3 Best Practices for Effective Segregation of Duties in Defense Contracts
Discover best practices for effective segregation of duties in defense contracting to enhance security.

Overview
This article highlights three best practices for effective segregation of duties (SoD) in defense contracts.
- First and foremost, clearly defined roles are essential. Without them, confusion can lead to errors and potential fraud.
- Next, implementing a SoD matrix provides a visual representation of responsibilities, ensuring that no single individual has control over all aspects of a transaction.
- Lastly, regular reviews are crucial; they help identify any gaps or weaknesses in the system, allowing for timely adjustments.
These practices not only mitigate risks but also enhance compliance with regulations such as the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC). By adhering to these guidelines, organizations can significantly improve their operational security. This, in turn, safeguards sensitive information in defense contracting, which is paramount in today’s security landscape.
Are you ready to take action? By adopting these best practices, you can fortify your defense contracts against potential threats. Consider implementing these strategies today to ensure a robust compliance framework.
Introduction
The integrity of defense contracts is fundamentally tied to the effective management of sensitive information and strict adherence to rigorous regulations. Implementing segregation of duties (SoD) is not just a best practice; it’s a critical necessity that protects against fraud and errors in complex processes. But how can organizations ensure that their SoD frameworks are not only established but also remain effective in a landscape increasingly fraught with compliance risks and insider threats?
Exploring best practices for SoD can illuminate pathways for defense contractors to enhance accountability and security while navigating the intricate web of regulatory demands. By understanding the significance of SoD, organizations can better position themselves to meet compliance requirements and safeguard their operations.
Consider this: what measures are currently in place to assess the effectiveness of your SoD? Regular evaluations and updates to these frameworks are essential in adapting to evolving threats. Engaging with industry standards and case studies can provide valuable insights into successful implementations.
In conclusion, establishing a robust SoD framework is not merely a checkbox on a compliance list; it is a proactive strategy that fortifies the integrity of defense contracts. By prioritizing SoD, organizations can navigate the complexities of regulatory demands with confidence.
Understand Segregation of Duties in Defense Contracting
The segregation of duties (SoD) is a vital internal control principle that is essential for distributing responsibilities among individuals to reduce the risk of errors and fraud. In defense contracting, the importance of SoD is heightened due to the critical need to protect sensitive information and comply with stringent regulations set by the Department of Defense (DoD). By implementing the segregation of duties to ensure that no single individual has control over all aspects of a crucial process, organizations can create a robust system of checks and balances that promotes accountability and transparency.
But why is SoD more than just a best practice? It’s a necessity under compliance frameworks like the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC). For example, the CMMC requires that the same person should not conduct security audits, test security mechanisms, and release software for delivery. This reinforces the critical role of segregation of duties in maintaining security integrity.
To effectively implement SoD, defense contractors should consider these best practices:
- Define Roles Clearly: Clearly outline roles and responsibilities to prevent overlap and confusion.
- Implement a Segregation of Duties Matrix: Use a segregation of duties matrix to define and enforce duty separation across critical processes.
- Conduct Regular Reviews: Regularly assess and update SoD methods to adapt to changes in processes or personnel.
Real-world examples highlight the effectiveness of SoD in defense contracts. A notable case is Electrosoft, which was awarded a contract to implement Identity, Credential, and Access Management (ICAM) Segregation of Duties controls for the Defense Logistics Agency. This initiative underscores how organized SoD methods can enhance cybersecurity postures and ensure compliance with DoD standards.
Statistics reveal that organizations employing effective segregation of duties can significantly reduce compliance risks. For instance, a nationwide study showed a 28% increase in insider threat incidents within DoD contracting between 2023 and 2024, emphasizing the urgent need for robust segregation of duties controls to mitigate such risks. Cybersecurity experts advocate for the segregation of duties as a core component of risk management strategies, highlighting its role in minimizing the potential for fraudulent actions and enhancing overall business performance.
In conclusion, understanding and applying segregation of duties is crucial for defense contractors aiming to navigate the complexities of regulations while safeguarding sensitive information. By integrating SoD into their operational frameworks, organizations can not only meet regulatory expectations but also bolster their defenses against potential threats. The CMMC Info Hub serves as a comprehensive resource, offering practical strategies and peer insights to facilitate the journey toward achieving and maintaining CMMC compliance.
