4 Essential Cyber Security Controls for Defense Contractors
Explore essential cyber security control measures for defense contractors to enhance compliance and security.

Introduction
In an era where cyber threats are more pronounced than ever, defense contractors confront the formidable task of safeguarding sensitive information while meeting rigorous regulatory standards. Implementing essential cybersecurity controls transcends mere compliance; it is a vital opportunity for organizations to bolster their security posture and protect their operational integrity. So, how can defense firms adeptly navigate this intricate landscape to ensure robust protection against the ever-evolving cyber risks?
Understand Core Cybersecurity Principles
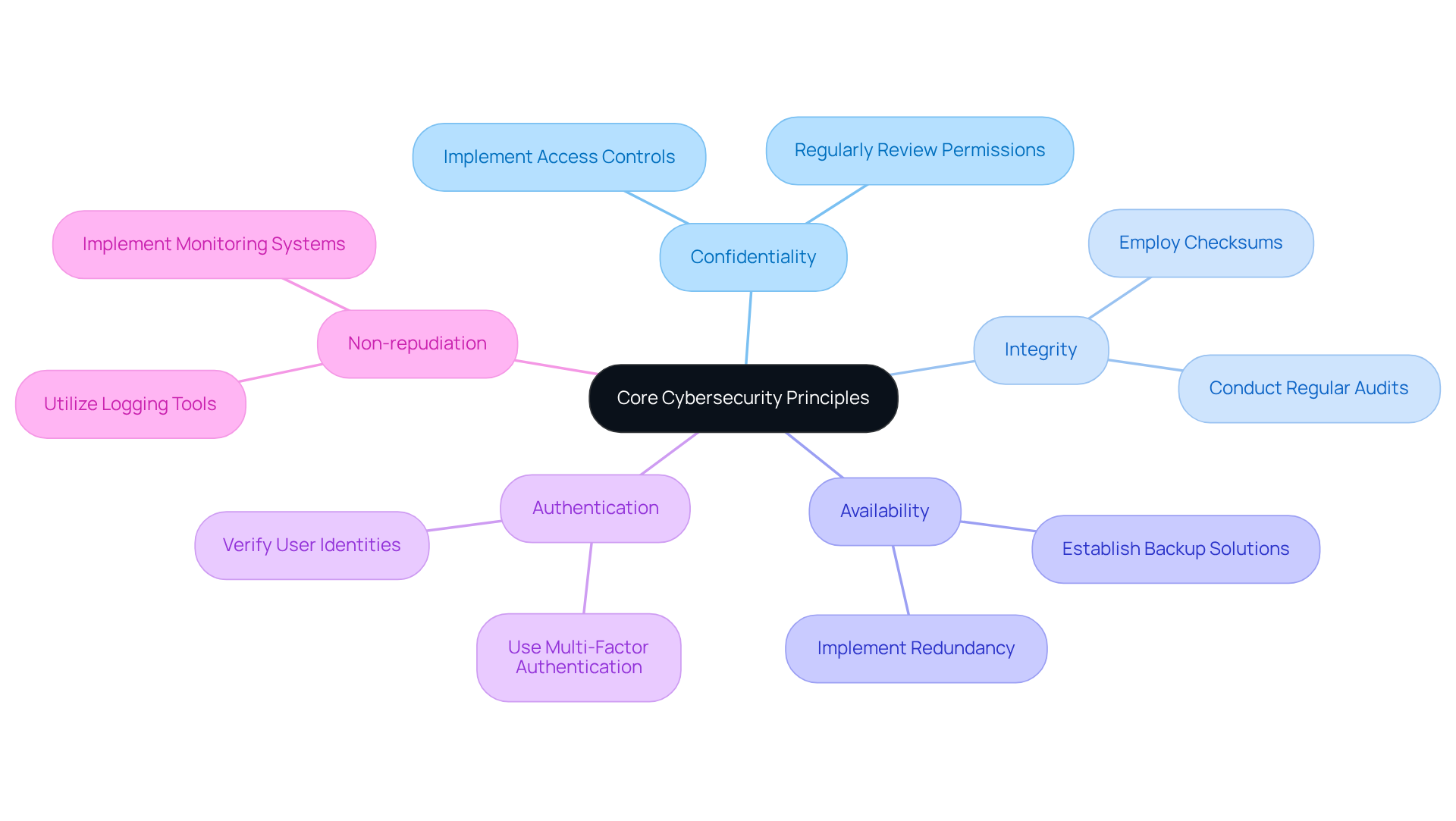
To effectively navigate the complexities of cybersecurity compliance, defense firms must grasp the core principles that underpin cyber security control. These principles are vital for safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring operational resilience:
-
Confidentiality: This principle ensures that sensitive information is accessible only to authorized individuals, protecting against unauthorized access and data breaches. Defense contractors should implement access controls and regularly review permissions to maintain confidentiality.
