10 Key Insights on NIST 800-171 Revision 3 for Defense Contractors
Explore essential insights on NIST 800-171 Revision 3 for defense contractors' compliance success.

Overview
The article provides critical insights into NIST 800-171 Revision 3 and its implications for defense contractors, emphasizing the necessity for robust compliance strategies to safeguard Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI). Key changes introduced by the revision include:
- Enhanced security controls
- An increased focus on supply chain risk management
- Integration with the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC)
These elements are essential for contractors aiming to bolster their cybersecurity posture and enhance their competitiveness in securing government contracts.
What does this mean for defense contractors? The shift towards more stringent compliance measures necessitates immediate action. Contractors must not only understand these changes but also implement effective strategies to meet the new requirements. By doing so, they can ensure the protection of sensitive information and position themselves favorably in the competitive landscape of government contracting.
Introduction
NIST 800-171 Revision 3 has emerged as a pivotal framework for defense contractors, fundamentally reshaping the landscape of cybersecurity and compliance. This article delves into ten key insights that illuminate the updated requirements, emphasizing the critical need for safeguarding Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) and enhancing supply chain security. As organizations grapple with the complexities of compliance, a pressing question arises: how can defense contractors not only meet these stringent standards but also leverage them to gain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving industry?
CMMC Info Hub: Your Essential Resource for NIST 800-171 Compliance
CMMC Info Hub serves as a comprehensive knowledge repository for organizations striving to meet NIST 800-171 Revision 3 requirements. It provides in-depth articles, guides, and practical strategies that demystify the complexities of these requirements. By leveraging the Hub, contractors in the security sector can access tailored roadmaps aligned with the Department of Defense's standards, ensuring they are thoroughly prepared for evaluation assessments and contract opportunities.
This platform may contain links to external websites. We have no control over the content of these external sites and accept no responsibility for their content or availability. The inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement by us.
The Hub's structured guidance is particularly advantageous in light of the recent updates to NIST 800-171 Revision 3, which emphasize the critical importance of protecting Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI). With 110 controls and 320 assessment objectives to navigate, contractors can utilize the Hub's insights to identify compliance gaps and implement effective strategies. This proactive approach is essential, as achieving compliance can take an estimated 12 to 18 months, making early action vital.
Moreover, professional perspectives included in the Hub highlight effective compliance strategies tailored for contractors in the security sector. These insights emphasize the necessity of meticulous documentation of policies and procedures, as well as the prioritization of essential security controls based on risk assessments. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement and collaboration, organizations can enhance their security posture while meeting regulatory requirements.
Ultimately, CMMC Info Hub significantly impacts compliance success for defense contractors by providing the essential tools and knowledge needed to navigate the evolving landscape of security requirements. This empowers businesses to not only achieve compliance standards but also to excel in a competitive environment where securing government contracts increasingly depends on robust cybersecurity practices.
Expanded Requirements for Safeguarding Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI)
NIST 800-171 Revision 3 significantly enhances the requirements for safeguarding Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) by mandating entities to adopt more rigorous access controls, data encryption, and monitoring protocols. Effective implementation of these measures is crucial for protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access and potential breaches. Organizations are encouraged to establish comprehensive data handling policies and conduct regular training for employees on best practices to mitigate risks associated with CUI.
Recent statistics indicate that approximately 70% of organizations have begun implementing access controls and data encryption to protect CUI, reflecting a growing recognition of the importance of these safeguards. For example, various defense contractors have effectively incorporated advanced access control systems and encryption technologies, showcasing a proactive strategy for adherence and risk management.
Best practices for safeguarding CUI include:
- Regularly updating access control policies to reflect current threats and organizational changes.
- Utilizing encryption for data at rest and in transit to ensure confidentiality and integrity.
- Holding regular training sessions for employees to emphasize the significance of data protection and adherence to NIST 800-171 revision 3 standards.
As organizations prepare for the forthcoming changes under CMMC 2.0, effective December 16, 2024, the focus on strong security measures will be essential. By adopting these best practices, contractors in the security sector can improve their protection stance and ensure adherence to changing regulatory requirements.
