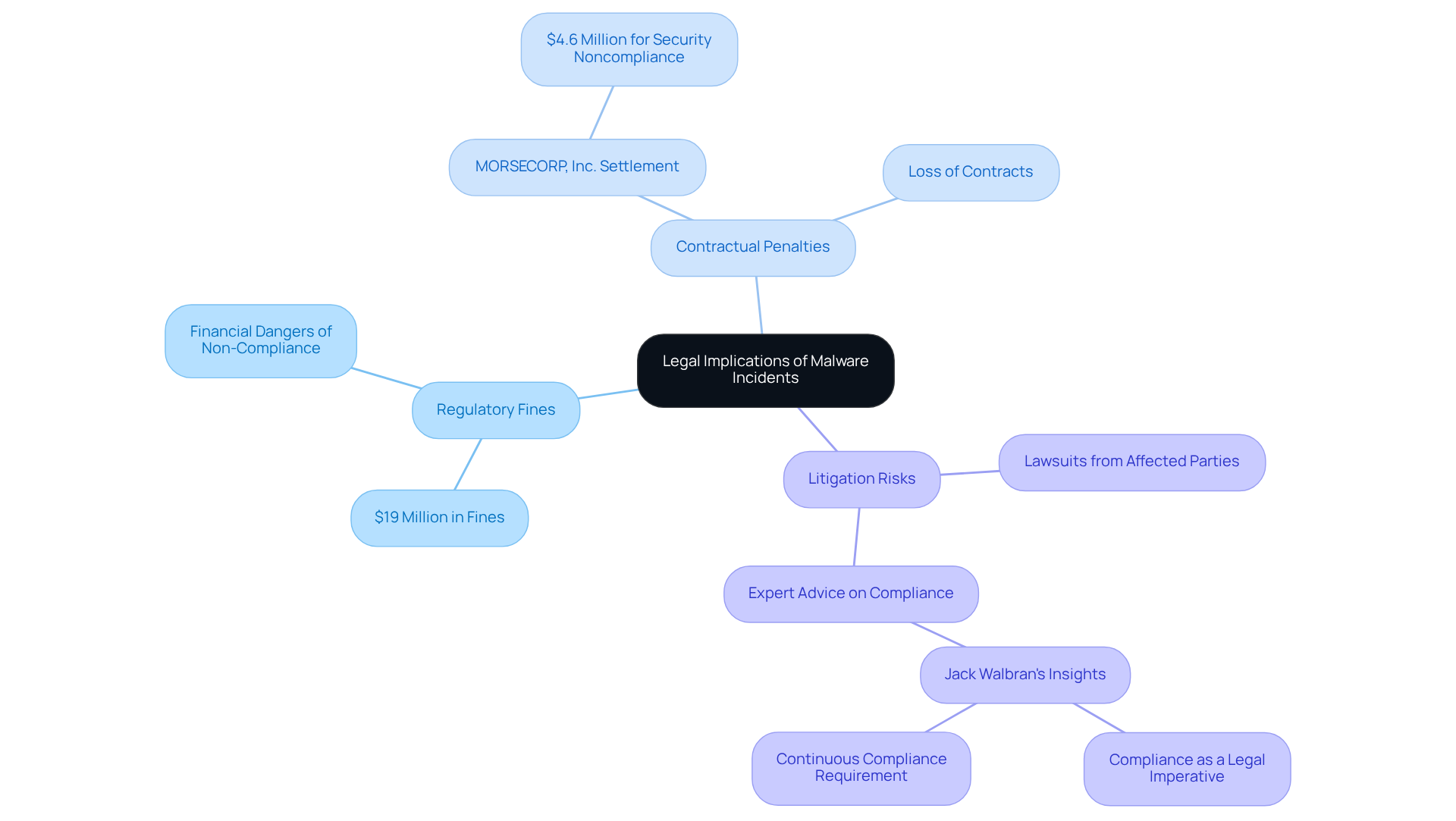
Malware incidents can have profound legal implications for defense contractors, touching on several critical areas that demand attention:
-
Regulatory Fines: Non-compliance with cybersecurity regulations can lead to substantial fines from regulatory bodies. For instance, the Department of Justice has enforced fines totaling $19 million on various firms for security breaches. This underscores the financial dangers linked to inadequate protective measures, particularly for military sector suppliers who must manage malware security risks while adhering to strict regulations.
-
Contractual Penalties: Breaches may result in the loss of contracts or penalties imposed by the Department of Defense. A recent example is the $4.6 million agreement with MORSECORP, Inc. for security noncompliance, illustrating the severe financial consequences that can arise from failing to meet contractual obligations related to data protection. This situation serves as a clear reminder of the repercussions of non-compliance, emphasizing the necessity for defense suppliers to uphold stringent security measures.
-
Litigation Risks: Organizations may face lawsuits from affected parties if sensitive data is compromised due to negligence. Legal experts, including Jack Walbran, stress that compliance is not merely a checkbox; it is a legal, financial, and operational imperative. The expectation is clear: those responsible must verifiably implement required controls and maintain continuous compliance to mitigate these risks.