-
Integrity: Maintaining the accuracy and completeness of data is crucial. This principle prevents unauthorized modifications, ensuring that information remains trustworthy and reliable. Contractors can enhance integrity by employing checksums and regular audits to verify data accuracy.
-
Availability: It is essential to guarantee that information and resources are accessible to authorized users when needed. This principle helps mitigate risks associated with downtime and service disruptions. Implementing redundancy and backup solutions can significantly improve availability.
-
Authentication: Verifying the identity of users and systems before granting access is critical. Strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, help prevent unauthorized access and enhance overall security.
-
Non-repudiation: This principle ensures that actions or transactions can be verified and attributed to specific users, preventing denial of involvement. It is essential for accountability and traceability in digital security practices. Utilizing logging and monitoring tools can support non-repudiation efforts.
Comprehending these principles enables security providers to align their protection strategies with the strict requirements for cyber security control established by the Department of Defense (DoD) and the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC). The CMMC Info Hub functions as a thorough resource, providing practical strategies and peer insights to assist professionals in achieving CMMC compliance with assurance. This fundamental understanding is crucial for applying effective security measures and attaining compliance, ultimately improving the organization's capacity to safeguard sensitive information and sustain a competitive advantage in the security sector. Furthermore, as emphasized in the case study 'Zero-Trust Becomes Operational Necessity,' adopting a Zero-Trust architecture is becoming increasingly essential for builders to ensure comprehensive security.
Implement Essential Cybersecurity Controls
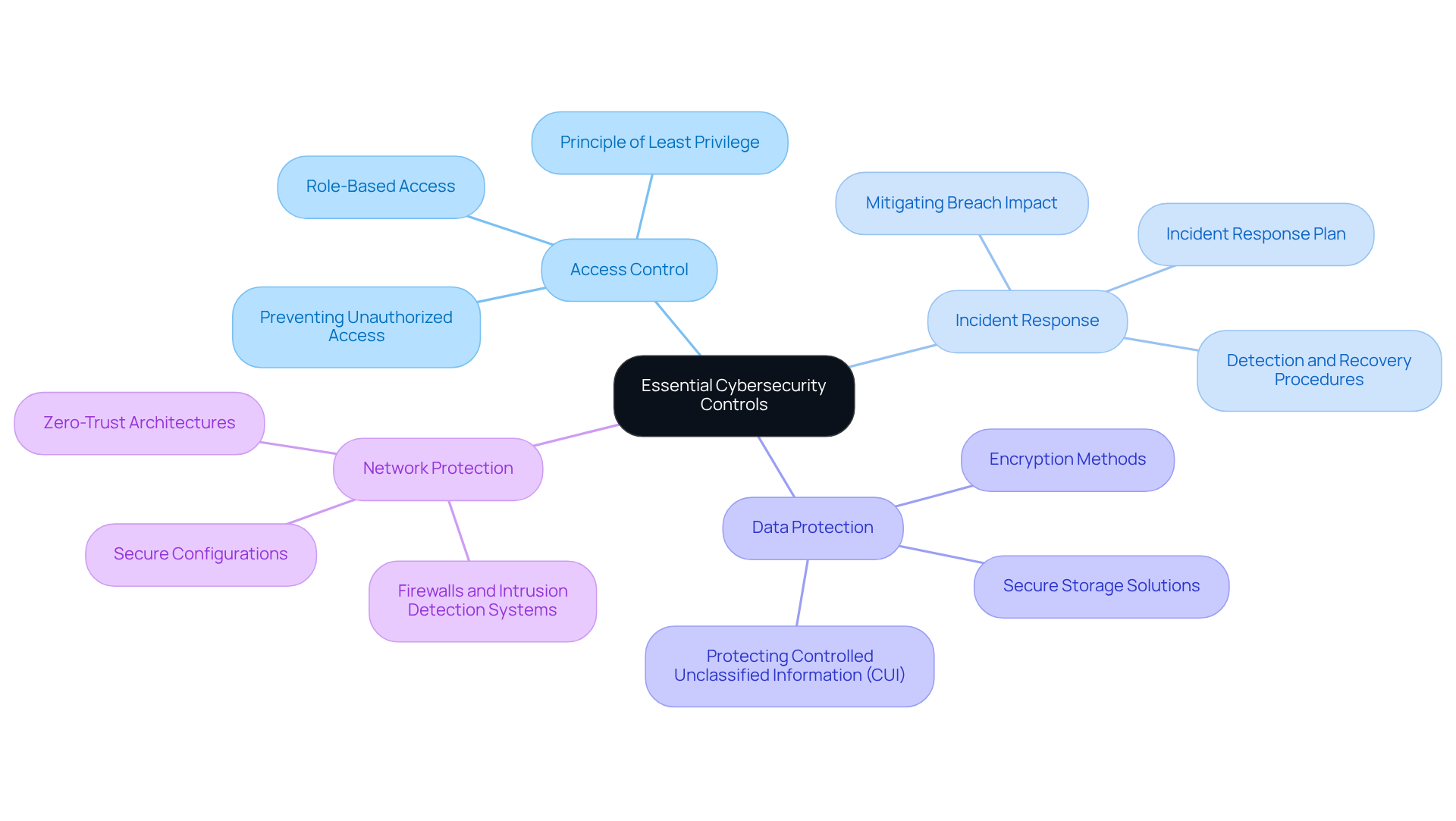
