Manage CUI Effectively at the Time of Creation of CUI Material
Ensure compliance and effective management of CUI at the time of creation of CUI material.

Overview
To effectively manage Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) at the time of its creation, organizations must:
- Clearly define roles
- Implement proper marking procedures
- Provide comprehensive training to staff
Establishing a robust management policy is not merely beneficial; it is crucial. This policy should include specific responsibilities for CUI handling and ongoing education, ensuring compliance with federal regulations and safeguarding sensitive data from unauthorized access.
How can organizations achieve this? By prioritizing CUI management, they can protect their information assets and enhance their overall security posture.
Introduction
Effectively managing Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) is essential for organizations that handle sensitive data. This guide explores critical practices for creating and safeguarding CUI materials, ensuring compliance with federal regulations while protecting vital information. With the evolving landscape of CUI regulations and the potential consequences of noncompliance, organizations must consider:
- How can they stay ahead and ensure their personnel are equipped to handle CUI appropriately?
By understanding these dynamics, organizations can not only comply but also enhance their operational integrity.
Define Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI)
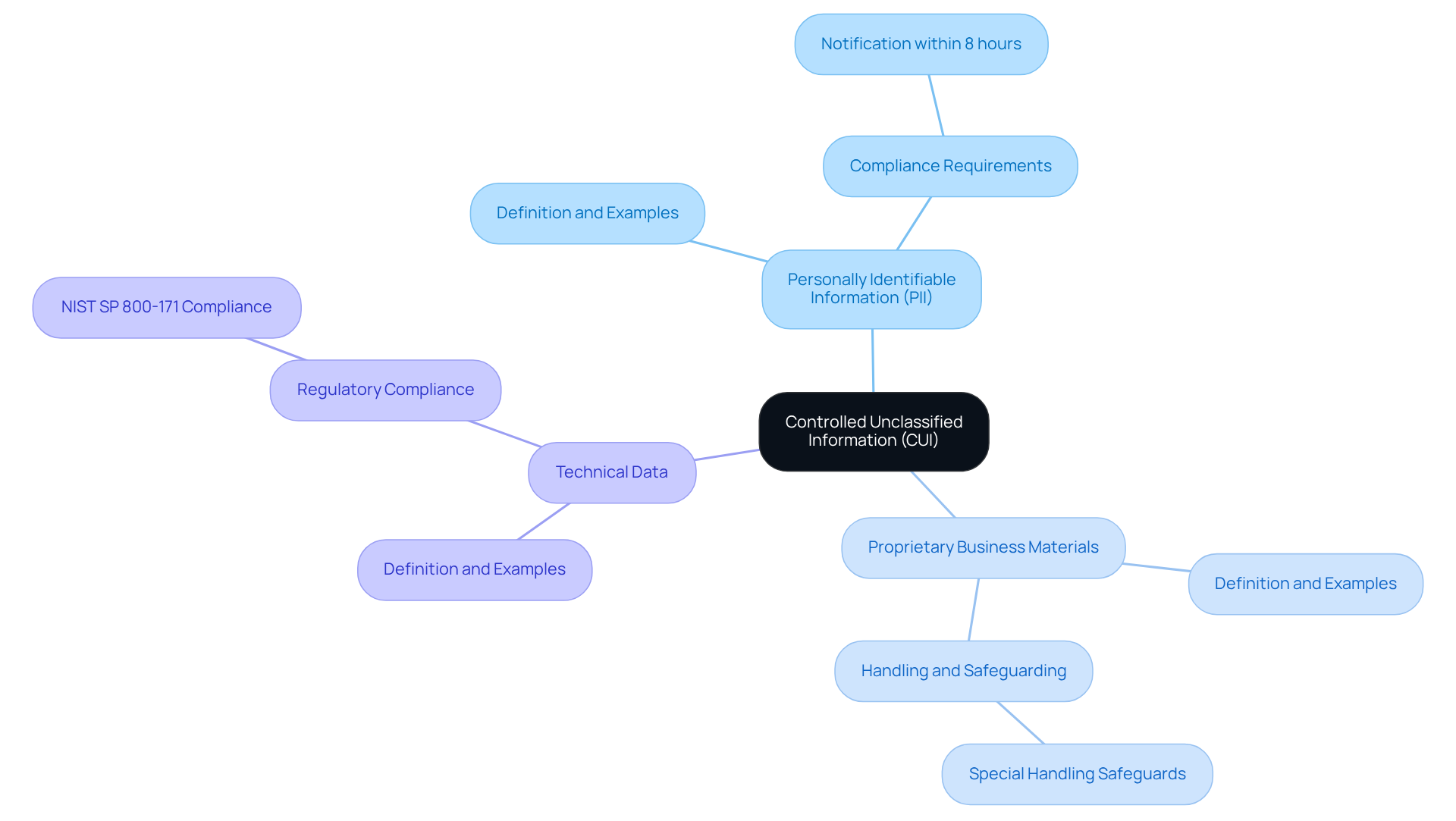
Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) refers to details that the U.S. government creates or possesses, requiring safeguarding or dissemination controls, yet is not classified. CUI encompasses various types of sensitive data, including:
- Personally identifiable information (PII)
- Proprietary business materials
- Technical data related to defense contracts
Understanding the specific categories of CUI is crucial, as it dictates how organizations must manage, label, and protect this data in compliance with federal regulations and standards, particularly those set by the Department of Defense (DoD).