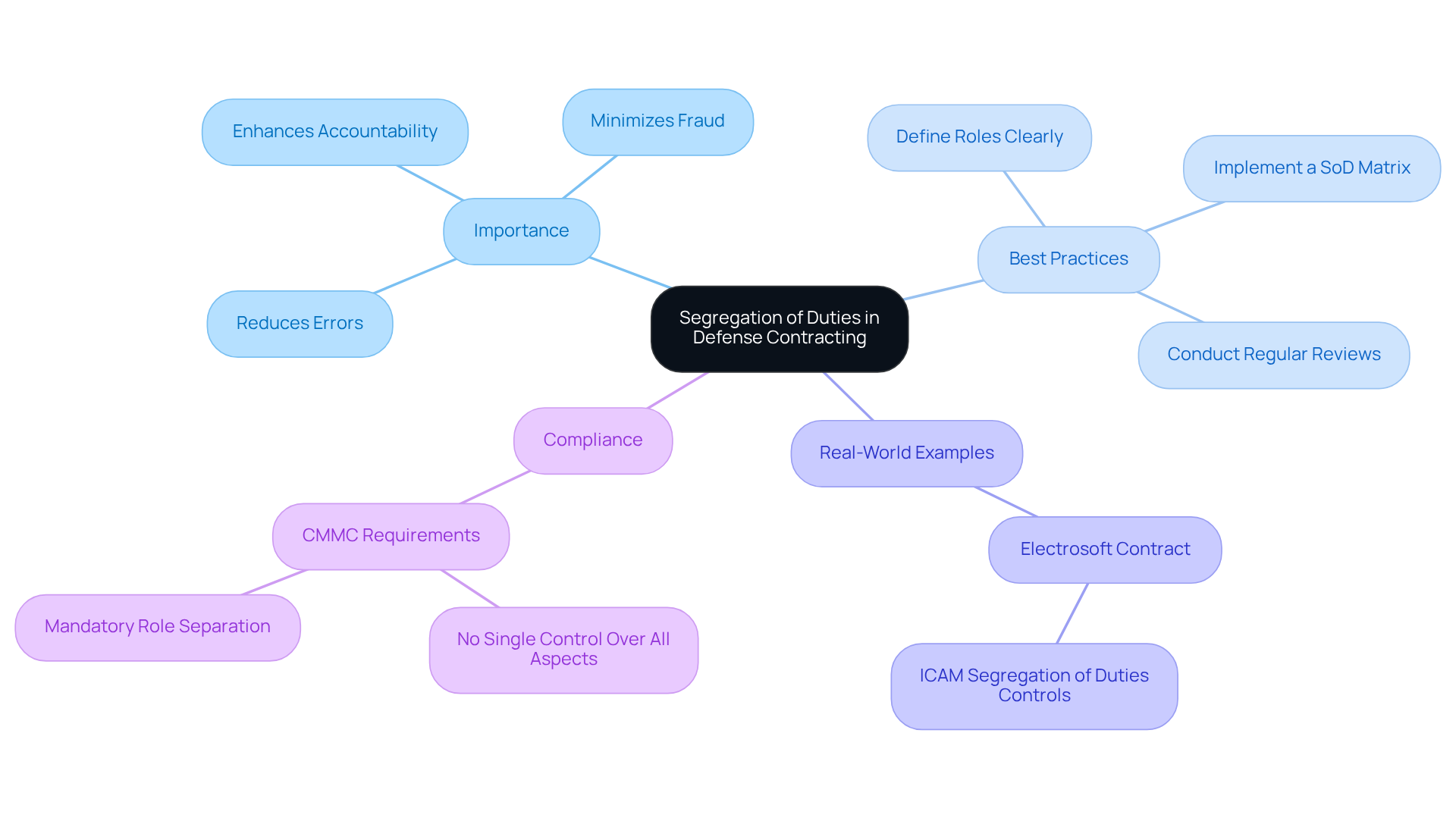
Implement Best Practices for Effective Segregation of Duties
To implement effective segregation of duties (SoD), organizations should adopt the following best practices:
-
Define Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly delineate the roles and responsibilities of each team member involved in critical processes. This clarity helps prevent overlaps that could lead to conflicts of interest and ensures accountability.
-
Utilize Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Implement RBAC to restrict access to information and systems based solely on the specific needs of each role. This reduces the risk of unauthorized actions and improves adherence to access control requirements.
-
Conduct Regular Risk Assessments: Periodically assess the risks associated with various processes and adjust SoD measures accordingly. This proactive approach helps identify potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited, ensuring that controls remain effective.
Implement a segregation of duties matrix by creating a visual representation of roles and responsibilities to ensure that all critical tasks are covered by different individuals. This matrix functions as a crucial reference for audits and regulatory checks, reinforcing the integrity of the SoD framework.
- Provide Training and Awareness: Educate employees about the significance of SoD and their specific responsibilities within this framework. Promoting awareness can nurture a culture of adherence and responsibility, vital for upholding strong security measures.