Integration with Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC)
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) framework heavily relies on NIST 800-171 Revision 3. Organizations pursuing CMMC certification are required to demonstrate compliance with NIST 800-171 Revision 3 requirements. This integration not only ensures that defense contractors meet baseline security standards but also enhances their overall security posture. Consequently, this improvement positions them competitively in securing defense contracts.
Why is compliance with NIST 800-171 crucial? It guarantees that organizations are not merely checking boxes but are genuinely enhancing their cybersecurity measures. By adopting these standards, contractors can significantly reduce vulnerabilities and build trust with stakeholders.
In summary, embracing NIST 800-171 Revision 3 is not just a regulatory necessity; it provides a strategic advantage in the defense contracting arena. Organizations are encouraged to leverage available resources to ensure compliance, thereby fortifying their defenses and boosting their marketability.
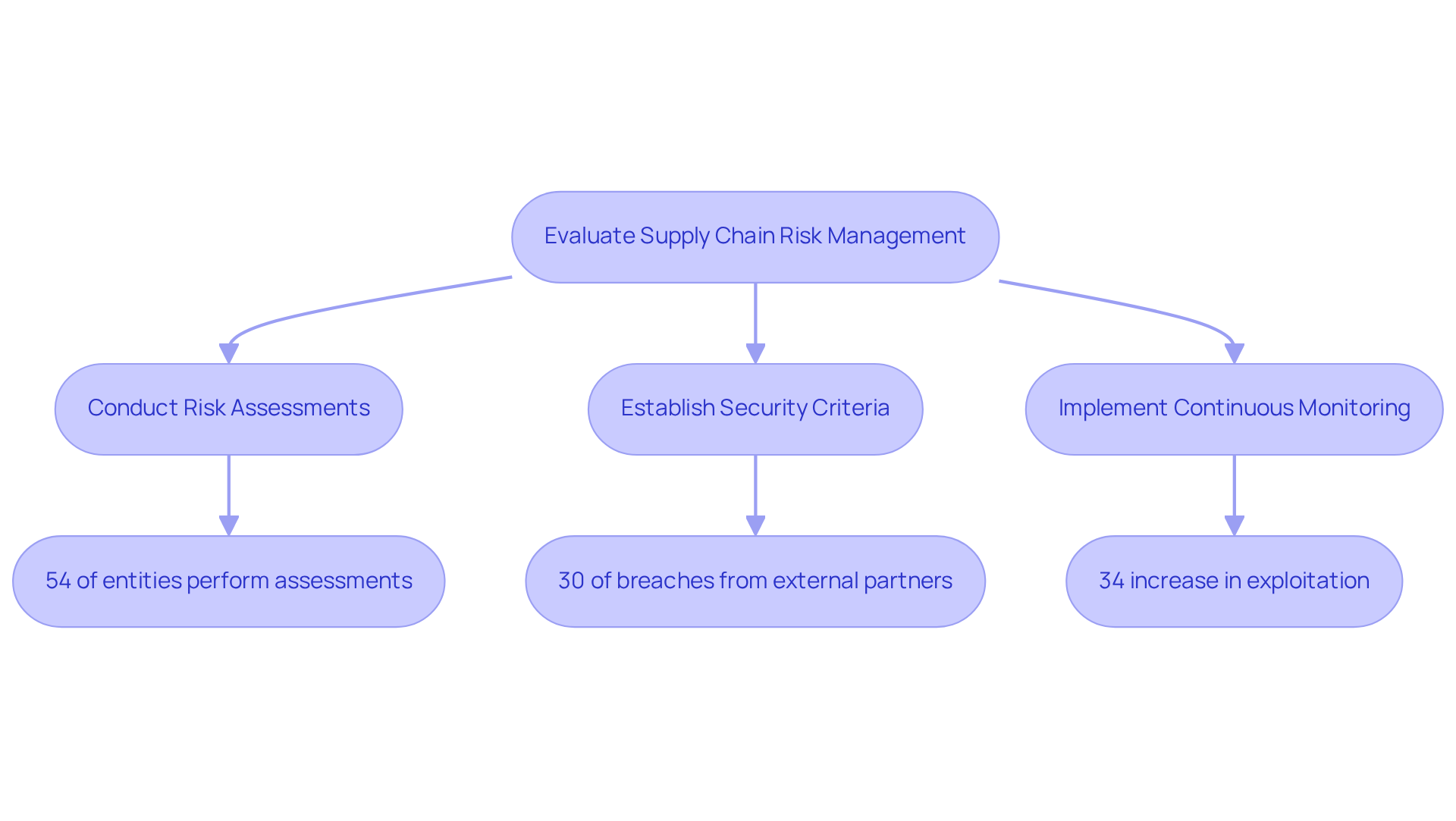
Greater Emphasis on Supply Chain Risk Management
NIST 800-171 Revision 3 significantly enhances the focus on supply chain risk management, highlighting the necessity for entities to rigorously evaluate the security practices of their suppliers and partners. This proactive strategy is crucial in preventing vulnerabilities from infiltrating their systems. Key components of this evaluation include:
- Conducting thorough risk assessments of third-party suppliers to identify potential security gaps. Recent data reveals that only about 54% of entities actively perform these assessments, highlighting a critical area for improvement.
- Establishing explicit security criteria for third parties, ensuring adherence to the entity's cybersecurity standards. This step is particularly vital, as nearly 30% of breaches now originate from external partners, a significant increase from previous years.
- Implementing continuous monitoring processes to maintain oversight of supply chain security. This ongoing vigilance is essential, given that the exploitation of vulnerabilities has surged by 34% since last year, making it imperative for organizations to remain vigilant against potential threats.