For instance, contractors are obligated to notify the government within eight hours of discovering information believed to be CUI, underscoring the significance of compliance. To gain a comprehensive overview of CUI categories, consult the CUI Registry provided by the National Archives. This platform may also include links to external sites offering additional insights on CUI and regulatory processes. It is important to note that we have no control over the content of these external sites and accept no responsibility for their content or availability; the inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement by us.
Moreover, with the recent introduction of CMMC 2.0 on December 16, 2024, contractors must remain vigilant regarding the updated regulatory requirements. Noncompliance with CUI regulations can result in serious repercussions, including potential liability for costs incurred by the government due to a CUI incident. Contractors should also participate in the ongoing public comment period for the FAR CUI Rule, which extends through May 17, 2025, to stay informed and influence the regulatory landscape.
Establish Responsibilities for CUI Creation
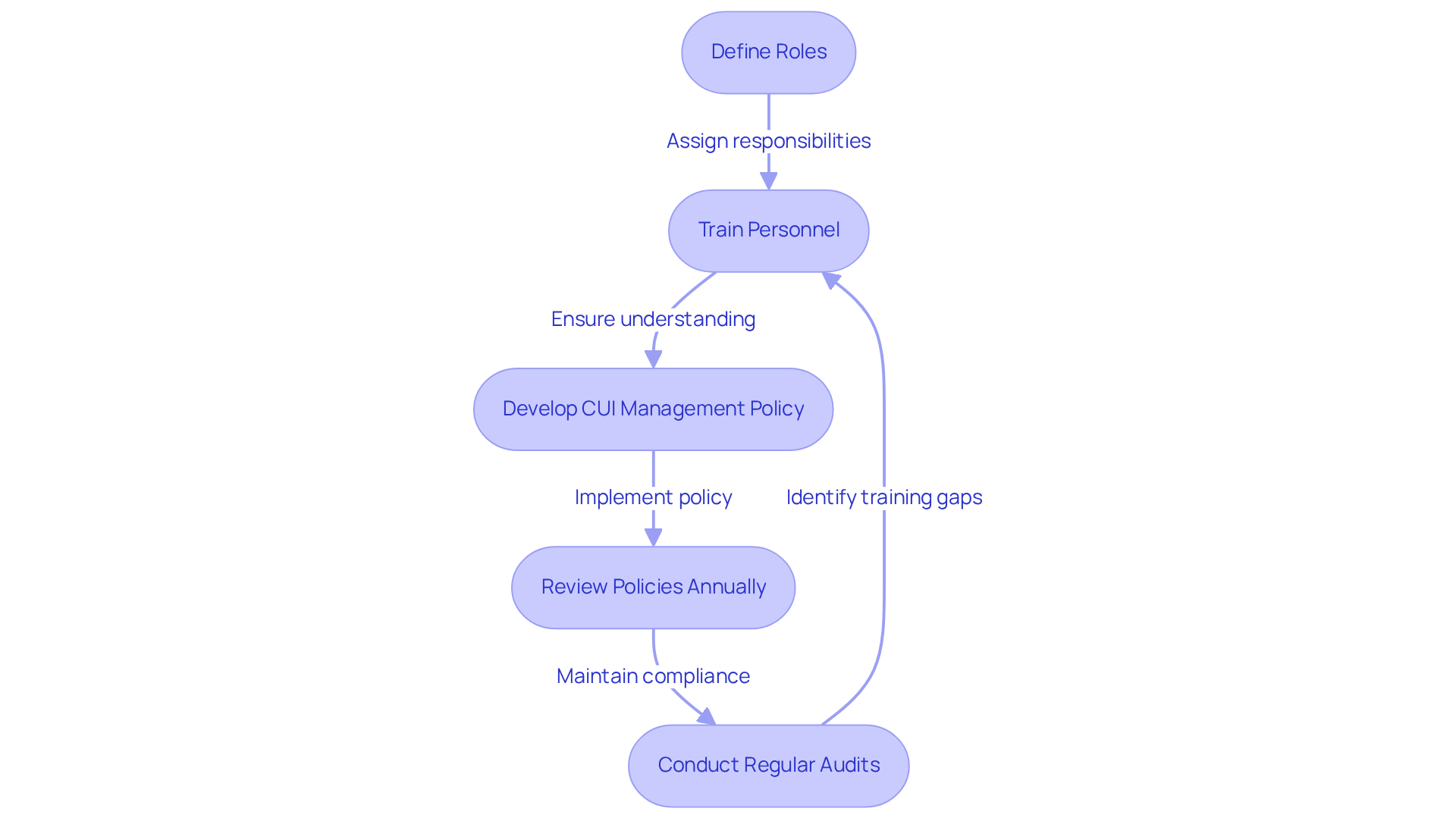
To effectively manage Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI), organizations must clearly define roles and responsibilities for its creation. This involves assigning specific individuals or teams responsible for recognizing data that qualifies as CUI. Are your personnel equipped with the necessary training? These individuals should undergo thorough instruction on relevant regulations, including the specific requirements outlined in 32CFR §2002 and NIST SP 800-171, to ensure compliance.
Developing a robust CUI management policy is essential. It should:
- Delineate who has the authority to mark information as CUI
- Document its creation
- Outline safeguarding procedures
- Maintain an archive of previous policy versions
Furthermore, policies and procedures should be reviewed at least annually to ensure they remain current and effective. A formal process for proposing and approving changes, along with maintaining version control of policies, is critical.
Employees must undergo instruction at orientation and yearly to maintain their understanding of CUI handling. Regular audits and reviews are crucial to verify adherence to these responsibilities and to identify any training gaps or misunderstandings among staff. Did you know that noncompliance with CUI requirements can lead to significant consequences, including contractual disputes and enforcement actions?
By adopting these optimal methods, including efficient communication of policy modifications to all impacted staff, defense contractors can improve their CUI management approaches, ensuring both adherence and the safeguarding of sensitive data.