By following these best practices, entities can create a robust segregation of duties framework that not only fulfills regulatory requirements but also enhances overall operational efficiency. This, in turn, protects sensitive information and decreases the risk of fraud. Did you know that entities lose approximately 5 percent of revenue to fraud annually? This statistic highlights the critical need for effective SoD measures. As Alison Gunnels states, "SoD reduces the chances for mistakes and opportunities for dishonesty in financial tracking and reporting periods." Continuous maintenance and adjustments to SoD are necessary due to changes in organizational structure or employee roles. Collaboration with external auditors is essential for disclosing security safeguards and breaches.
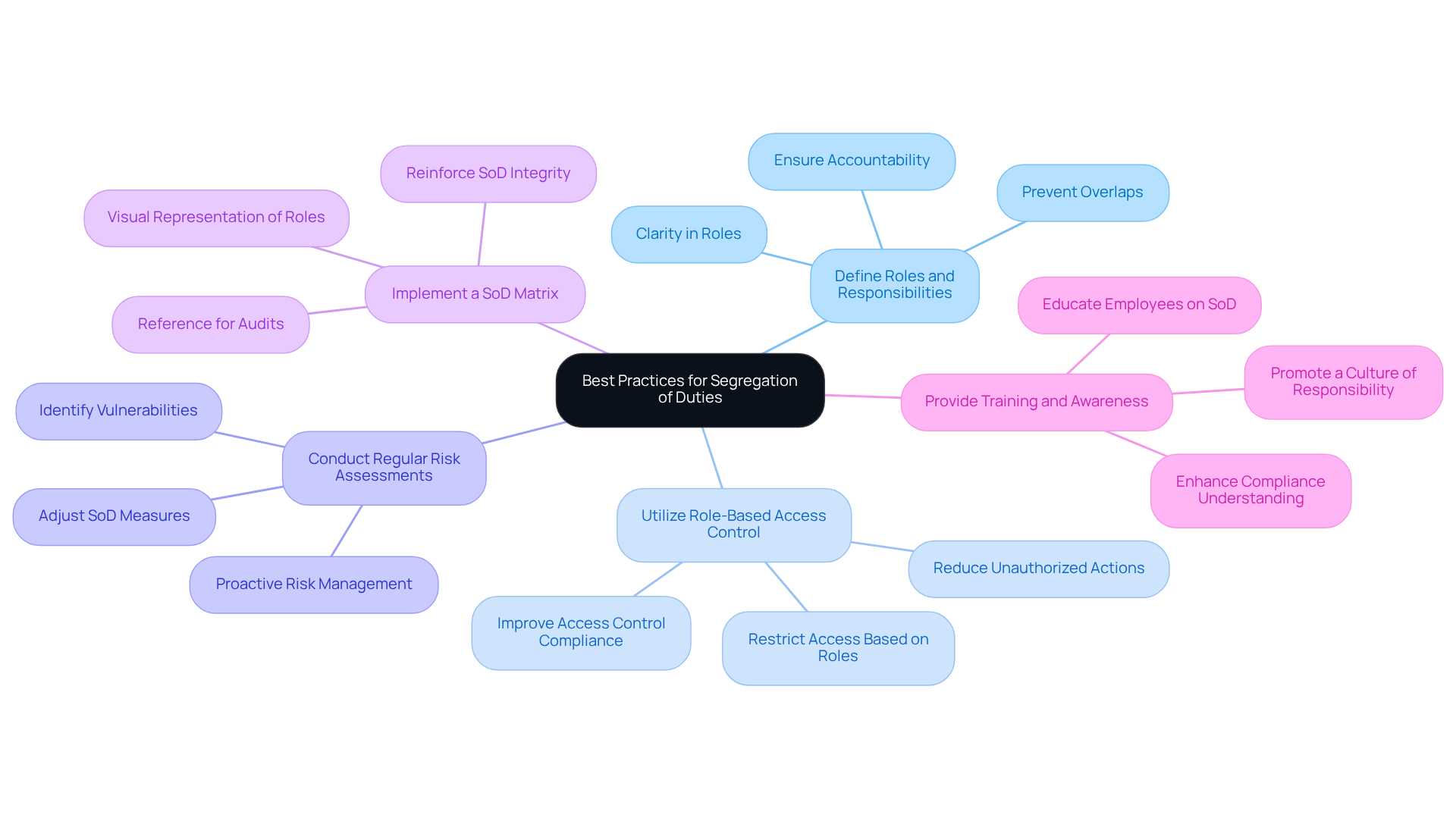
Monitor and Audit Segregation of Duties Compliance
To ensure compliance with segregation of duties (SoD), organizations must adopt comprehensive monitoring and auditing practices that are both effective and proactive:
-
Regular Audits: Periodic audits are essential for evaluating the effectiveness of SoD controls. These audits assess adherence to defined roles and identify any unauthorized access, ensuring that security measures function as intended.