Cybersecurity experts stress the importance of rigorously evaluating supplier practices. One expert noted, "the biggest risks are loss of visibility into indirect dependencies and delayed detection of compromises upstream," reinforcing the necessity for comprehensive assessments. Organizations such as DeepStrike have successfully integrated these practices, utilizing penetration testing and risk analysis to bolster their defenses against supply chain attacks, resulting in improved security outcomes.
By prioritizing these supply chain cybersecurity practices, defense contractors can not only comply with NIST 800-171 Revision 3 but also strengthen their overall security posture, safeguarding sensitive information and preserving trust within the defense ecosystem.
Focus on Incident Response and Recovery Plans
NIST 800-171 Revision 3 emphasizes the critical importance of robust incident response and recovery plans for entities managing Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI). Alarmingly, around 60% of organizations have not tested their incident response plans, which significantly heightens risks in the event of a cyber incident.
Developing effective recovery plans necessitates:
- Clearly defining roles and responsibilities
- Establishing communication protocols
- Conducting regular drills to simulate potential breaches
Cybersecurity experts assert that evaluating these plans transcends mere regulatory compliance; it is an essential practice to ensure preparedness. For instance, entities like the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia Research Institute have integrated comprehensive cybersecurity frameworks, including regular internal audits and NIST SP 800-171A assessments, to validate their incident response capabilities.
By aligning operations with NIST standards, they demonstrate their commitment to safeguarding sensitive data and adhering to regulatory requirements. Furthermore, a systematic approach termed 'Stop, Assess, and Report' is recommended for managing cyber incidents, aligning with NIST 800-171 Revision 3 requirements. This proactive stance not only mitigates risks but also enhances a company's ability to uphold federal contracts and protect critical information.