Implement Proper CUI Marking Procedures
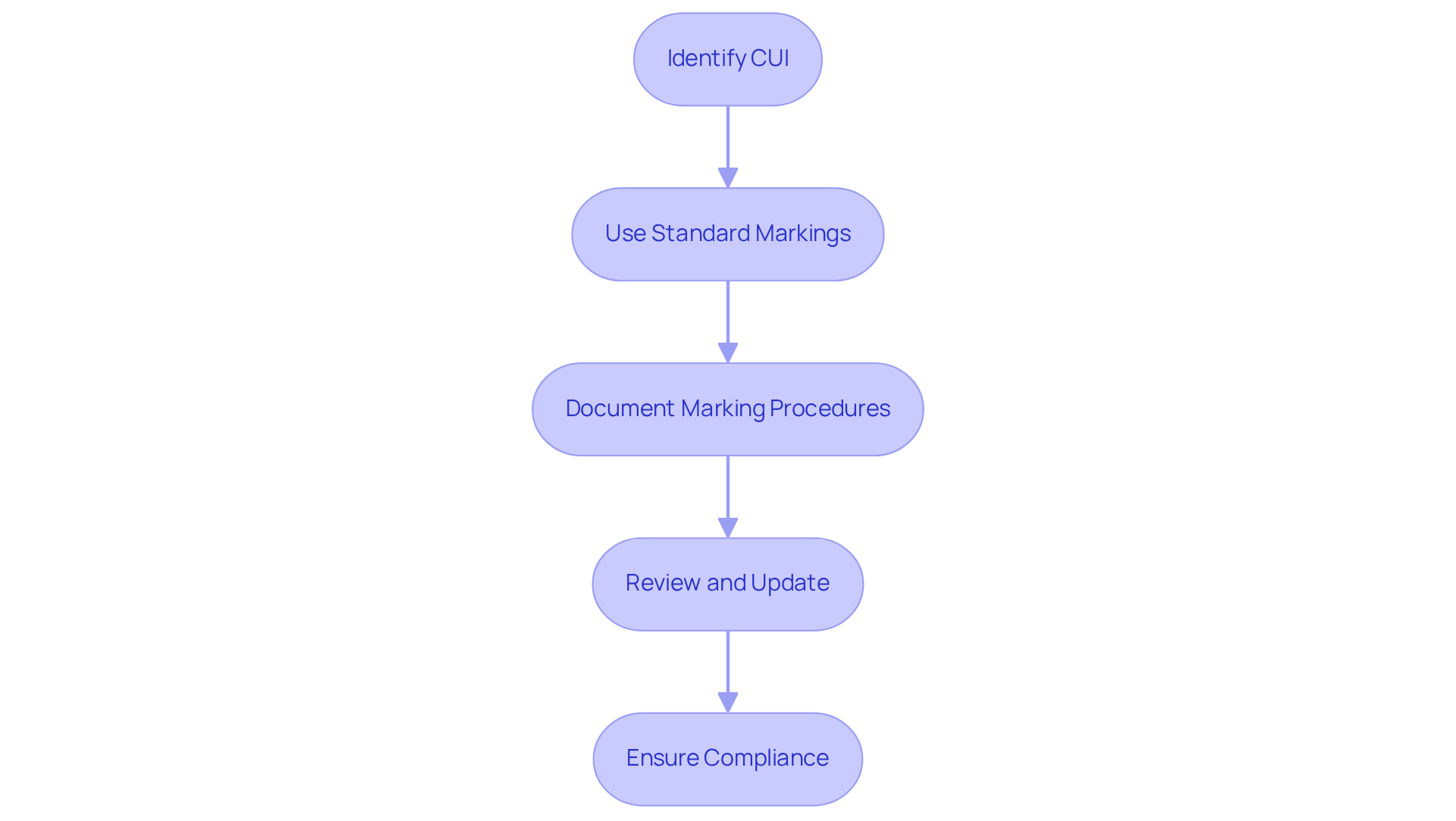
Establishing suitable marking procedures for Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) is essential for adherence to Department of Defense regulations and effective data management. This is particularly crucial in light of FAR 52.204-21, which outlines the fundamental safeguarding requirements for covered contractor systems. Organizations must follow these steps to ensure compliance:
-
Identify CUI: Assess and determine which data qualifies as CUI based on established criteria and categories, including sensitive personally identifiable information (PII), proprietary business materials, and export-controlled technical data.
-
Use Standard Markings: Apply required markings as outlined in the CUI Marking Handbook. This includes placing 'CUI' prominently at the top and bottom of each page, along with specific category markings like 'CUI//PRIVACY' or 'CUI//EXPORT CONTROLLED' where applicable.
-
Document Marking Procedures: Maintain comprehensive records of marking procedures. Ensure that all staff are sufficiently trained on these protocols at the time of creation of CUI material to promote a culture of adherence and awareness. At the time of creation of CUI material, the responsibility for applying proper markings rests with the creator or first disseminator of CUI, ensuring accountability in the marking process.
-
Review and Update: Conduct regular reviews of marking practices to ensure alignment with current regulations, including those set forth in FAR 52.204-21. Revise procedures as needed to reflect any alterations in CUI categories or handling requirements, thus ensuring compliance and protecting sensitive data.
