4 Best Practices for Your GDPR Compliance Framework
Discover essential best practices for establishing a robust GDPR compliance framework.

Introduction
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) stands as a pivotal element in the realm of data privacy, fundamentally influencing how organizations manage personal information. As businesses grapple with the intricacies of compliance, grasping and applying effective practices transcends mere legal obligation; it paves the way for cultivating trust with customers. But with regulations constantly evolving and data threats becoming more sophisticated, how can organizations guarantee that their compliance frameworks are not only effective but also resilient?
This article explores essential strategies for establishing a robust GDPR compliance framework. We will highlight key principles, outline actionable steps, and underscore the critical need for ongoing training and monitoring. By the end, you'll be equipped with the insights necessary to navigate the complexities of GDPR compliance confidently.
Understand the Key Principles of GDPR Compliance
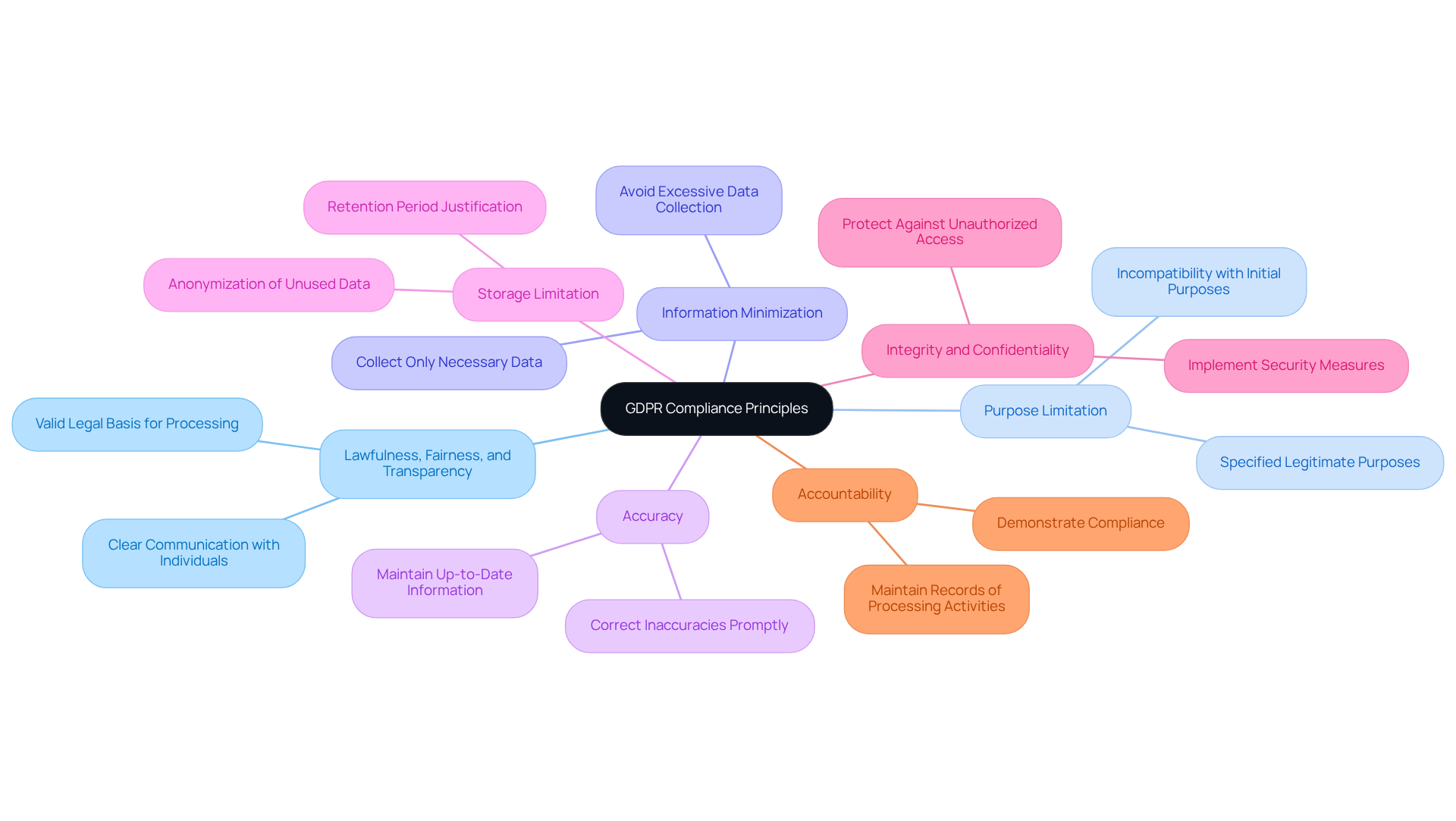
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) stands on several key principles that govern the handling of personal information. Understanding these principles is essential for organizations aiming to establish a robust GDPR compliance framework that meets legal obligations and fosters trust with customers and stakeholders.
