4 Best Practices for Cybersecurity GRC Compliance in Defense Contracts
Master cybersecurity GRC best practices to boost compliance and success in defense contracts.

Introduction
The landscape of defense contracting is transforming. Cybersecurity governance, risk management, and compliance (GRC) are now critical components for success. With the Department of Defense enforcing stringent compliance requirements - especially the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) - defense contractors must adapt to safeguard their operations and maintain a competitive edge.
What strategies can these organizations implement to not only meet compliance standards but also enhance their overall cybersecurity posture? By exploring effective practices for GRC compliance, we can uncover the path forward in navigating the complexities of defense contracts. This exploration is essential for mitigating risks and ensuring resilience against evolving cyber threats.
As we delve deeper, consider how these strategies can not only fulfill compliance requirements but also strengthen your organization’s cybersecurity framework. The time to act is now.
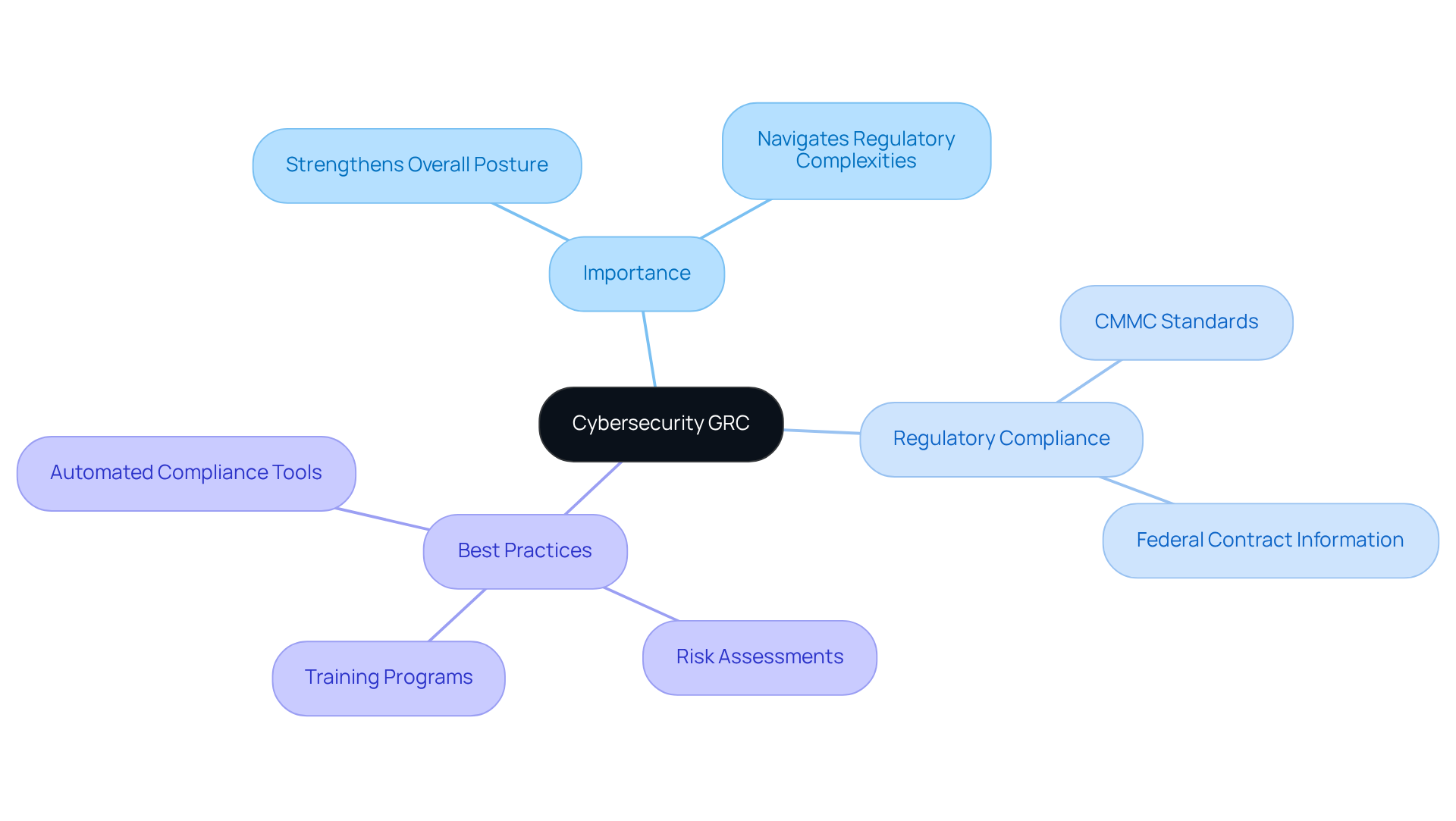
Define Cybersecurity GRC and Its Importance for Defense Contractors
Cybersecurity GRC serves as a crucial framework for organizations, particularly security providers, to effectively manage their cybersecurity initiatives. This structured approach includes vital policies, processes, and technologies that ensure compliance with regulations like the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC). Establishing a robust cybersecurity GRC framework not only supports regulatory adherence but also significantly strengthens the overall posture of contractors.