Effective CUI marking not only fulfills regulatory obligations but also enhances the overall security posture of organizations engaged in defense contracts. This ensures that sensitive information is properly protected from unauthorized access. Non-compliance can lead to significant financial implications, which underscores the importance of adhering to proper marking procedures.
Provide Training and Resources for CUI Management
To effectively manage Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI), organizations must implement comprehensive education and resources for their employees. This can be achieved through the following steps:
-
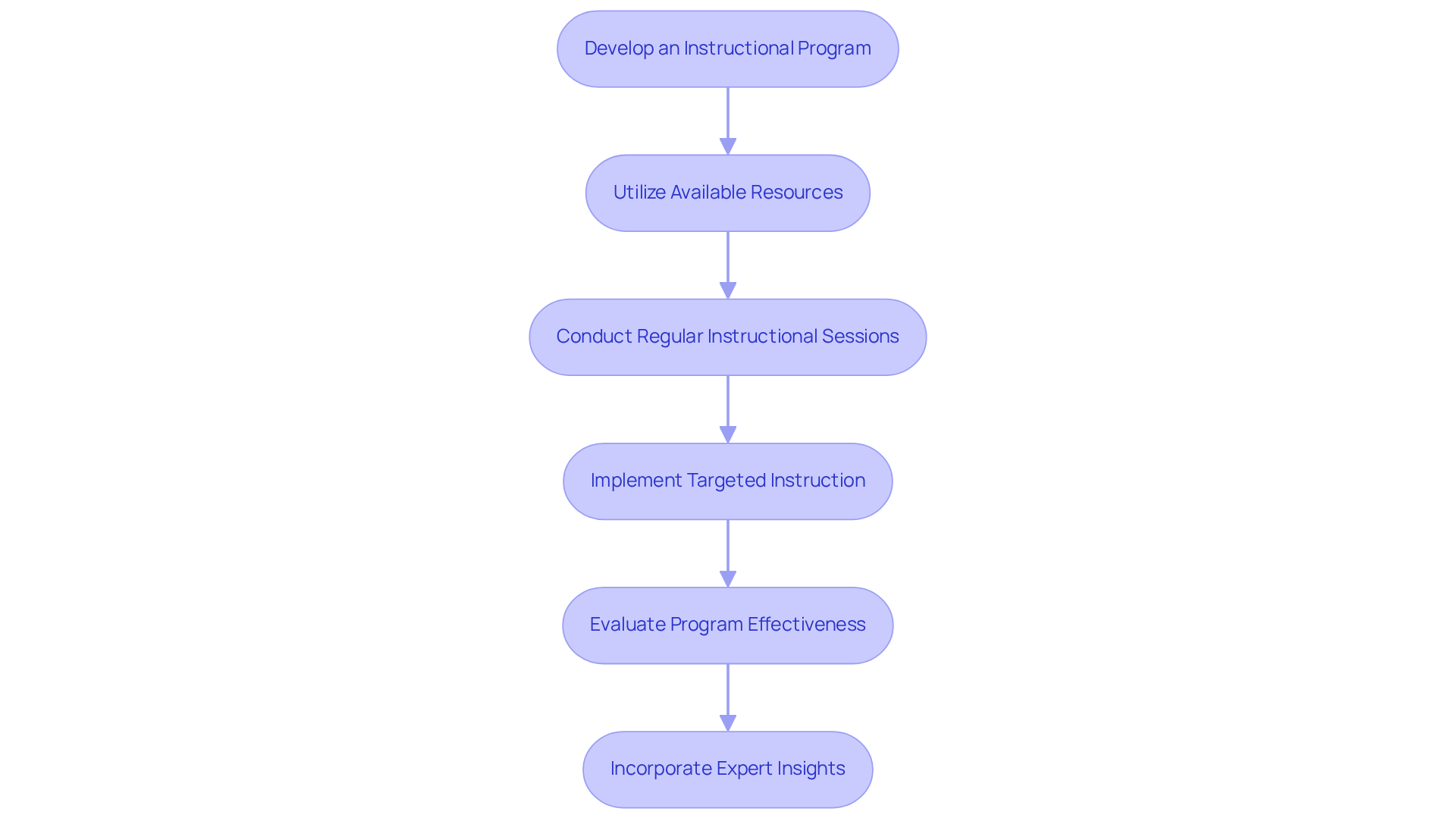
Develop an Instructional Program: Establish a structured instructional program that covers the essentials of CUI, including its definition, categories, marking procedures, and handling requirements. This foundational knowledge is crucial for compliance and security.