-
Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency: Organizations must handle personal information lawfully, fairly, and transparently. This requires a valid legal basis for processing and clear communication with individuals about how their information will be used.
-
Purpose Limitation: Data should only be collected for specified, legitimate purposes. Further processing must not be incompatible with those initial purposes.
-
Information Minimization: Organizations should collect only the information necessary for the intended purpose, avoiding excessive data collection.
-
Accuracy: Personal information must be accurate and kept up to date. Organizations are responsible for taking reasonable steps to correct or remove inaccurate information.
-
Storage Limitation: Information should not be retained in a way that allows for the identification of individuals longer than necessary for the purposes for which it was processed.
-
Integrity and Confidentiality: Organizations must implement appropriate security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized processing, loss, or damage.
-
Accountability: Organizations are responsible for demonstrating compliance with these principles and must be able to show how they fulfill their obligations under data protection regulations.
Grasping these principles is crucial for creating a strong GDPR compliance framework that not only meets legal obligations but also cultivates trust with customers and stakeholders.
Create a Structured Action Plan for GDPR Implementation
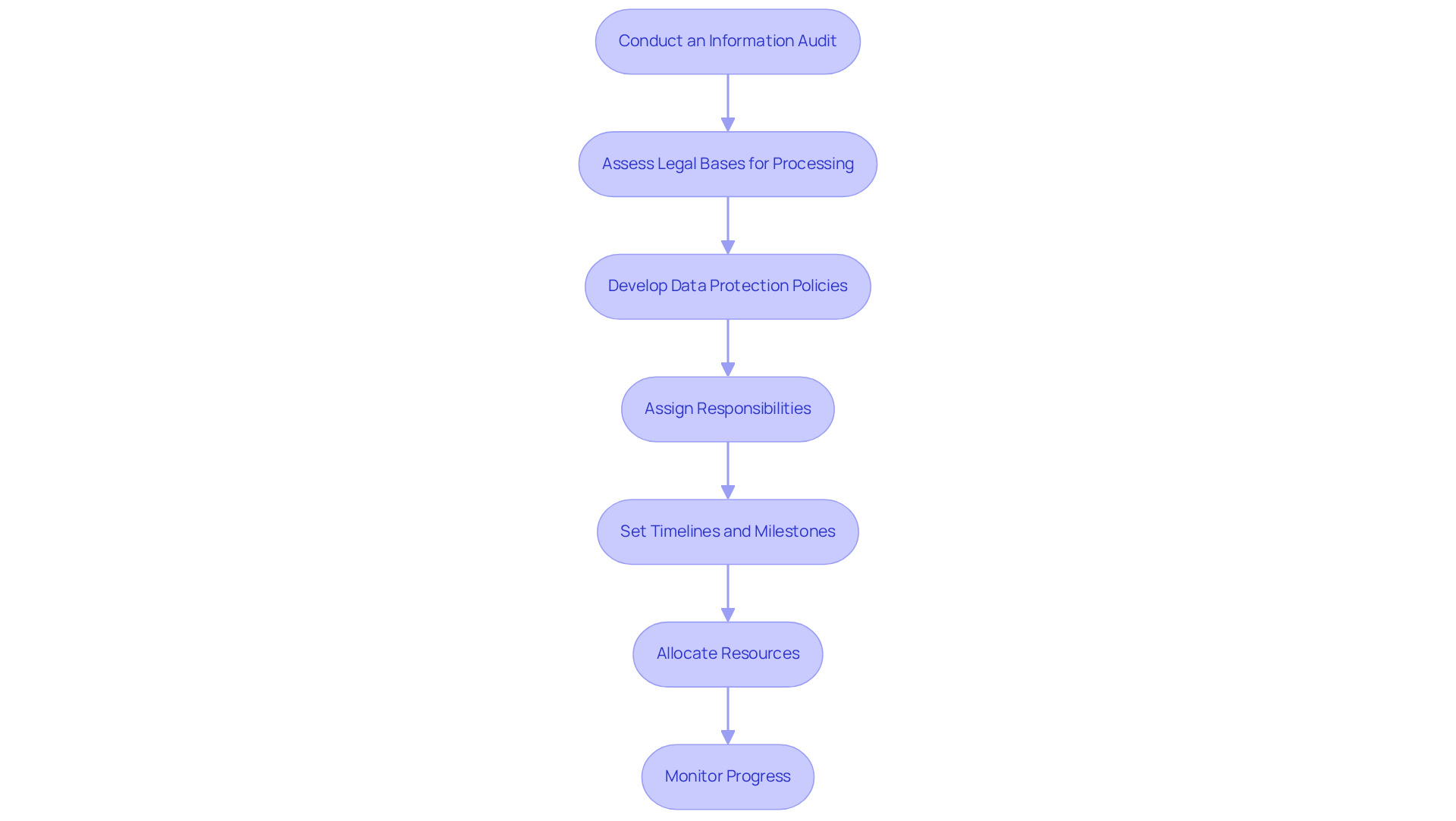
To effectively implement GDPR compliance, organizations must develop a structured action plan that encompasses several critical steps:
-