Why is this alignment so critical? The Department of Defense mandates compliance with CMMC standards for all contracts involving Federal Contract Information (FCI) or Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI), effective November 10, 2028. Organizations that prioritize cybersecurity GRC are better positioned to navigate the complexities of regulatory requirements. In fact, 64% of regulatory leaders are focusing on enhanced privacy controls this year, underscoring the importance of GRC in today’s landscape.
The evolution of the CMMC program, transitioning from self-attestation to a more rigorous verification process, further emphasizes the growing relevance of cybersecurity GRC in the security sector. By implementing effective cybersecurity GRC practices - such as conducting regular risk assessments, offering comprehensive training programs, and utilizing automated compliance tools - defense providers can bolster their adherence capabilities, mitigate risks, and ultimately improve their success rates in securing vital defense contracts.
In conclusion, adopting a strong cybersecurity GRC framework is not just about compliance; it’s also about enhancing your organization’s resilience and readiness in a competitive environment. Are you prepared to take the necessary steps to ensure compliance and secure your future in defense contracting?
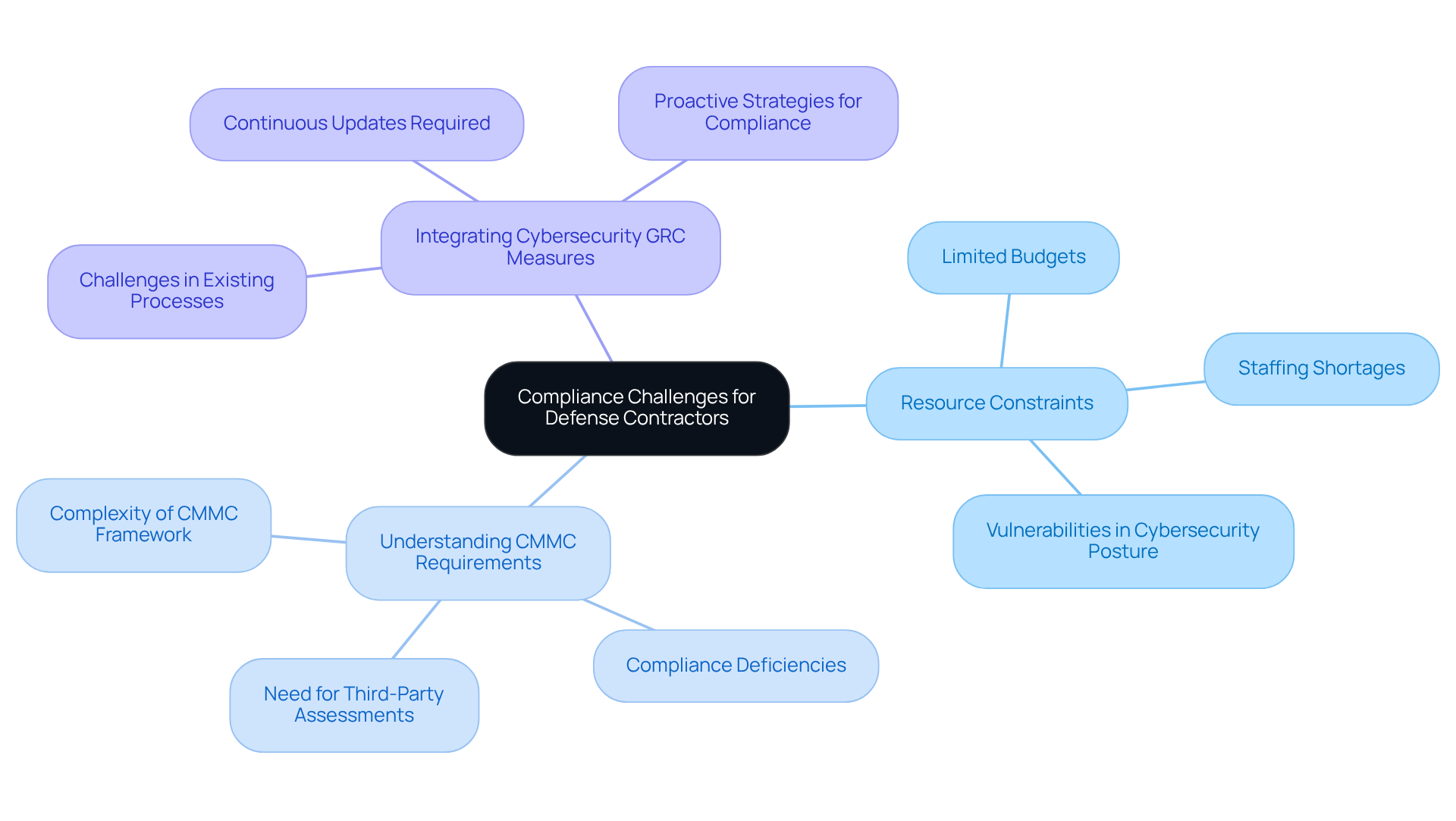
Identify Common Compliance Challenges for Defense Contractors
Defense contractors face significant regulatory challenges that can hinder their operations. These include:
- Resource constraints
- A lack of understanding of CMMC requirements
- The complexities of integrating cybersecurity GRC measures into existing processes
Many organizations underestimate the intricacies of the CMMC framework, leading to compliance deficiencies. Moreover, the rapid evolution of cybersecurity threats necessitates continuous updates to cybersecurity GRC strategies.
By recognizing these challenges, suppliers in the security sector can develop targeted strategies to navigate them effectively. This proactive approach not only ensures compliance with cybersecurity GRC but also enhances competitiveness in the contracting environment. Are you prepared to tackle these issues head-on? Embrace the resources available to fortify your compliance efforts and stay ahead in this dynamic landscape.
