Best Practices for Managing Unclassified Information in Defense Contracts
Learn best practices for managing unclassified information in defense contracts effectively.

Introduction
Understanding the complexities of Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) is crucial for organizations involved in defense contracts. The stakes are high, and the margin for error is slim. With over 350,000 contractors navigating stringent regulatory frameworks, the risks of mishandling sensitive data are significant. These risks aren't just theoretical; they can lead to financial losses that reach millions.
So, how can organizations ensure they are compliant while effectively protecting this critical information? By exploring best practices for managing unclassified information, we uncover essential strategies that not only safeguard national interests but also enhance cybersecurity postures across the defense sector.
Consider this: what steps can your organization take today to bolster its defenses against potential data breaches? The answer lies in understanding and implementing robust compliance measures.
Define Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI)
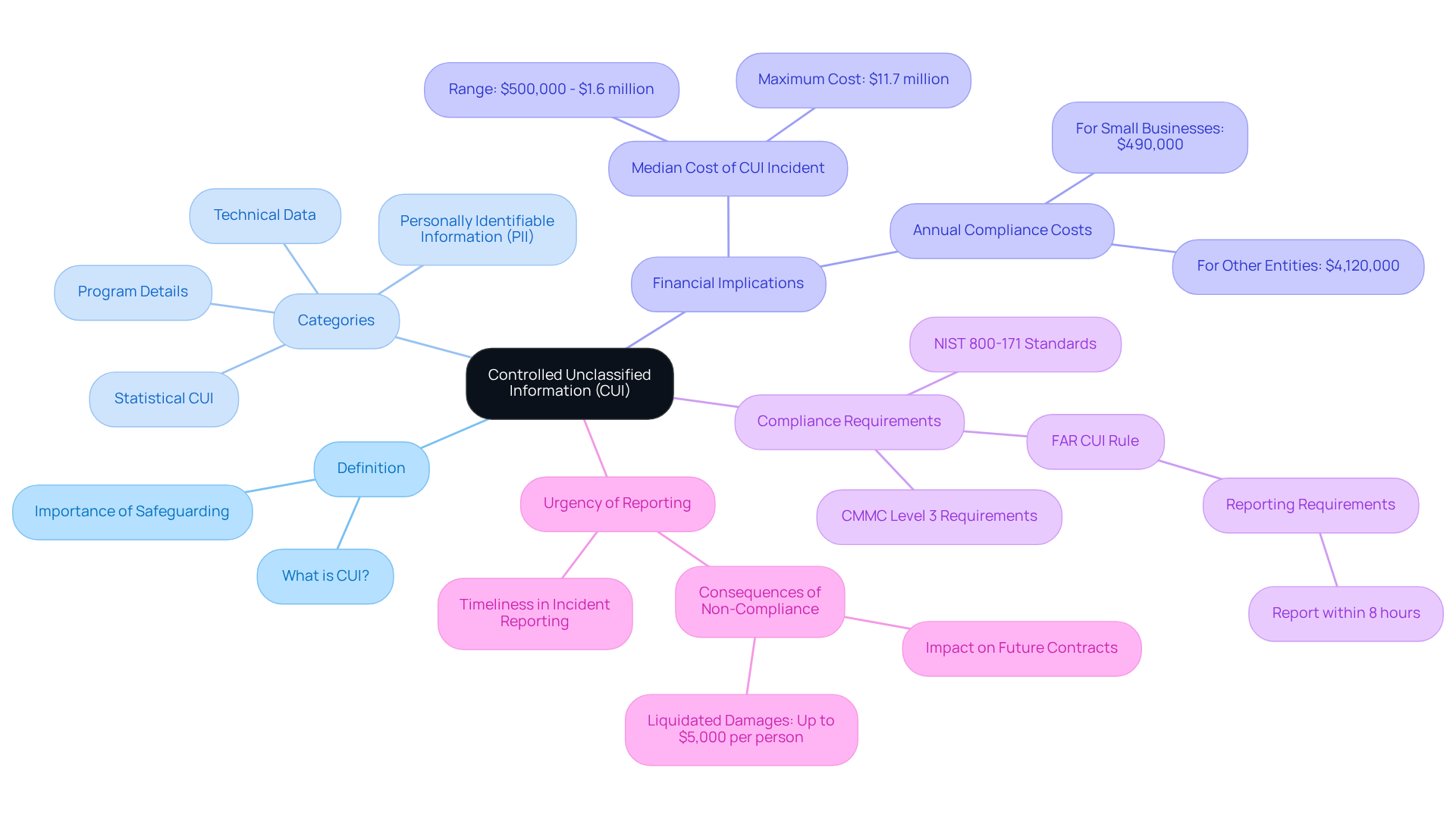
Unclassified information, specifically Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI), is a critical category of sensitive data that, while not classified, requires stringent safeguarding and dissemination controls mandated by law, regulation, or government-wide policy. This includes technical data, program details, and other sensitive information that, if improperly disclosed, could jeopardize national security.