To achieve compliance with the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC), military suppliers must implement a series of essential protective measures designed to safeguard sensitive information and ensure operational resilience. Here are the key controls:
-
Access Control: Establishing stringent access controls is crucial. This means implementing role-based access and adhering to the principle of least privilege, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information. Cybersecurity experts stress that effective access control mechanisms are foundational in preventing unauthorized data access and breaches.
-
Incident Response: Developing and maintaining a robust incident response plan is vital. This plan should outline procedures for detecting, responding to, and recovering from cybersecurity incidents. Real-world examples show that organizations with well-defined incident response strategies can significantly mitigate the impact of breaches, reducing downtime and financial losses.
-
Data Protection: Utilizing encryption and secure storage solutions is essential for protecting sensitive data both at rest and in transit. As cyber threats evolve, the importance of safeguarding data through advanced encryption methods cannot be overstated, particularly for entities managing Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI).
-
Network Protection: Implementing comprehensive network protection measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and secure configurations, is critical for safeguarding network infrastructure from unauthorized access and attacks. Current trends indicate that security providers are increasingly adopting zero-trust architectures, which emphasize continuous verification and monitoring of network traffic to enhance safety.
By focusing on these crucial controls, security providers can significantly reduce their risk of cyber threats and improve their overall compliance with CMMC requirements. Incorporating these practices not only strengthens their security posture but also aligns with the evolving regulatory landscape, ensuring preparedness for future challenges.