-
Utilize Available Resources: Leverage resources from the National Archives and the Department of Defense (DoD) to ensure that instructional materials are current and compliant with existing regulations. These resources provide valuable insights into CUI management and best practices.
-
Conduct Regular Instructional Sessions: Schedule ongoing instructional sessions to keep employees informed about updates in CUI regulations and best practices. This can include workshops, webinars, and e-learning modules, which are essential for reinforcing knowledge and adapting to regulatory changes. Furthermore, integrating spontaneous development techniques, such as unannounced phishing simulations and real-time security drills, can significantly enhance employee engagement and emphasize the significance of cybersecurity.
-
Implement Targeted Instruction: Customize instructional content to specific roles within the organization. This focused strategy improves employee involvement by making the development relevant to their daily tasks and challenges, ensuring that all staff members comprehend their responsibilities concerning CUI handling.
-
Evaluate Program Effectiveness: Implement assessments to gauge the effectiveness of the educational program. Regular evaluations help identify areas for improvement, ensuring that staff understand and comply with CUI handling protocols. This continuous feedback loop is vital for maintaining a robust cybersecurity posture. According to a recent study, companies adopting regular cybersecurity education programs experience a 70% decrease in security incidents, underscoring the significance of continuous instruction.
-
Incorporate Expert Insights: Include quotes and insights from specialists on effective CUI development strategies to enhance the authoritative tone of the program. For instance, specialists stress that effective cybersecurity awareness programs should encompass core elements such as insider threat education, CUI handling protocols, and incident response guidelines.
By following these steps, organizations can create a comprehensive training program that not only meets compliance requirements but also fosters a culture of cybersecurity awareness and responsibility among employees.
Conclusion
Effectively managing Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) from its inception is paramount for organizations dealing with sensitive data. By comprehensively understanding the nature of CUI and implementing robust management strategies, organizations can ensure compliance with federal regulations while safeguarding critical information.
Key steps include:
- Clearly defining roles and responsibilities for CUI creation
- Establishing proper marking procedures
- Providing comprehensive training for employees
These elements synergistically create a culture of compliance and awareness, significantly mitigating the risk of noncompliance and its potential repercussions. Furthermore, regular audits, updates to policies, and leveraging available resources enhance an organization's capacity to protect sensitive information.
Ultimately, the significance of diligent CUI management cannot be overstated. Organizations must prioritize these practices not only to meet regulatory requirements but also to cultivate a secure environment for handling sensitive data. By embracing these strategies, organizations will achieve improved data security and a stronger compliance posture, ensuring they can navigate the complexities of CUI effectively and responsibly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI)?
Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) refers to information created or possessed by the U.S. government that requires safeguarding or dissemination controls but is not classified. It includes sensitive data such as personally identifiable information (PII), proprietary business materials, and technical data related to defense contracts.
Why is it important to understand CUI categories?
Understanding the specific categories of CUI is crucial because it dictates how organizations must manage, label, and protect this data in compliance with federal regulations and standards, particularly those set by the Department of Defense (DoD).
What are the obligations of contractors regarding CUI?
Contractors are obligated to notify the government within eight hours of discovering information believed to be CUI, highlighting the importance of compliance with CUI regulations.
Where can I find a comprehensive overview of CUI categories?
A comprehensive overview of CUI categories can be found in the CUI Registry provided by the National Archives, which may also include links to external sites with additional insights on CUI and regulatory processes.
What are the consequences of noncompliance with CUI regulations?
Noncompliance with CUI regulations can lead to serious repercussions, including potential liability for costs incurred by the government due to a CUI incident.
What is CMMC 2.0 and when was it introduced?
CMMC 2.0 is an updated regulatory framework introduced on December 16, 2024, that contractors must adhere to regarding CUI compliance.
How can contractors stay informed about regulatory changes related to CUI?
Contractors should participate in the ongoing public comment period for the FAR CUI Rule, which extends through May 17, 2025, to stay informed and influence the regulatory landscape.