Shift Toward a Proactive Compliance Model
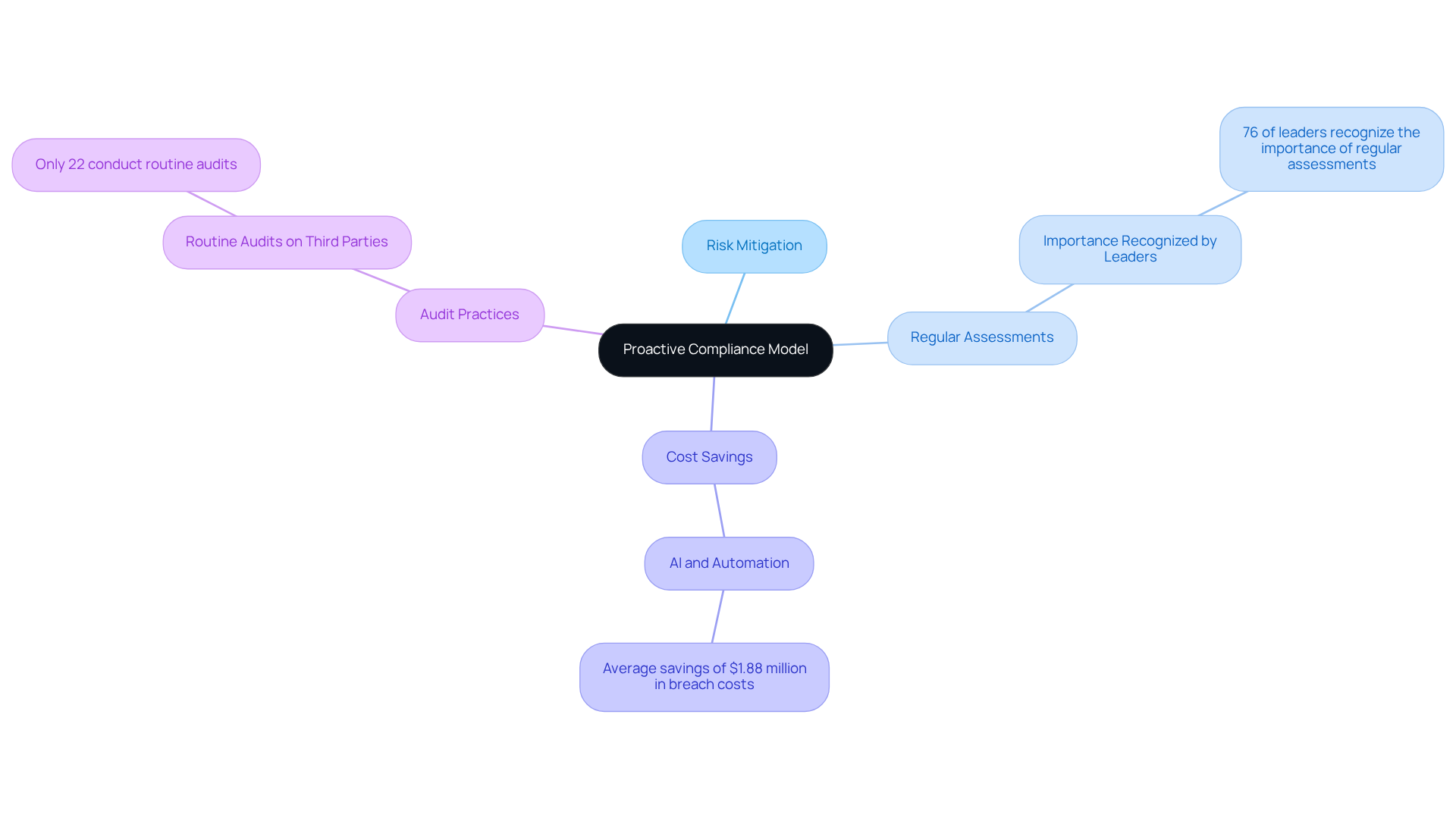
The shift to a proactive regulatory approach in NIST 800-171 Revision 3 empowers entities to foresee and mitigate risks before they escalate. This strategy underscores the necessity of conducting regular assessments of security controls and implementing continuous monitoring of systems to stay ahead of emerging threats.
Studies indicate that organizations adopting such proactive measures not only enhance their security posture but also significantly reduce expenses associated with data breaches. For instance, companies utilizing AI and automation in their regulatory processes have reported an average savings of $1.88 million in breach costs. A notable example is Secureframe, which has aided numerous organizations in optimizing their regulatory efforts and achieving substantial cost savings.
Furthermore, 76% of regulatory leaders recognize that regular security evaluations are crucial for identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring compliance with NIST 800-171 Revision 3. As Gaspard de Lacroix, CEO and co-founder, articulates, "Organizations should view adherence to regulations as a dynamic capability rather than a static obligation."