Establish Continuous Monitoring and Assessment
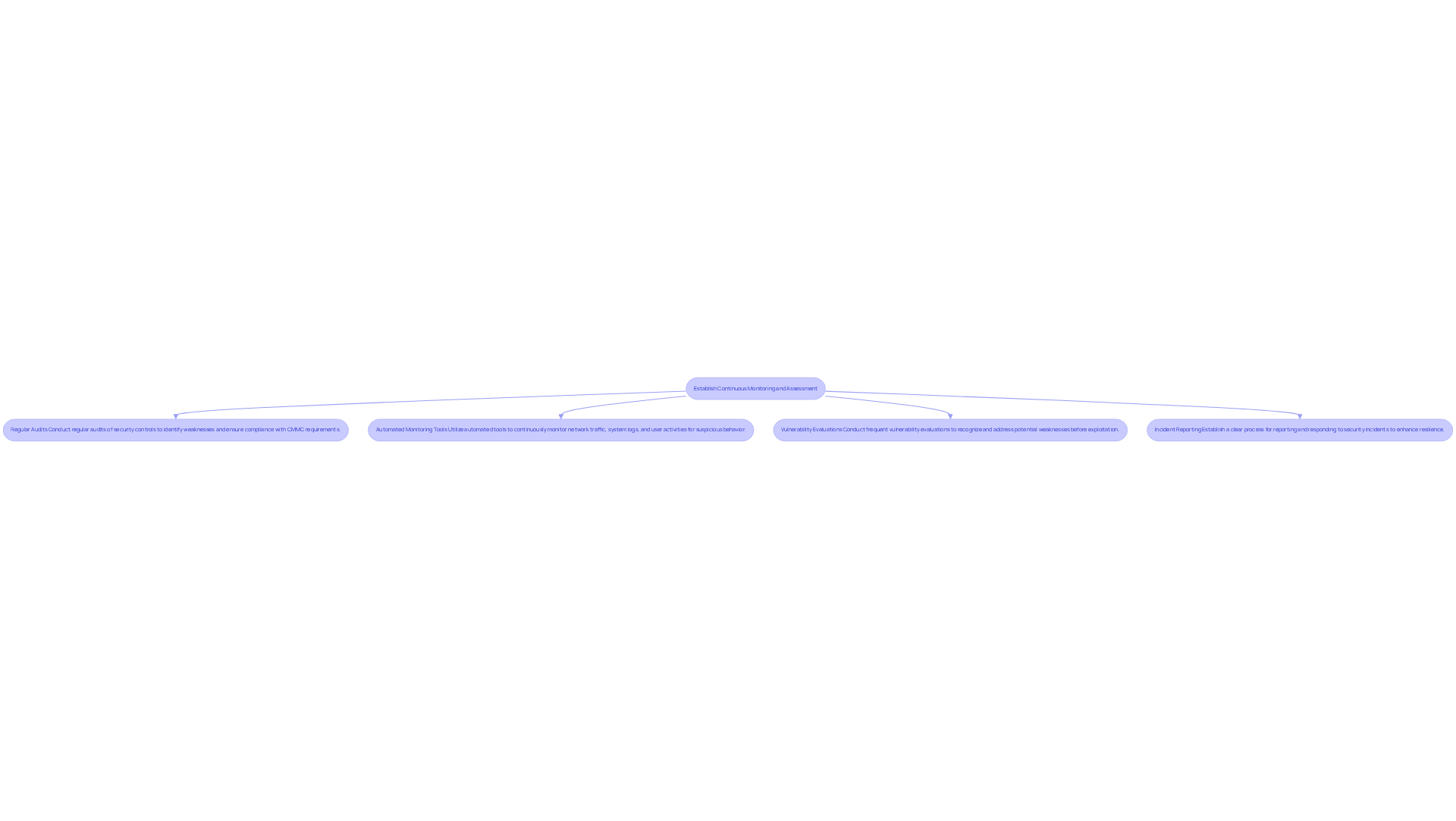
Ongoing observation and evaluation are vital components of a successful cyber security control strategy for defense suppliers. To effectively safeguard sensitive information and ensure compliance with CMMC requirements, contractors should adopt the following practices:
-
Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of security controls to identify weaknesses and ensure compliance with CMMC requirements. Research shows that organizations performing regular supplier audits are better positioned to maintain compliance across their supply chains.
-
Automated Monitoring Tools: Utilize automated tools as a cyber security control to continuously monitor network traffic, system logs, and user activities for signs of suspicious behavior. Tools like IPKeys Cyber-Lab-as-a-Service (CLaaS)® provide unified cybersecurity monitoring, enabling organizations to make informed decisions based on actionable insights.
-
Cyber Security Control: Conduct frequent vulnerability evaluations as a cyber security control to recognize and address potential weaknesses before they can be exploited. Organizations that utilize cyber security control by monitoring effectiveness metrics often report enhanced protective outcomes, with many achieving top-tier encryption through disciplined measurement practices.
-
Incident Reporting: Establish a clear process for reporting and responding to security incidents within the framework of cyber security control. This ensures that lessons learned are integrated into future practices, enhancing overall resilience against cyber threats through effective cyber security control.
By fostering a culture of ongoing observation and leveraging insights from colleagues, suppliers can significantly enhance their ability to respond to emerging threats and maintain adherence to evolving security standards. As the landscape becomes increasingly complex, incorporating automated monitoring tools and routine audits will be crucial for establishing effective cyber security control.