Conduct an Information Audit: Start by identifying and documenting all personal information processing activities within your organization. What information are you gathering? How is it utilized? Where is it stored? Understanding these aspects is crucial.
-
Assess Legal Bases for Processing: Next, determine the legal grounds for processing personal information. This could be based on consent, contractual necessity, or legitimate interests. Ensure that these bases are well-documented.
-
Develop Data Protection Policies: Create or update internal policies that reflect data protection regulations. This includes guidelines on data retention, data subject rights, and breach notification procedures.
-
Assign Responsibilities: Designate a Data Protection Officer (DPO) or a dedicated team responsible for overseeing the GDPR compliance framework and ensuring ongoing adherence to the regulations.
-
Set Timelines and Milestones: Establish clear timelines for each phase of your action plan. Set deadlines for audits, policy development, and training sessions to keep your organization on track.
-
Allocate Resources: Identify the necessary resources for compliance, including personnel, technology, and budget. This ensures that your action plan can be executed effectively.
-
Monitor Progress: Regularly review the progress of your action plan. Make adjustments as necessary to stay aligned with regulatory goals.
By following this systematic approach, organizations can effectively tackle data protection regulations and significantly reduce the risk of non-compliance within the GDPR compliance framework.
Implement Continuous Training and Awareness Programs
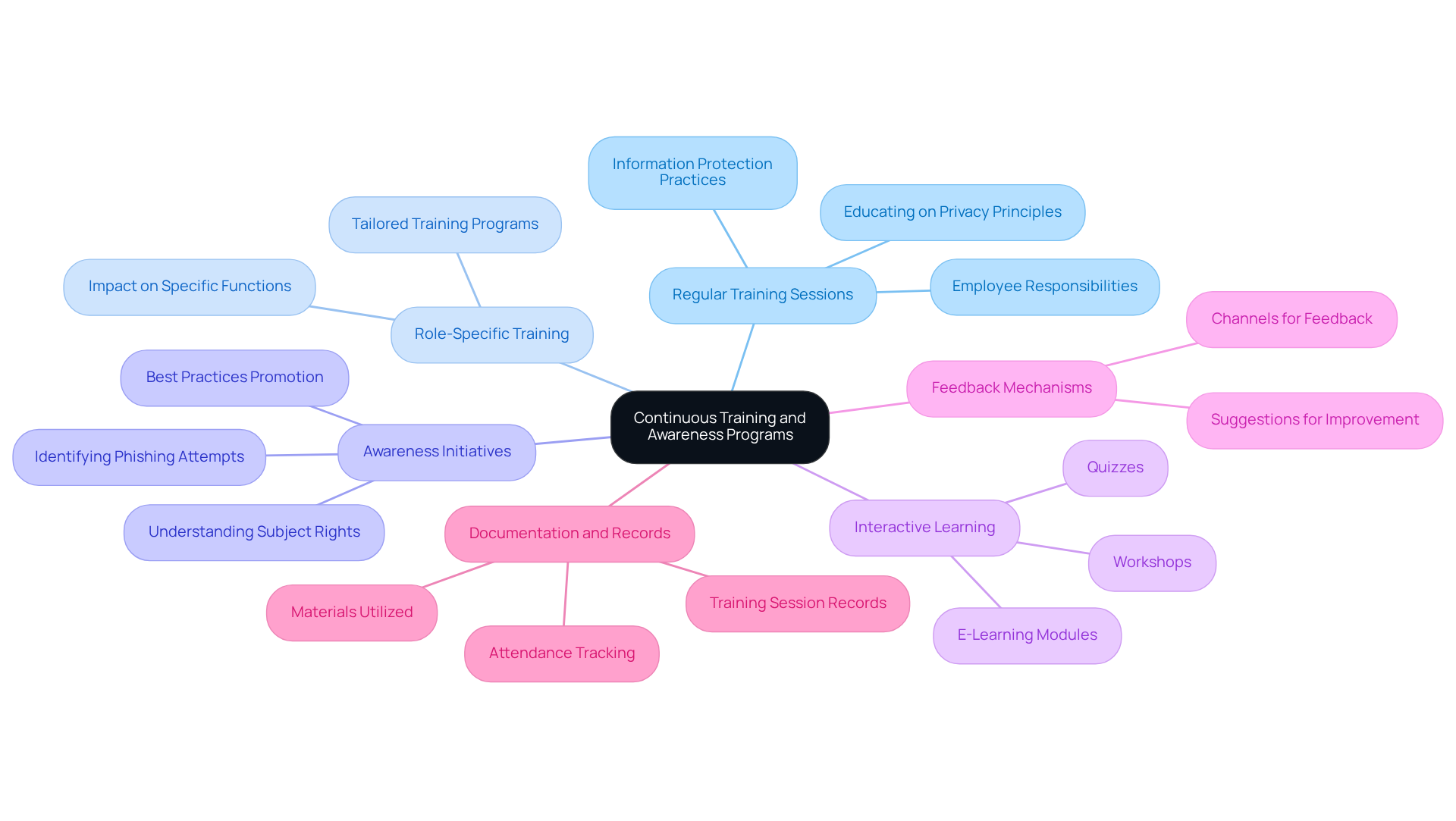
To ensure GDPR compliance, organizations must prioritize continuous training and awareness programs that encompass the following key elements:
-
Regular Training Sessions: It’s essential to conduct training sessions for all employees, educating them on privacy principles, information protection practices, and their specific responsibilities regarding personal information handling. How well do your employees understand these critical aspects?
-
Role-Specific Training: Tailoring training programs to different roles within the organization is crucial. This ensures that employees grasp how the GDPR compliance framework impacts their specific functions and responsibilities, fostering a more compliant workplace.
-
Awareness Initiatives: Initiate awareness initiatives that promote best practices in information protection. This includes secure information handling, identifying phishing attempts, and understanding subject rights. Are your employees aware of the risks they face?
-
Interactive Learning: Engage employees through interactive training methods, such as workshops, e-learning modules, and quizzes. These approaches not only reinforce learning but also make the training experience more enjoyable.
-
Feedback Mechanisms: Establish channels for employees to provide feedback on training programs and suggest improvements. This fosters a culture of continuous learning and adaptation, essential for maintaining compliance.
-
Documentation and Records: Maintain thorough records of training sessions, attendance, and materials utilized. This documentation illustrates adherence efforts and helps pinpoint areas for enhancement.
By emphasizing training and awareness, companies empower their staff to act as the first line of defense in safeguarding personal information and ensuring adherence to the GDPR compliance framework. Are you ready to take action and enhance your compliance efforts?