Alarmingly, only 22% of entities currently conduct routine audits on third parties, highlighting a critical area for improvement. By leveraging practical strategies and insights from the CMMC Info Hub, organizations can transform confusion into clarity, better safeguard their assets, and maintain ongoing compliance with evolving regulatory standards.
Increased Technical Requirements for Authentication and Encryption
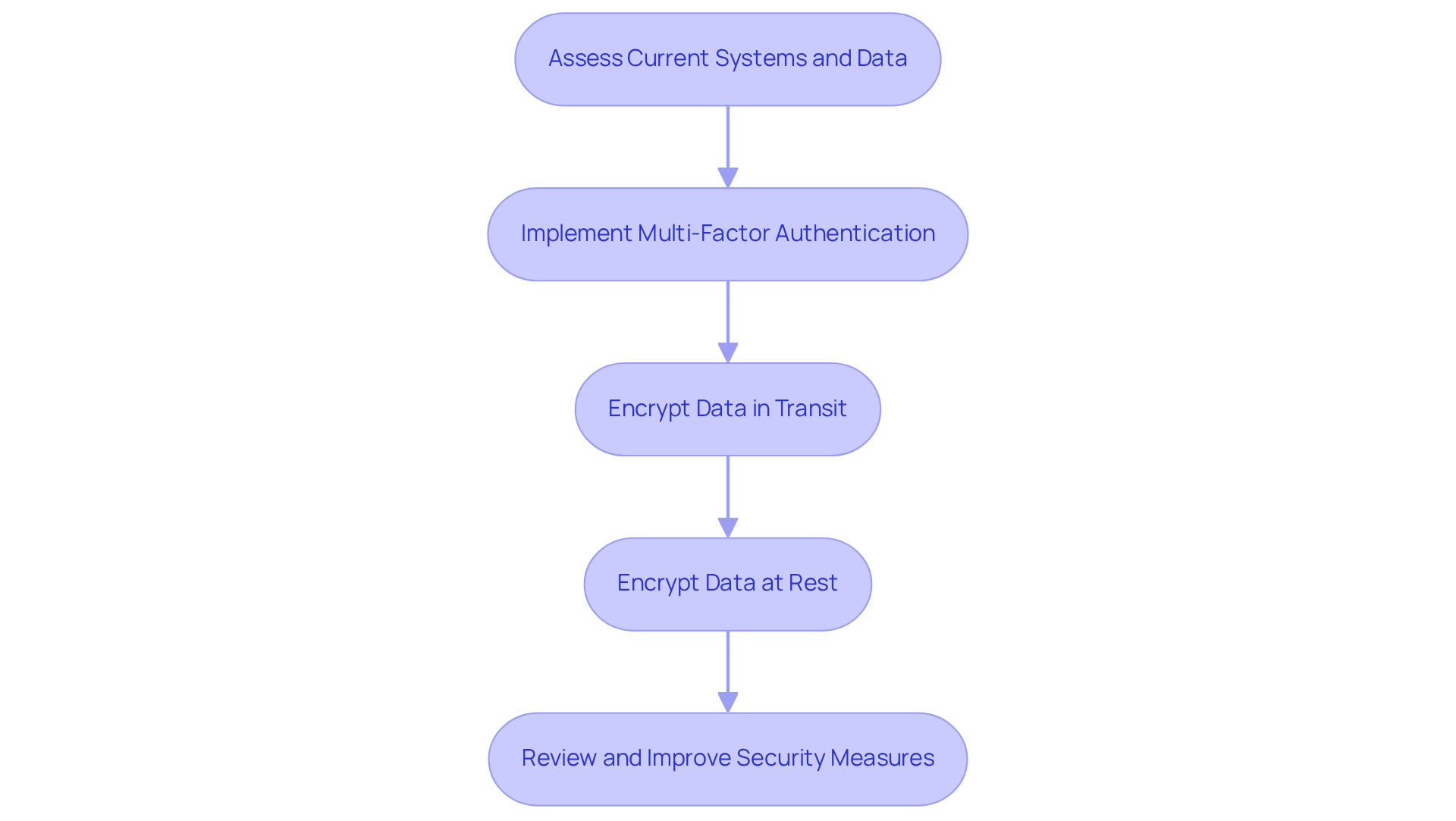
NIST 800-171 Revision 3 establishes heightened technical requirements for authentication and encryption. It emphasizes the necessity of multi-factor authentication (MFA) for accessing sensitive systems. This requirement is crucial for safeguarding Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) and preventing unauthorized access.