Foster Employee Training and Awareness
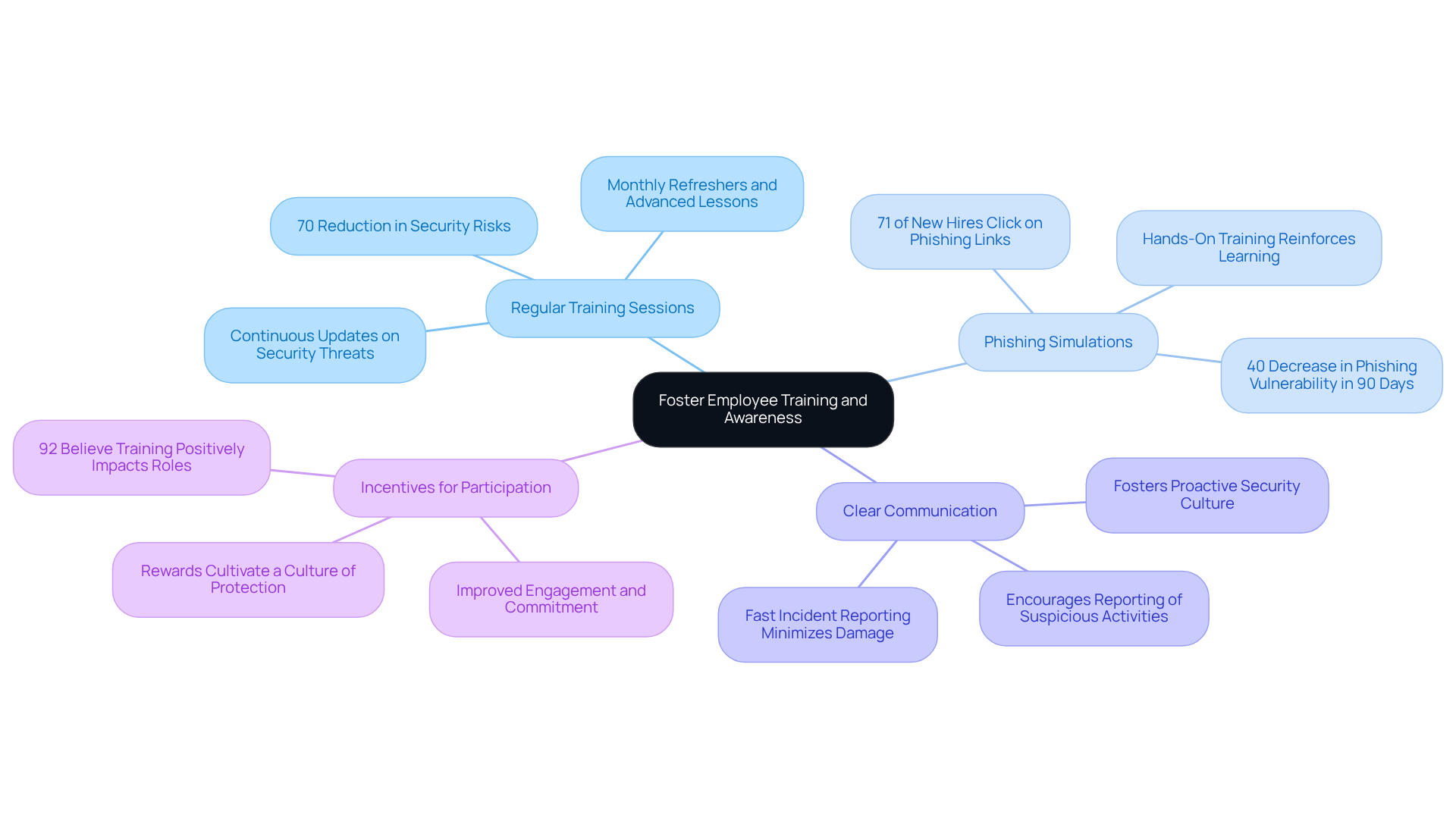
To effectively mitigate cybersecurity risks, defense contractors must prioritize employee training and awareness through several key strategies:
-
Regular Training Sessions: Continuous training is crucial to keep employees updated on the latest online security threats and best practices for prevention. Organizations that engage in ongoing training experience a remarkable 70% reduction in security-related risks. This statistic underscores the effectiveness of regular education in safeguarding sensitive information.