-
Automated Monitoring Tools: Implementing automated monitoring tools is crucial for overseeing access and modifications to critical systems. These tools provide real-time notifications for suspicious activities, enabling organizations to respond swiftly to potential segregation of duties violations. They also play a vital role in detecting abnormal insider behavior, especially considering the 28% increase in insider-driven data exposure events between 2023 and 2024.
-
Review Access Logs: Regularly reviewing access logs is vital to confirm that individuals access only the information necessary for their roles. This practice helps identify anomalies that may require further investigation, thereby strengthening the integrity of the segregation of duties framework. Additionally, access should be revoked immediately upon employee termination or resignation to prevent unauthorized access.
-
Feedback Mechanism: Establishing a feedback mechanism empowers employees to report concerns or observations regarding the segregation of duties. This proactive approach helps organizations identify and rectify potential weaknesses in their controls, fostering a culture of accountability.
-
Continuous Improvement: Organizations should leverage audit findings and monitoring results to consistently enhance their segregation of duties methods. Adapting to changes in regulatory requirements and organizational structures is essential for maintaining compliance and effectiveness. Recognizing the challenges in aligning SoD policies across diverse systems can also aid in developing more effective strategies.
By adopting these robust monitoring and auditing methods, organizations can ensure their segregation of duties framework remains effective and compliant with Department of Defense requirements. Case studies highlighting the risks of excessive permissions and the importance of continuous monitoring further illustrate the necessity of these practices.
Conclusion
The implementation of segregation of duties (SoD) in defense contracting is not just a recommended practice; it’s a critical necessity for ensuring security and compliance in this highly regulated industry. By distributing responsibilities among individuals, organizations can significantly mitigate the risks of errors and fraudulent activities. This approach safeguards sensitive information and ensures adherence to stringent Department of Defense regulations.
Key practices for effective SoD include:
- Clearly defining roles and responsibilities
- Utilizing a segregation of duties matrix
- Conducting regular reviews and audits
These strategies not only enhance operational efficiency but also ensure compliance with frameworks like the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC). For instance, Electrosoft’s successful implementation showcases the tangible benefits of a well-structured SoD framework in enhancing cybersecurity and reducing compliance risks.
Ultimately, the importance of robust segregation of duties cannot be overstated. As organizations navigate the complexities of defense contracting, prioritizing SoD will fulfill regulatory requirements and fortify defenses against potential threats. A proactive approach, characterized by continuous monitoring and improvement, is essential for maintaining an effective SoD framework. Embracing these best practices empowers defense contractors to protect their operations, uphold accountability, and contribute to a secure contracting environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the segregation of duties (SoD) in defense contracting?
Segregation of duties (SoD) is an internal control principle that distributes responsibilities among individuals to reduce the risk of errors and fraud, particularly in defense contracting where protecting sensitive information and complying with regulations is critical.
Why is SoD necessary in defense contracting?
SoD is necessary in defense contracting to create a robust system of checks and balances that promotes accountability and transparency, especially due to stringent regulations from the Department of Defense (DoD).
How does the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) relate to SoD?
The CMMC requires that the same person should not conduct security audits, test security mechanisms, and release software for delivery, highlighting the importance of SoD in maintaining security integrity.
What are some best practices for implementing SoD in defense contracting?
Best practices for implementing SoD include defining roles clearly, using a segregation of duties matrix to enforce duty separation, and conducting regular reviews to adapt to changes in processes or personnel.
Can you provide an example of effective SoD in defense contracts?
A notable example is Electrosoft, which implemented Identity, Credential, and Access Management (ICAM) Segregation of Duties controls for the Defense Logistics Agency, enhancing cybersecurity and ensuring compliance with DoD standards.
What statistics highlight the importance of SoD in defense contracting?
A nationwide study showed a 28% increase in insider threat incidents within DoD contracting between 2023 and 2024, emphasizing the urgent need for robust SoD controls to mitigate compliance risks.
How does SoD contribute to risk management strategies?
SoD is considered a core component of risk management strategies as it minimizes the potential for fraudulent actions and enhances overall business performance.
What resources are available for defense contractors to understand and implement SoD?
The CMMC Info Hub serves as a comprehensive resource, offering practical strategies and peer insights to help defense contractors achieve and maintain CMMC compliance.