Recent statistics reveal that entities utilizing MFA can decrease the risk of security breaches by up to 80-90%. This significant reduction underscores MFA as a critical component of a robust cybersecurity strategy. Moreover, organizations must ensure that data is encrypted both in transit and at rest. Currently, approximately 21% of organizations encrypt over 60% of their classified data, highlighting a significant area for improvement.
Experts in cybersecurity advocate for the implementation of strong encryption protocols, as they are vital for protecting sensitive information from potential threats. As contractors in security navigate the complexities of regulations, adopting measures outlined in NIST 800-171 Revision 3 not only aligns with legal requirements but also strengthens their overall security posture.
To enhance your adherence efforts, consider adopting a phased strategy for MFA and encryption. Begin with the most essential systems and data to ensure a solid foundation for compliance.
Impact on Defense Contractors
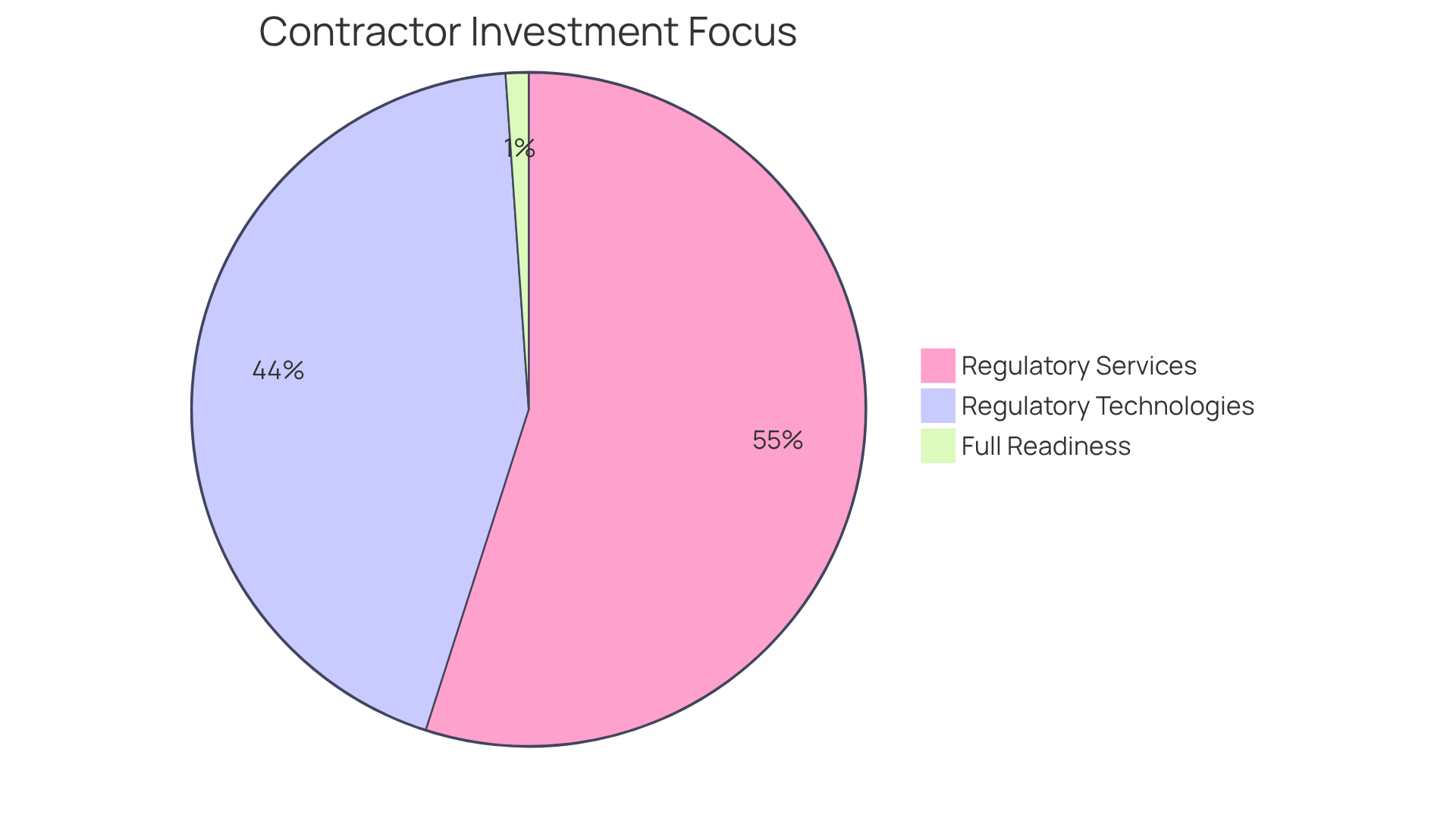
NIST 800-171 Revision 3 introduces significant changes that will transform the regulatory environment for defense contractors. Organizations must adapt their regulatory strategies to align with these updated requirements, which may necessitate investments in new technologies, enhanced training programs, and comprehensive policy revisions. Notably, around 50% of contractors surveyed are investing in regulatory services, with 40% specifically dedicating resources to regulatory technologies. This indicates an increasing awareness of the importance of robust security measures.
For instance, numerous entities are implementing sophisticated security measures to address the challenges posed by the new standards. This shift not only assists in fulfilling regulatory obligations but also enhances their overall security posture, making them more competitive in the defense industry.
However, the transition to these new requirements is fraught with challenges. A significant percentage of contractors report feeling unprepared for the upcoming changes, with only 1% indicating full readiness for CMMC audits. The Defense Industrial Base is running out of time, underscoring the urgency for entities to prioritize adherence and cybersecurity efforts.