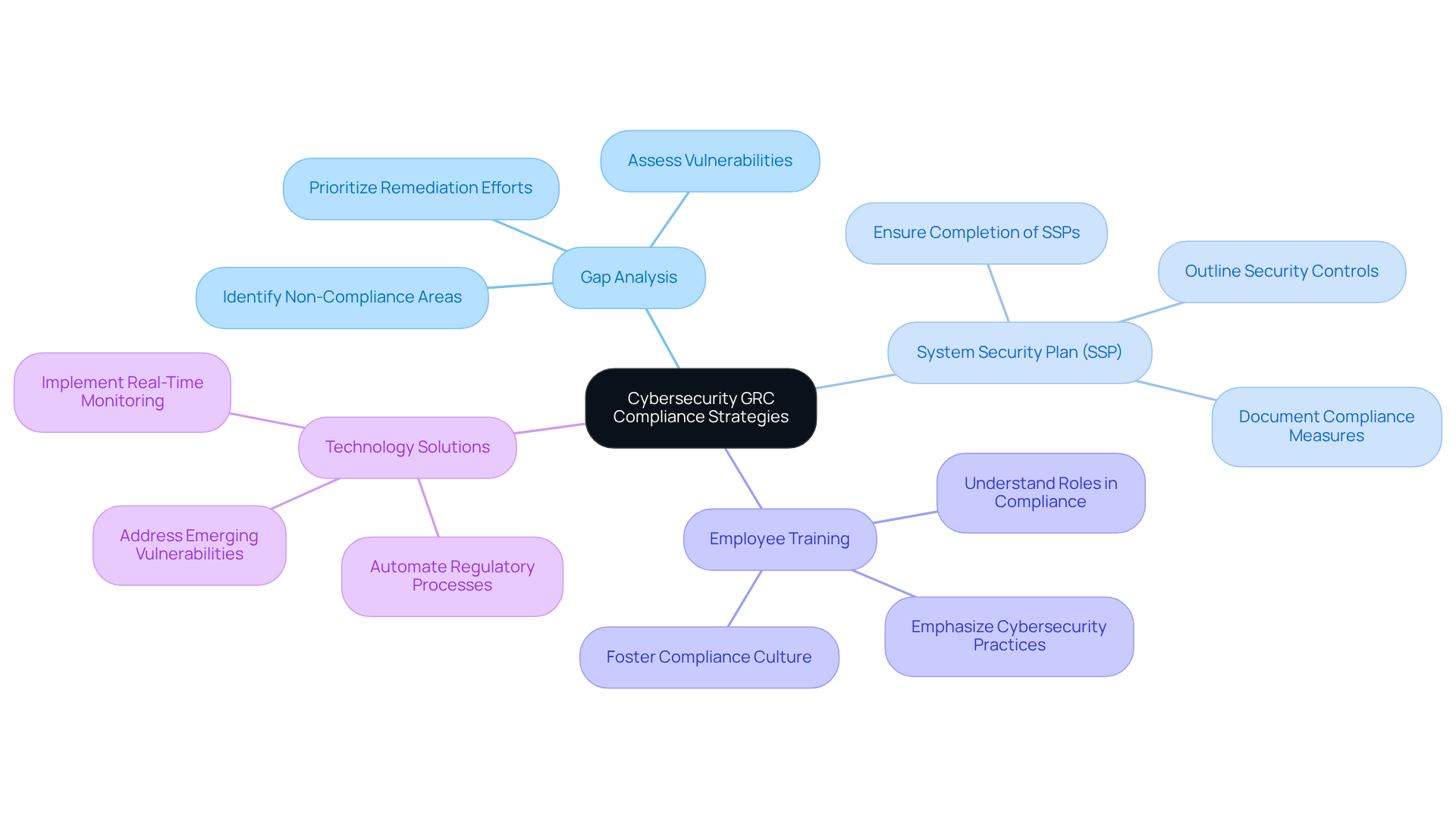
Implement Effective Strategies for Cybersecurity GRC Compliance
To achieve effective cybersecurity governance, risk management, and compliance (GRC) in defense contracts, contractors must implement several essential strategies:
-
Conduct a Comprehensive Gap Analysis: This process is crucial for identifying areas of non-compliance with CMMC requirements. A thorough gap analysis allows organizations to pinpoint vulnerabilities and prioritize remediation efforts. For instance, many suppliers have discovered that a significant portion of their systems lack essential security measures, underscoring the urgency of this assessment.
-
Create a Comprehensive System Security Plan (SSP): An SSP outlines the specific security controls and adherence measures that an organization will implement. Data indicates that less than 50% of defense contractors have completed the necessary documentation, including SSPs, which is vital for demonstrating compliance during evaluations.
-
Invest in Employee Training Programs: It’s essential that all employees understand their roles in upholding regulations. Training programs should emphasize the importance of cybersecurity practices and the specific requirements of the CMMC framework, fostering a culture of compliance throughout the organization.
-
Leverage Technology Solutions: Utilizing technology to automate regulatory processes can significantly enhance efficiency. Real-time monitoring of security controls through automated systems helps organizations maintain compliance and quickly address any emerging vulnerabilities.