Establish Monitoring and Auditing Mechanisms for Compliance
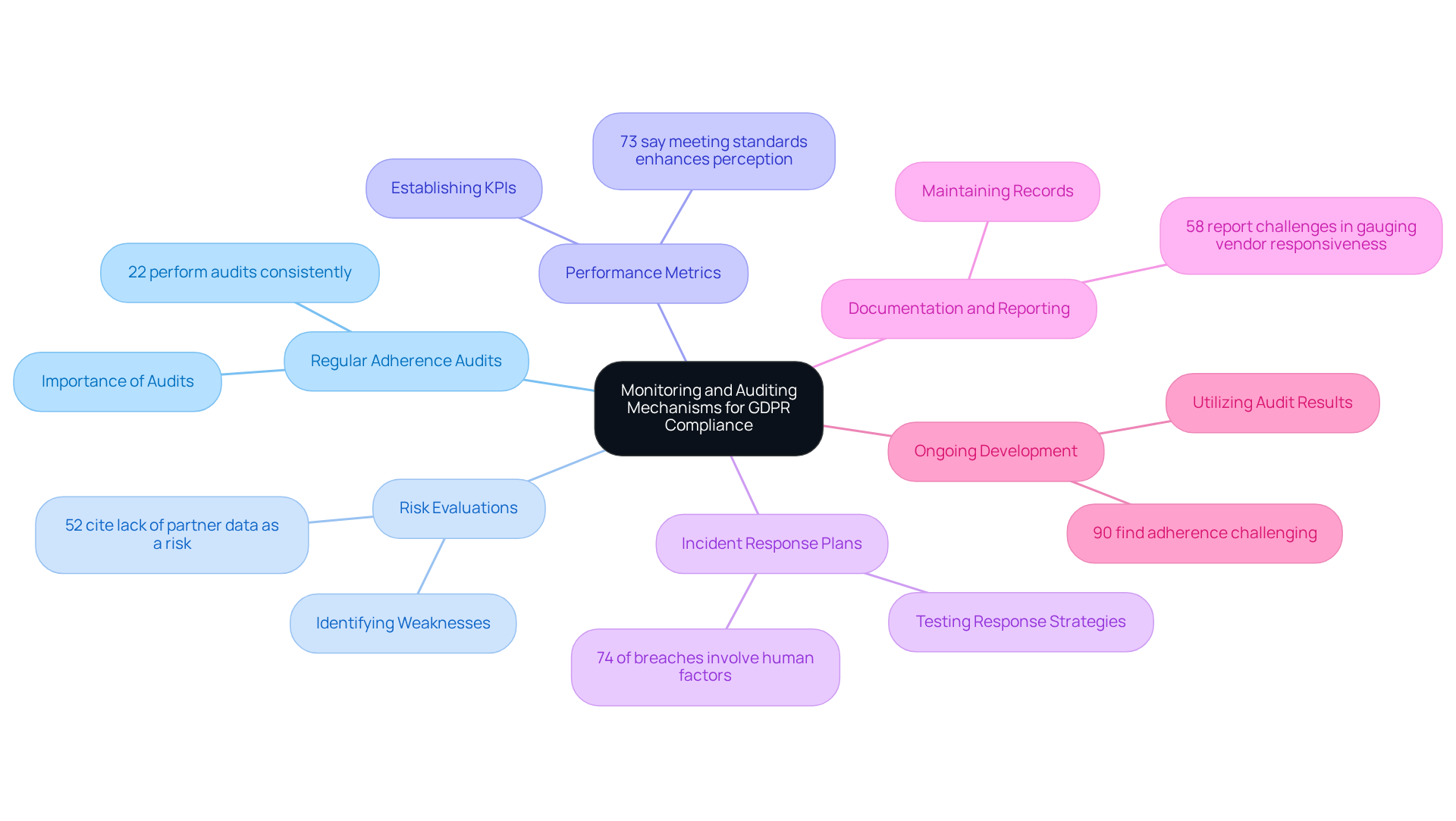
To ensure ongoing GDPR compliance, organizations must establish robust monitoring and auditing mechanisms that include:
-
Regular Adherence Audits: Periodic audits are essential for evaluating conformity with GDPR requirements, including data processing activities, security measures, and employee training effectiveness. Did you know that only 22% of entities perform these audits consistently? This highlights a significant gap in compliance practices. Furthermore, only 69% of employees feel their organization is at least 'good' at engaging in ongoing monitoring and risk management with third parties, underscoring the critical need for regular audits.