Industry leaders emphasize that adjusting regulatory strategies is essential. As one expert noted, "Compliance is no longer about interpretation; it’s about precision." This perspective is further illustrated by Emil Sayegh's assertion, "Eighty thousand defense contractors need Level 2 certification, yet only 270 of these organizations currently hold final CMMC certificates," highlighting the gap in adherence and the urgency of the situation.
Moreover, the introduction of a new tailoring category, ORC, in NIST 800-171 Revision 3 is a crucial change that contractors must consider when adjusting their compliance strategies. Additionally, the elimination of 33 withdrawn requirements in NIST 800-171 Revision 3 adds another layer of complexity to the compliance landscape.
In summary, while the modifications introduced by NIST 800-171 Revision 3 present challenges, they also offer contractors a unique opportunity to enhance their security frameworks and solidify their positions in the competitive military market.
Applicability and Compliance Requirements of NIST 800-171 Revision 3
NIST 800-171 Revision 3 is essential for all organizations that manage Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) in federal contracts, which includes contractors, subcontractors, and entities within the military supply chain. Compliance requires the implementation of specific security controls, which must be regularly assessed and audited to demonstrate their effectiveness. Currently, a significant number of defense contractors are meeting these standards, reflecting a growing awareness of the necessity for robust security measures.
As industry specialists emphasize, the evolving landscape of digital security necessitates that companies view adherence not merely as a legal obligation but as a fundamental aspect of their operational integrity. For instance, entities that have effectively implemented security measures have shown marked improvements in their audit results, underscoring the importance of a proactive approach to cybersecurity.
Moreover, with new regulations for NIST 800-171 Revision 3 anticipated in 2025, it is imperative for defense contractors to adopt a proactive stance, ensuring their practices align with NIST 800-171 Revision 3 standards to safeguard sensitive information and maintain their eligibility for federal contracts.