By adopting these strategies, military suppliers can streamline their compliance efforts, strengthen their cybersecurity posture, and better position themselves for success in securing military contracts through effective cybersecurity GRC.
Establish a Continuous Improvement Framework for GRC Practices
Implementing a continuous improvement framework for Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) practices in cybersecurity GRC is not just beneficial; it’s essential for defense contractors facing evolving regulations and emerging cybersecurity threats. How can organizations effectively measure the success of their GRC initiatives? Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) is critical. For instance, monitoring metrics like the percentage of scheduled risk evaluations completed on time and the average incident response duration can provide insights into operational readiness and regulatory compliance.
Regular audits and assessments play a vital role in this process. They not only identify areas for enhancement but also help incorporate lessons learned into future compliance efforts. By fostering a culture of ongoing improvement, organizations can significantly bolster their resilience against cyber threats and ensure adherence to evolving standards. This proactive approach ultimately positions them for success in securing contracts.
Consider the financial implications: the global average cost of a data breach in 2024 was a staggering $4.88 million. This figure underscores the necessity of robust practices in cybersecurity GRC. Moreover, with 66% of global compliance teams anticipating an increase in the cost of senior compliance staff, investing in compliance resources is becoming increasingly important. As Benjamin Franklin wisely noted, 'Without continual growth and progress, such words as improvement, achievement, and success have no meaning.'
However, organizations must remain vigilant about potential pitfalls in implementing GRC practices. For example, failing to maintain an updated System Security Plan (SSP) can lead to adverse readiness determinations during assessments. By learning from case studies, particularly the consequences of failed pre-assessments, defense contractors can gain a deeper understanding of the critical importance of robust cybersecurity GRC practices.
Conclusion
Establishing a robust cybersecurity Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) framework is not just essential; it’s a strategic imperative for defense contractors navigating the complexities of regulatory requirements. By honing in on GRC, organizations can ensure compliance with critical standards like the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) and position themselves to excel in a competitive contracting landscape.
Why is this important? Implementing effective strategies is key. Consider these practices:
- Conducting comprehensive gap analyses
- Developing System Security Plans
- Investing in employee training
- Leveraging technology solutions
These are crucial for overcoming common compliance challenges. By addressing these areas, defense contractors can significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture and ensure adherence to evolving regulations.
In a landscape where cybersecurity threats loom large and regulations shift constantly, the commitment to continuous improvement in GRC practices is paramount. Organizations must proactively measure their success, learn from audits, and adapt their strategies to maintain compliance and safeguard their operations. The future of defense contracting depends on the ability to not only meet standards but to cultivate a culture of resilience and readiness. Embracing these best practices today is vital for securing a competitive edge and ensuring long-term success in the defense sector.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Cybersecurity GRC?
Cybersecurity GRC (Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance) is a framework that helps organizations, particularly security providers, manage their cybersecurity initiatives through structured policies, processes, and technologies.
Why is Cybersecurity GRC important for defense contractors?
Cybersecurity GRC is crucial for defense contractors as it ensures compliance with regulations like the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC), which is mandated by the Department of Defense for contracts involving Federal Contract Information (FCI) or Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI).
What regulatory requirements must defense contractors comply with?
Defense contractors must comply with CMMC standards, which will be mandatory for all relevant contracts starting November 10, 2028.
How does prioritizing Cybersecurity GRC benefit organizations?
Organizations that prioritize Cybersecurity GRC are better equipped to navigate regulatory complexities, enhance their privacy controls, and strengthen their overall cybersecurity posture.
What recent changes have been made to the CMMC program?
The CMMC program is evolving from a self-attestation model to a more rigorous verification process, highlighting the increasing importance of cybersecurity GRC in the security sector.
What practices can defense contractors implement to improve their cybersecurity GRC?
Defense contractors can conduct regular risk assessments, provide comprehensive training programs, and utilize automated compliance tools to enhance their adherence capabilities and mitigate risks.
How does a strong Cybersecurity GRC framework impact an organization's competitiveness?
A strong Cybersecurity GRC framework not only ensures compliance but also enhances an organization’s resilience and readiness, improving its chances of securing vital defense contracts.