Understanding unclassified information is essential for organizations aiming to comply with Department of Defense (DoD) requirements and effectively protect sensitive data. Are you aware of the definitions and categories of CUI? This knowledge is crucial for implementing necessary protective measures and educating staff on proper handling procedures. With the DoD collaborating with over 350,000 contractors, the importance of managing unclassified information cannot be overstated, especially considering the potential risks associated with mishandling such information.
For instance, did you know that the median cost of a CUI incident can range from $500,000 to $1.6 million? In some cases, maximum costs have soared as high as $11.7 million. These figures highlight the financial implications of non-compliance. Organizations must proactively assess their cybersecurity posture and align with NIST 800-171 standards to ensure robust protection of unclassified information, thereby safeguarding national interests and maintaining eligibility for defense contracts.
Additionally, the FAR CUI Rule requires contractors to report cybersecurity incidents involving CUI within 8 hours of discovery. This underscores the urgency of compliance. For further information, please refer to our FAQs and external resources linked below.
Understand Regulatory Requirements for CUI Management
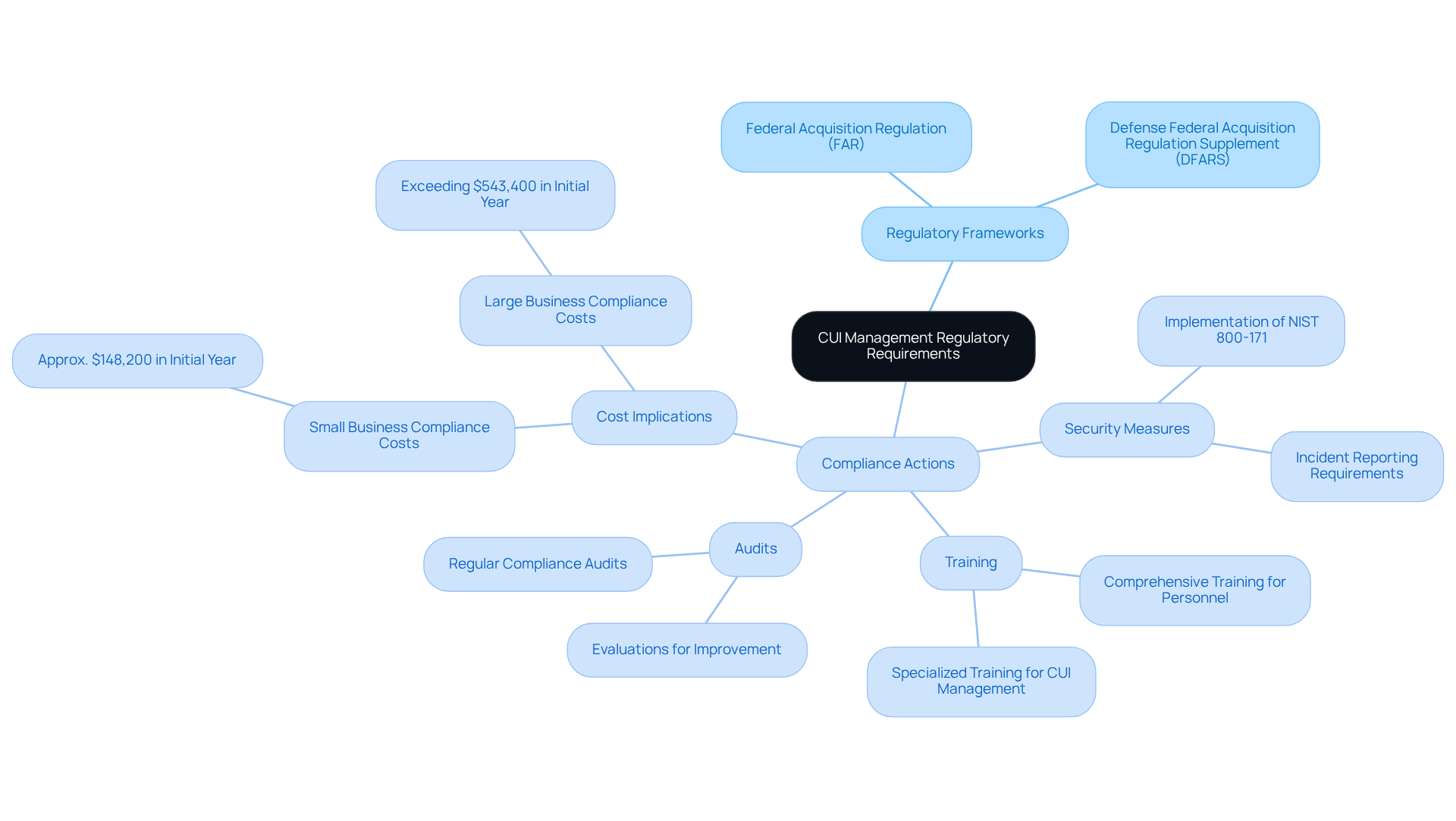
Organizations managing unclassified information face stringent regulatory frameworks, notably the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) and the Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement (DFARS). These regulations are crucial for establishing protective measures necessary to safeguard unclassified information from unauthorized access and disclosure.
The FAR CUI Rule mandates that contractors implement specific security measures and ensures that all personnel handling unclassified information receive comprehensive training to understand their responsibilities. Have you considered the implications of non-compliance? Regular audits and evaluations are essential for confirming adherence to these regulations. Recent statistics reveal that companies can expect significant investments in compliance processes - small businesses may incur costs around $148,200 in the initial year, while larger entities could face expenses exceeding $543,400.
These evaluations not only ensure compliance but also help identify areas for improvement, ultimately enhancing an entity's cybersecurity posture. As the regulatory landscape evolves, staying informed about updates and implementing robust security controls is vital for those involved in federal contracting.
For additional resources and guidance, please refer to the external links provided by CMMC Info Hub. Taking action now can safeguard your organization and ensure compliance with these critical regulations.