The repercussions of failing to comply with security standards are not merely theoretical, as they include significant malware security risks. The MORSE settlement provides a practical checklist for compliance-minded organizations, highlighting the necessity for complete system security plans and accurate compliance reporting. Moreover, companies can inadvertently fall out of compliance due to routine operational changes, such as expanding network boundaries or shifting to cloud infrastructure, complicating their legal standing.
In summary, the legal landscape surrounding malicious software incidents is fraught with challenges. Security firms must prioritize robust protective measures to guard against regulatory fines, contractual penalties, and potential lawsuits. Are you prepared to take action and ensure compliance in your organization?
Detection and Response: Strategies for Mitigating Malware Threats
To effectively mitigate malware threats, defense contractors should adopt the following strategies:
-
Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular audits is essential for identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring compliance with cybersecurity standards. Organizations that perform regular audits have been shown to have a 40% lower risk of experiencing a data breach. This statistic highlights the critical role of these assessments in maintaining a robust security posture. Are you ready to take your security measures to the next level?
-
Real-Time Monitoring: Implementing advanced monitoring tools allows for the detection of suspicious activities in real-time, enabling prompt responses to potential threats. In 2024, 94% of ransomware attacks included a data exfiltration element. This underscores the necessity for continuous monitoring to safeguard sensitive information. How prepared is your organization to respond to such threats?
-
Incident Response Plans: Developing and regularly updating incident response plans is crucial for ensuring quick and effective action during a malware attack, particularly in mitigating malware security risks. A well-rehearsed plan can significantly minimize damage and downtime, allowing organizations to respond swiftly to incidents and recover more effectively. Have you tested your incident response plan lately?
-
Threat Intelligence Sharing: Collaborating with industry peers to exchange threat intelligence improves overall protection. By pooling insights and experiences, organizations can better anticipate and respond to emerging threats, fostering a more resilient cybersecurity environment. Are you leveraging the power of collaboration to enhance your security posture?

Employee Training: Building Awareness Against Malware Risks
Creating awareness among employees is crucial for preventing malware infections within contracting organizations. To effectively mitigate risks, defense contractors should implement the following strategies:
-
Conduct Regular Training Sessions: Ongoing training is essential for equipping employees with the skills to recognize phishing attempts and practice safe browsing. Regular sessions enhance employees' ability to identify potential threats, significantly reducing the likelihood of successful attacks. Notably, 62% of companies lack adequate security awareness training, underscoring the necessity of these initiatives.
-
Simulate Phishing Attacks: Utilizing simulated phishing exercises is an effective method to test employee awareness and response. These simulations have shown that trained employees are 30% less likely to click on phishing links, demonstrating the value of practical training in real-world scenarios. For instance, a case study from KnowBe4 revealed that before training, the average click rate among three companies was 36.67%. After a four-week Internet Security Awareness Training program, phishing susceptibility among employees dropped dramatically, achieving a 75% reduction in phishing response rates.
-
Promote a Security Culture: Fostering a culture of security within the organization encourages employees to report suspicious activities and prioritize information security. A robust security culture leads to an engaged workforce, increased compliance with security measures, and a lower risk of insider incidents. Leadership plays a pivotal role in establishing this culture by reinforcing security-first values through continuous training and open communication. As one specialist observed, "Without leadership support, security policies remain merely guidelines seldom adhered to."
By adopting these tactics, security providers can greatly improve their protection measures and more effectively safeguard sensitive data from malicious software.

Patch Management: Keeping Defense Systems Secure from Malware
To effectively combat malware threats, defense contractors must adopt stringent patch management practices:
-
Regularly Update Software: Keeping all software and systems current with the latest security patches is essential. Did you know that nearly 60% of breaches exploit known vulnerabilities? This statistic underscores the importance of timely updates. As noted by Jun Cyber, "CMMC compliance will require up-front investments in technology, process, and training," highlighting the critical nature of regular updates in maintaining compliance.
-
Automate Patch Deployment: Implementing automated tools can significantly streamline the patching process. This minimizes the risk of human error and ensures that critical updates are applied promptly. For instance, using tools like Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) or third-party solutions such as Automox can enhance efficiency and help maintain compliance with CMMC requirements.
-
Conduct Vulnerability Assessments: Regular vulnerability assessments are crucial for identifying weaknesses within systems. By prioritizing patching efforts based on risk levels, organizations can effectively allocate resources to mitigate the most pressing threats. According to industry statistics, organizations that conduct regular assessments can reduce their risk of breaches by up to 70%.
Integrating these practices not only strengthens safeguards against harmful software but also aligns with the changing security environment. Proactive actions are essential for compliance and operational integrity.
Expert Collaboration: Partnering with Cybersecurity Professionals for Malware Defense
Defense contractors must prioritize collaboration with cybersecurity professionals to bolster their malware defense strategies.