-
Phishing Simulations: Implementing phishing simulations is essential for testing employees' ability to recognize and respond to phishing attempts. Studies reveal that organizations employing continuous awareness training can decrease phishing vulnerability by over 40% within just 90 days. This hands-on approach not only reinforces training but also prepares employees to handle real-world threats effectively. Moreover, 71% of new hires are more likely to click on phishing links during their first 90 days, highlighting the urgent need for targeted training for newcomers.
-
Clear Communication: Establishing transparent communication pathways for reporting suspicious activities encourages employees to actively engage in protecting information security. Rapid incident reporting can significantly reduce breach damage. Training should emphasize the importance of identifying and reporting incidents without fear of blame, fostering a proactive security culture.
-
Incentives for Participation: Creating rewards for employees who actively participate in safety training cultivates a culture of protection. Organizations that recognize and reward participation see improved engagement and commitment, with 92% of employees believing that workplace training positively impacts their roles.
By fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness, defense contractors empower their employees to act as the first line of defense against cyber threats. This proactive approach not only enhances their overall security posture but also instills a sense of responsibility among staff, ultimately leading to a more secure organizational environment.
Conclusion
Understanding and implementing essential cybersecurity controls is crucial for defense contractors who need to protect sensitive information and comply with industry regulations. By grasping the core principles of confidentiality, integrity, availability, authentication, and non-repudiation, organizations can establish a solid foundation for their cybersecurity strategy. These principles not only guide the development of effective security measures but also align with the stringent requirements set forth by regulatory bodies like the Department of Defense and the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification.
To enhance their security posture, defense contractors should adopt several key practices:
- Establish strict access controls.
- Develop comprehensive incident response plans.
- Protect data through encryption.
- Implement continuous monitoring and assessment strategies.
Additionally, fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness through regular training and communication is vital. By prioritizing these controls, defense contractors can significantly reduce their vulnerability to cyber threats and ensure compliance with evolving regulatory standards.
The importance of cybersecurity in the defense industry cannot be overstated. As cyber threats continue to evolve, organizations must remain vigilant and proactive in their approach to security. Embracing best practices and investing in employee training will not only safeguard sensitive information but also empower staff to act as the first line of defense against potential breaches. By taking decisive action now, defense contractors can secure their operations and maintain a competitive edge in a complex and challenging landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the core principles of cybersecurity that defense firms must understand?
The core principles of cybersecurity include Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability, Authentication, and Non-repudiation. These principles are essential for safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring operational resilience.
What does the principle of confidentiality entail?
Confidentiality ensures that sensitive information is accessible only to authorized individuals, protecting against unauthorized access and data breaches. Defense contractors should implement access controls and regularly review permissions to maintain confidentiality.
How is integrity maintained in cybersecurity?
Integrity involves maintaining the accuracy and completeness of data, preventing unauthorized modifications. Contractors can enhance integrity by employing checksums and conducting regular audits to verify data accuracy.
Why is availability important in cybersecurity?
Availability guarantees that information and resources are accessible to authorized users when needed, mitigating risks associated with downtime and service disruptions. Implementing redundancy and backup solutions can significantly improve availability.
What role does authentication play in cybersecurity?
Authentication is critical for verifying the identity of users and systems before granting access. Strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, help prevent unauthorized access and enhance overall security.
What is non-repudiation and why is it important?
Non-repudiation ensures that actions or transactions can be verified and attributed to specific users, preventing denial of involvement. It is essential for accountability and traceability in digital security practices, supported by logging and monitoring tools.
How do these principles align with the requirements set by the Department of Defense and CMMC?
Understanding these principles allows security providers to align their protection strategies with the strict cybersecurity control requirements established by the Department of Defense (DoD) and the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC).
What resources are available to assist professionals in achieving CMMC compliance?
The CMMC Info Hub serves as a comprehensive resource, providing practical strategies and peer insights to assist professionals in achieving CMMC compliance with assurance.
What is the significance of adopting a Zero-Trust architecture in cybersecurity?
Adopting a Zero-Trust architecture is becoming increasingly essential for builders to ensure comprehensive security, as emphasized in the case study 'Zero-Trust Becomes Operational Necessity.