-
Risk Evaluations: Regular risk evaluations are vital for pinpointing potential weaknesses in information processing practices and assessing the effects of any recognized risks. This proactive approach is crucial, as 52% of regulatory specialists assert that a lack of information about partners exposes businesses to third-party risks. Clearly, these evaluations play a significant role in regulatory strategies.
-
Performance Metrics: Establishing essential performance indicators (KPIs) allows organizations to assess the efficiency of their information protection strategies and adherence efforts. Evidence-based decision-making is key here; 73% of leaders indicate that meeting regulatory standards enhances business perception, reinforcing the importance of effective metrics.
-
Incident Response Plans: Organizations should establish and regularly test incident response plans to ensure they can effectively respond to data breaches or regulatory failures. With 74% of breaches involving human factors, a well-prepared response strategy is crucial. This highlights the need for comprehensive employee training programs.
-
Documentation and Reporting: Maintaining comprehensive records of adherence efforts, audit findings, and corrective actions is essential for demonstrating accountability and transparency. Regulatory oversight is critical; 58% of adherence teams report challenges in gauging vendor responsiveness, making thorough documentation indispensable.
-
Ongoing Development: Utilize audit results and performance indicators to guide ongoing development initiatives. Adjusting policies and practices as needed to improve adherence is vital. Ninety percent of regulatory professionals consider data protection adherence one of the most challenging goals to achieve, making ongoing enhancement crucial.
By implementing these monitoring and auditing mechanisms, organizations can proactively manage their GDPR compliance and mitigate the risk of non-compliance.
Conclusion
Establishing a robust GDPR compliance framework is not merely a legal obligation; it’s essential for building trust and accountability in our data-driven world. Are you ready to enhance your organization’s reputation? By grasping and applying the key principles of GDPR, you can manage personal information lawfully and transparently, ultimately boosting your standing with customers and stakeholders.
This article outlines crucial best practices for achieving GDPR compliance. Understanding GDPR principles is paramount, as is creating a structured action plan. Prioritizing continuous training and awareness programs, along with establishing strong monitoring and auditing mechanisms, are vital steps. Each of these components is critical in ensuring that your organization not only meets regulatory requirements but also effectively protects individuals' personal data.
As you navigate the complexities of GDPR compliance, consider this: Are you taking proactive steps to foster a culture of data protection? By investing in training, conducting regular audits, and implementing clear action plans, your business can significantly mitigate the risk of non-compliance. This positions you as a leader in data stewardship. Embracing these best practices will not only safeguard personal information but also pave the way for long-term success in a landscape where data privacy is paramount.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)?
The GDPR is a regulation that governs the handling of personal information, establishing principles that organizations must follow to ensure compliance and protect individuals' data rights.
What are the key principles of GDPR compliance?
The key principles include Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency; Purpose Limitation; Information Minimization; Accuracy; Storage Limitation; Integrity and Confidentiality; and Accountability.
What does "Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency" mean in GDPR?
It means organizations must handle personal information lawfully, fairly, and transparently, requiring a valid legal basis for processing and clear communication with individuals about how their information will be used.
What is meant by "Purpose Limitation" in GDPR?
Purpose Limitation stipulates that data should only be collected for specific, legitimate purposes, and further processing must not be incompatible with those initial purposes.
What is "Information Minimization" in the context of GDPR?
Information Minimization refers to the principle that organizations should only collect the information necessary for the intended purpose, avoiding excessive data collection.
Why is "Accuracy" important in GDPR compliance?
Accuracy is important because personal information must be kept accurate and up to date, and organizations are responsible for taking reasonable steps to correct or remove inaccurate information.
What does "Storage Limitation" entail under GDPR?
Storage Limitation requires that information should not be retained in a way that allows for the identification of individuals longer than necessary for the purposes for which it was processed.
How does "Integrity and Confidentiality" relate to GDPR compliance?
Organizations must implement appropriate security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized processing, loss, or damage to ensure integrity and confidentiality.
What is the significance of "Accountability" in GDPR?
Accountability means organizations are responsible for demonstrating compliance with GDPR principles and must show how they fulfill their obligations under data protection regulations.