- Engage Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs): MSSPs provide round-the-clock monitoring and incident response capabilities, ensuring threats are detected and addressed promptly. Their expertise allows organizations to focus on core operations while enhancing their cybersecurity posture. With the managed security services market projected to grow to USD 29.7 billion by 2033, the reliance on these services is clearly increasing.
- Engage in Cybersecurity Communities: Joining industry associations fosters the exchange of knowledge and effective methods for combating harmful software. Active participation in these communities not only enhances understanding but also builds a supportive network among peers facing similar challenges. Statistics show that security providers involved in these communities report a 30% increase in their malware protection effectiveness.
- Consult with Experts: Regular consultations with security specialists are crucial for assessing and enhancing protective measures. These experts can provide tailored strategies that align with the unique needs of security suppliers, ensuring robust protection against emerging threats. As Shay Solomon, BD Director at Check Point Software Technologies, aptly states, "Resilience is not achieved in isolation but through strategic collaboration."
In summary, security providers should critically evaluate their existing cybersecurity collaborations and consider reaching out to MSSPs for guidance to enhance their threat protection strategies.
Emerging Trends: Staying Ahead of Malware Threats in Defense
To stay ahead of malware threats, defense contractors must closely monitor emerging trends, including:
-
AI-Powered Malware: Cybercriminals are increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence to create sophisticated malware that can adapt its code in real-time, evading traditional detection methods. This evolution in malicious software capabilities presents significant malware security risks. In fact, IBM's Cost of a Data Breach 2025 report indicates that 86% of business leaders experienced at least one AI-related incident in the past year. How prepared is your organization to face this challenge?
-
Supply Chain Attacks: Attacks targeting third-party vendors are surging. A single compromised vendor can lead to widespread breaches across multiple organizations, highlighting the need for robust supply chain security measures. Statistics show that supply chain attacks exploit trust and scale, allowing attackers to infect numerous downstream customers through a single software provider. Are your security protocols up to the task?
-
Fileless Threats: This type of threat operates directly in memory, making it particularly challenging to detect and mitigate. Organizations must enhance their detection capabilities and adopt proactive measures to effectively address these evolving threats. The emergence of fileless malware emphasizes the significance of ongoing surveillance and sophisticated threat detection approaches. Is your organization equipped to handle this new wave of threats?
By understanding these trends, defense contractors can better prepare their cybersecurity strategies to mitigate risks and protect sensitive information. It's crucial to take action now to safeguard your organization against these evolving threats.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this article highlights the urgent need for defense contractors to address malware security risks, especially given the rapidly changing landscape of cyber threats. Alarming statistics show that many organizations are still not adequately prepared for the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC). Clearly, a proactive and comprehensive approach to cybersecurity is essential for protecting sensitive information and ensuring national security.
Key insights include:
- The various types of malware that contractors must be aware of.
- The serious consequences of malware incidents—ranging from operational disruptions to legal ramifications.
- The different delivery methods through which these threats can infiltrate defense networks.
- The necessity of robust detection and response strategies, employee training, and effective patch management.
- Collaborating with cybersecurity professionals is also crucial for strengthening defenses against emerging threats.
As the threat landscape evolves, defense contractors must prioritize their cybersecurity measures and stay vigilant against malware risks. By implementing best practices and fostering a culture of security awareness, organizations can significantly enhance their resilience against cyber attacks. Taking decisive action now is imperative to safeguard not only their operations but also the integrity of national security.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the CMMC Info Hub?
The CMMC Info Hub provides comprehensive guidance on malware security risks for military suppliers, helping organizations strengthen their security posture against software threats.
How prepared are U.S. security suppliers for the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC)?
Only 1% of U.S. security suppliers feel fully prepared for the CMMC, highlighting a significant need for effective threat risk management.
What types of malware should defense contractors be aware of?
Defense contractors should be aware of several key malware types, including ransomware, spyware, Trojans, worms, adware, and fileless malware.
What are the financial implications of ransomware attacks?
Ransomware accounts for about 20% of all cyberattacks, with average ransom payments nearing $1 million in 2025, indicating significant financial stakes for victims.
What are the consequences of malware attacks on defense operations?
Malware attacks can lead to operational disruptions, data breaches, national security risks, and legal repercussions, all of which can have severe impacts on defense operations.
How frequent are cyber incidents in the military sector?
In 2025, the military sector reported approximately 1,250 cyber incidents weekly, indicating a high frequency of malware-related disruptions.
What are the average costs associated with data breaches in the security sector?
The average expense of a data breach in the security sector is roughly $5.46 million, with many companies facing compliance fees exceeding $100,000 after a breach.
How can defense contractors protect sensitive information from malware threats?
Contractors can protect sensitive information by applying robust cyber hygiene practices and adopting a Zero Trust strategy to mitigate malware security risks.
What is the significance of integrating security criteria into supplier agreements?
Integrating security criteria into supplier agreements can enhance resilience against cyber threats, though currently, only 22% of CMMC organizations adopt this practice.
What should organizations do to improve their cybersecurity posture?
Organizations should assess their existing protective strategies and identify areas for improvement to strengthen their overall cybersecurity posture against evolving threats.