Implement Best Practices for Safeguarding CUI
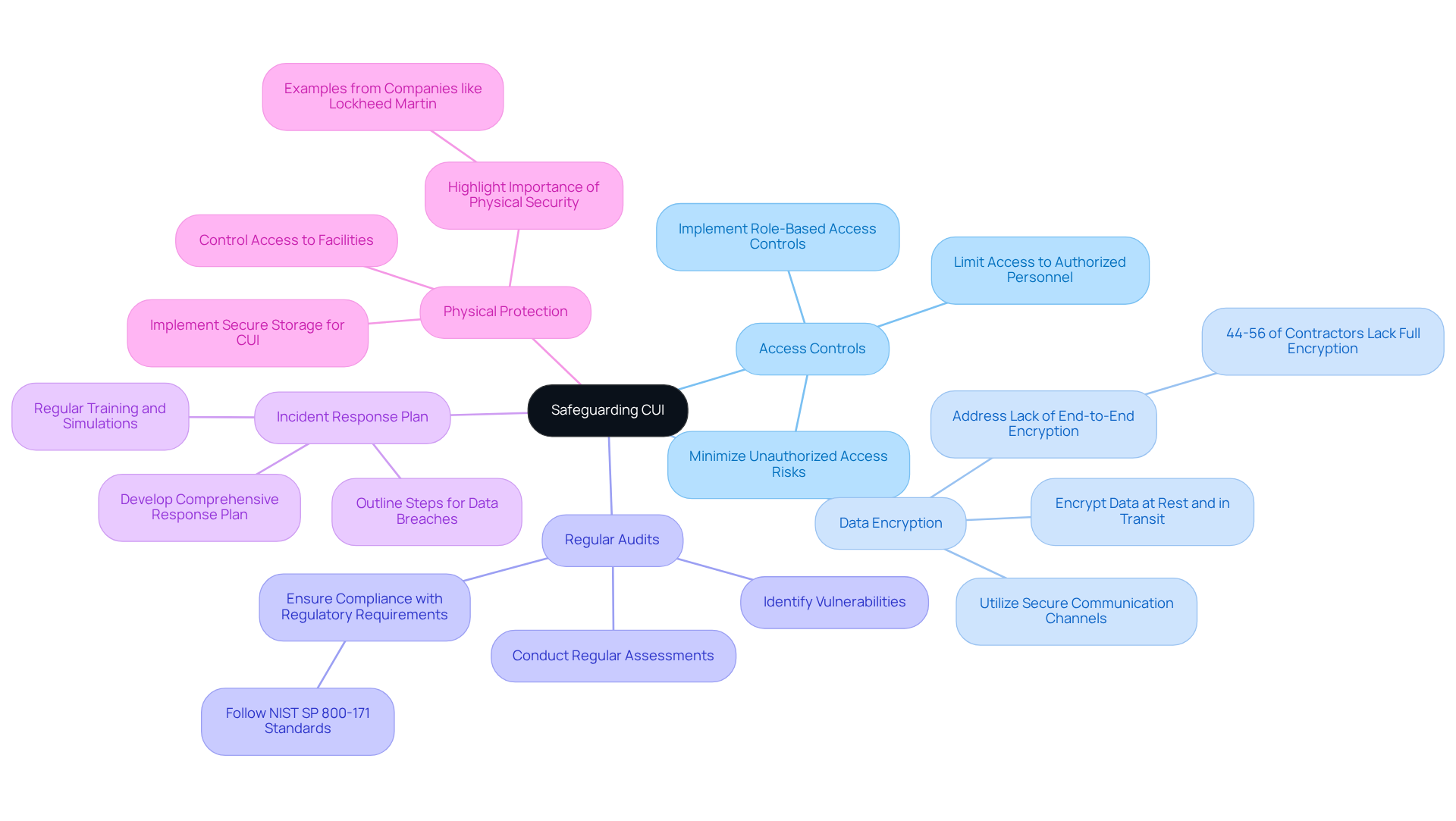
To effectively safeguard Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI), organizations must adopt essential best practices:
-
Access Controls: Limit access to CUI strictly to authorized personnel. Implement role-based access controls to ensure individuals can only access information necessary for their job functions. This approach minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
-
Data Encryption: Encrypt unclassified information both at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access. Utilizing secure communication channels for transmitting CUI is essential. Did you know that 44-56% of defense contractors lack full end-to-end encryption for sensitive data? This statistic underscores the urgent need for immediate action in this area.
-
Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits and assessments of CUI handling practices to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. This proactive measure helps companies stay ahead of potential threats and maintain compliance with standards regarding unclassified information, such as NIST SP 800-171. Organizations that conduct frequent audits are better positioned to mitigate risks effectively.
-
Incident Response Plan: Develop and maintain a comprehensive incident response plan specifically for CUI breaches. This plan should outline clear steps to take in the event of a data compromise, ensuring a swift and effective response to mitigate damage. Experts recommend regular training and simulations to prepare staff for potential incidents.
-
Physical Protection: Implement robust physical protection measures, including secure storage for CUI documents and controlled access to facilities where CUI is processed or stored. Effective physical protection is crucial in preventing unauthorized access and safeguarding sensitive information. Companies like Lockheed Martin highlight the significance of stringent physical security measures in protecting sensitive data.