Perform a Gap Analysis for Compliance Readiness
Conducting a gap analysis is crucial for organizations aiming to assess their preparedness for compliance with NIST 800-171 Revision 3. This systematic process evaluates current security practices against the requirements of NIST 800-171 Revision 3, identifying areas of non-compliance. Organizations must meticulously document their findings during this analysis, as it lays the groundwork for prioritizing remediation efforts. A well-organized roadmap is essential for achieving compliance, guiding entities through the necessary steps to prepare for evaluations and inspections. For instance, firms like SCB have successfully assisted defense contractors by providing comprehensive reports that pinpoint adherence gaps and outline practical correction strategies.
Furthermore, cybersecurity experts emphasize the importance of readiness evaluations, noting that a thorough gap analysis not only uncovers vulnerabilities but also strengthens a company’s overall security posture. By proactively addressing identified gaps, organizations can significantly improve their readiness and mitigate risks associated with potential audits. Continuous monitoring and maintenance practices—such as regular vulnerability scans, timely patch management, and ongoing incident monitoring—are vital for sustaining compliance and enhancing security posture.
Conclusion
NIST 800-171 Revision 3 introduces critical updates that defense contractors must navigate to ensure compliance and protect Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI). This revision not only enhances security requirements but also emphasizes the importance of proactive measures, continuous monitoring, and robust incident response strategies. By understanding and implementing these updated standards, organizations can significantly improve their cybersecurity posture and maintain competitiveness in the defense contracting landscape.
Key insights throughout the article reveal:
- The necessity of conducting thorough gap analyses to identify compliance readiness.
- The integration of CMMC with NIST 800-171 for enhanced security.
- The growing emphasis on supply chain risk management.
Organizations must adopt best practices such as:
- Regular training.
- Robust authentication protocols.
- Comprehensive documentation to address the evolving challenges presented by these regulations.
The proactive compliance model encourages entities to anticipate risks and implement solutions before they escalate, highlighting the strategic advantage of adhering to these standards.
Ultimately, embracing NIST 800-171 Revision 3 is not simply about meeting regulatory requirements; it is an opportunity for defense contractors to solidify their security frameworks and enhance their marketability. As the industry moves towards stricter compliance standards, organizations are urged to leverage available resources, like the CMMC Info Hub, to navigate these changes effectively. Taking decisive action now will not only safeguard sensitive information but also position contractors favorably in an increasingly competitive environment for government contracts.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the CMMC Info Hub?
The CMMC Info Hub serves as a comprehensive resource for organizations aiming to meet NIST 800-171 Revision 3 requirements, providing articles, guides, and strategies to help contractors in the security sector prepare for evaluation assessments and contract opportunities.
How does the CMMC Info Hub assist with NIST 800-171 compliance?
The Hub offers structured guidance and tailored roadmaps that help contractors identify compliance gaps and implement effective strategies to navigate the complexities of NIST 800-171 Revision 3, which includes 110 controls and 320 assessment objectives.
Why is early action important for achieving compliance with NIST 800-171?
Achieving compliance can take an estimated 12 to 18 months, so early action is vital to ensure organizations are thoroughly prepared for evaluations and can secure contract opportunities.
What are the key updates in NIST 800-171 Revision 3 regarding Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI)?
NIST 800-171 Revision 3 enhances requirements for safeguarding CUI by mandating stricter access controls, data encryption, and monitoring protocols to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and breaches.
What best practices are recommended for safeguarding CUI?
Recommended best practices include regularly updating access control policies, utilizing encryption for data at rest and in transit, and conducting regular training sessions for employees on data protection and NIST 800-171 standards.
How is the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) related to NIST 800-171?
The CMMC framework relies on NIST 800-171 Revision 3, requiring organizations pursuing CMMC certification to demonstrate compliance with its requirements, thereby enhancing their overall security posture and competitiveness in securing defense contracts.
Why is compliance with NIST 800-171 important for organizations?
Compliance with NIST 800-171 is crucial as it ensures that organizations are genuinely enhancing their cybersecurity measures, reducing vulnerabilities, and building trust with stakeholders, rather than just meeting regulatory requirements.