By prioritizing these best practices, defense contractors can enhance their cybersecurity posture and protect vital information, transforming confusion into clarity in their compliance efforts.
Enhance Training and Awareness for CUI Handling
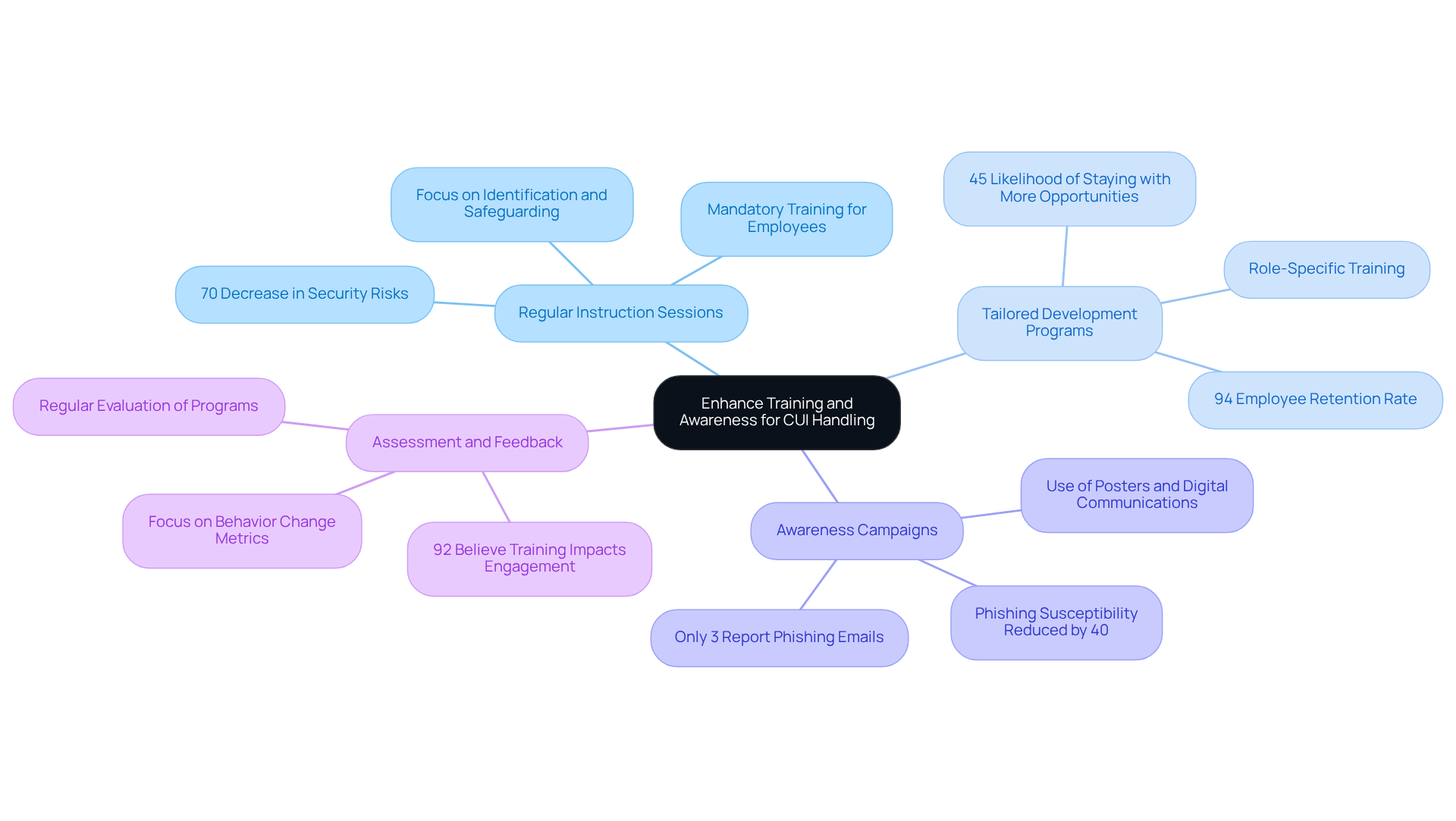
To enhance training and awareness for handling Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI), organizations must adopt effective strategies:
-
Regular Instruction Sessions: Mandatory instruction sessions for all employees handling CUI are essential. These sessions should focus on the identification, marking, safeguarding, and reporting procedures for unclassified information. Why is this foundational knowledge crucial? Entities that engage in ongoing security awareness education experience a remarkable 70% decrease in security-related risks.
-
Tailored Development Programs: Organizations should create educational programs tailored to the specific roles and responsibilities of employees. This ensures that they grasp the unique requirements related to unclassified information in their job functions. Customized programs significantly enhance employee engagement and retention; in fact, 94% of employees indicate they would stay longer at organizations that invest in their development. Moreover, 45% of employees are likely to remain in their positions if offered more development opportunities, underscoring the importance of investing in education and retention strategies.
-
Launching awareness campaigns is vital to reinforce the importance of unclassified information protection and compliance. Utilizing posters, newsletters, and digital communications keeps the management of unclassified information at the forefront, fostering a culture of safety. Organizations that implement continuous development programs see substantial improvements in employee awareness, with phishing susceptibility reduced by over 40% within just 90 days. Alarmingly, only 3% of employees report phishing emails to management, highlighting a critical area for improvement in security awareness.
-
Assessment and Feedback: Regular evaluation of educational programs through quizzes and feedback sessions is necessary. This practice enables ongoing enhancement and adjustment to evolving regulations, ensuring that instruction remains relevant and effective. Companies that assess the ROI of their development initiatives often find that effective programs lead to improved employee performance and organizational competitiveness. Notably, 92% of employees believe that workplace training positively impacts their engagement and commitment, emphasizing the benefits of effective training programs.
Conclusion
Managing Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) is crucial for organizations involved in defense contracts. This sensitive data, while unclassified, demands stringent protective measures. Effective CUI management not only ensures compliance with regulatory frameworks but also safeguards national security interests and mitigates potential financial repercussions from data breaches.
Understanding CUI definitions and regulatory requirements is essential. Organizations must implement best practices for safeguarding sensitive information and enhance training and awareness among personnel. Robust security measures, regular audits, and tailored training programs are vital to cultivating a culture of compliance and security awareness. The financial implications of non-compliance further highlight the necessity for a proactive approach in managing unclassified information.
Given the evolving regulatory landscape and the rising risks of mishandling sensitive data, prioritizing CUI management is imperative. By embracing best practices and fostering a culture of continuous learning and vigilance, defense contractors can protect vital information and maintain eligibility for future contracts. Taking action today ensures that organizations are well-prepared to navigate the complexities of CUI management effectively, safeguarding both their interests and national security.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI)?
Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) is a category of sensitive data that, while not classified, requires strict safeguarding and dissemination controls as mandated by law, regulation, or government-wide policy.
Why is understanding CUI important for organizations?
Understanding CUI is essential for organizations to comply with Department of Defense (DoD) requirements and effectively protect sensitive data, thereby preventing potential risks associated with mishandling such information.
What types of information are considered CUI?
CUI includes technical data, program details, and other sensitive information that, if improperly disclosed, could jeopardize national security.
What are the financial implications of CUI incidents?
The median cost of a CUI incident can range from $500,000 to $1.6 million, with maximum costs reaching as high as $11.7 million, highlighting the importance of compliance.
What standards should organizations align with to protect CUI?
Organizations should align with NIST 800-171 standards to ensure robust protection of unclassified information and maintain eligibility for defense contracts.
What is the reporting requirement for contractors regarding CUI cybersecurity incidents?
The FAR CUI Rule requires contractors to report cybersecurity incidents involving CUI within 8 hours of discovery, emphasizing the urgency of compliance.
How can organizations educate their staff on handling CUI?
Organizations can implement necessary protective measures and provide training to educate staff on proper handling procedures for CUI.




