Master Cybersecurity Compliance in the Financial Sector: A Step-by-Step Guide
Navigate cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector with this comprehensive step-by-step guide.

Overview
Mastering cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector is crucial for safeguarding sensitive information. Key regulations, such as the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, set the foundation for these efforts. But compliance goes beyond merely ticking boxes; it’s about cultivating a culture of security that adapts to the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Why is this culture so essential? Because it not only protects your organization but also builds trust with clients and stakeholders. Implementing robust security measures and continuous monitoring is vital. For instance, organizations that prioritize compliance often see a significant reduction in data breaches and security incidents.
In conclusion, embracing cybersecurity compliance is not just a legal obligation; it’s a strategic advantage. By fostering a proactive security culture, you position your organization to thrive in a complex regulatory environment. Take action now—invest in the resources and training necessary to enhance your compliance efforts and protect your valuable data.
Introduction
The financial sector is at a pivotal moment, where the convergence of technology and regulatory demands presents both opportunities and challenges. Organizations are striving to master cybersecurity compliance, making it crucial to grasp the intricate web of regulations—like the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act and PCI DSS. Yet, with only a small percentage of institutions feeling ready for the impending changes, a pressing question emerges: how can financial entities not only comply with these evolving standards but also cultivate a security culture that anticipates potential threats?
This guide explores essential strategies for navigating the complexities of cybersecurity compliance. It ensures that organizations are not merely ticking boxes but are actively enhancing their overall security posture. By understanding these dynamics, financial institutions can position themselves not just to meet requirements but to thrive in an increasingly regulated environment.
Understand Cybersecurity Compliance Requirements in the Financial Sector
To effectively navigate cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector, understanding the key rules that govern operations is crucial. These include:
-
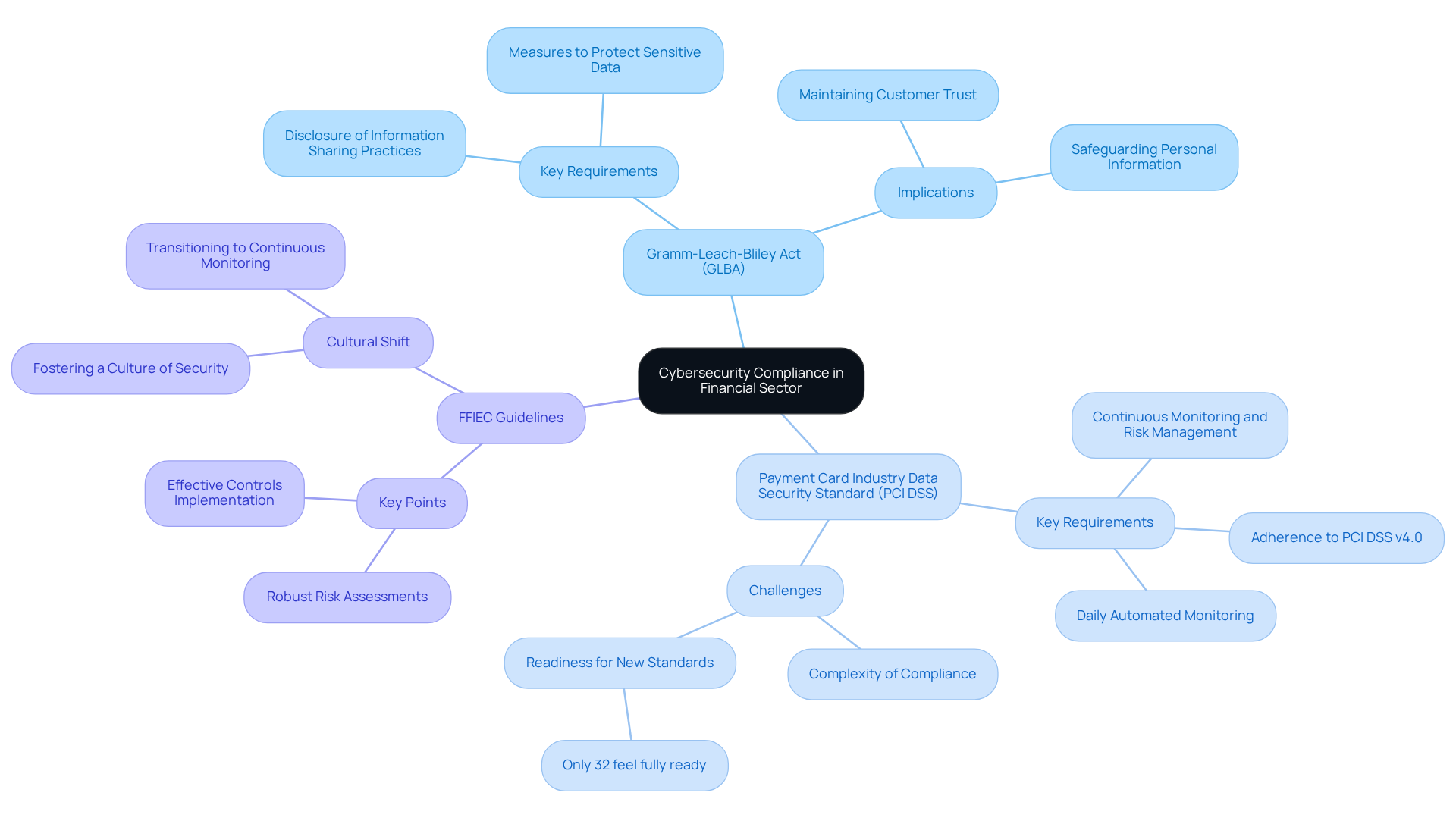
Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA): This act mandates that financial institutions disclose their information-sharing practices to customers and implement measures to protect sensitive data. Compliance with GLBA is essential for achieving cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector, which helps maintain customer trust and safeguard personal information.
-
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): Organizations processing credit card transactions must adhere to PCI DSS to ensure the protection of cardholder data. The latest version, PCI DSS v4.0, introduces 64 new requirements, emphasizing continuous monitoring and risk-based security management. As of March 2025, adherence to these revised standards will be required, yet only 32% of entities currently feel entirely ready for this shift. Moreover, 64% of entities cite increasing complexity as a significant obstacle to achieving cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector, highlighting the challenges in managing these regulations.
The Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC) guidelines provide a comprehensive framework for managing cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector. They emphasize the need for robust risk assessments and the implementation of effective controls to mitigate potential threats.
Grasping these regulations related to cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector goes beyond mere compliance; it’s about fostering a culture of security within your establishment. For instance, a consultative BSA/AML-oriented risk reduction program executed by a U.S. community bank effectively aligned its operations with FDIC guidelines, enhancing its overall regulatory stance and minimizing risks.
Furthermore, the evolving landscape of digital security threats necessitates that entities implement proactive measures to ensure cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector. Recent discussions underscore the importance of transitioning from checklist conformity to continuous, risk-oriented security management, which is vital for addressing operational challenges and ensuring a robust defense against emerging threats.
By thoroughly investigating each regulation and its implications, organizations can develop a strategic approach to cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector that not only fulfills statutory obligations but also strengthens their security framework.
Assess Your Current Cybersecurity Posture
To effectively enhance cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector, begin with a thorough evaluation of your current measures. Follow these essential steps:
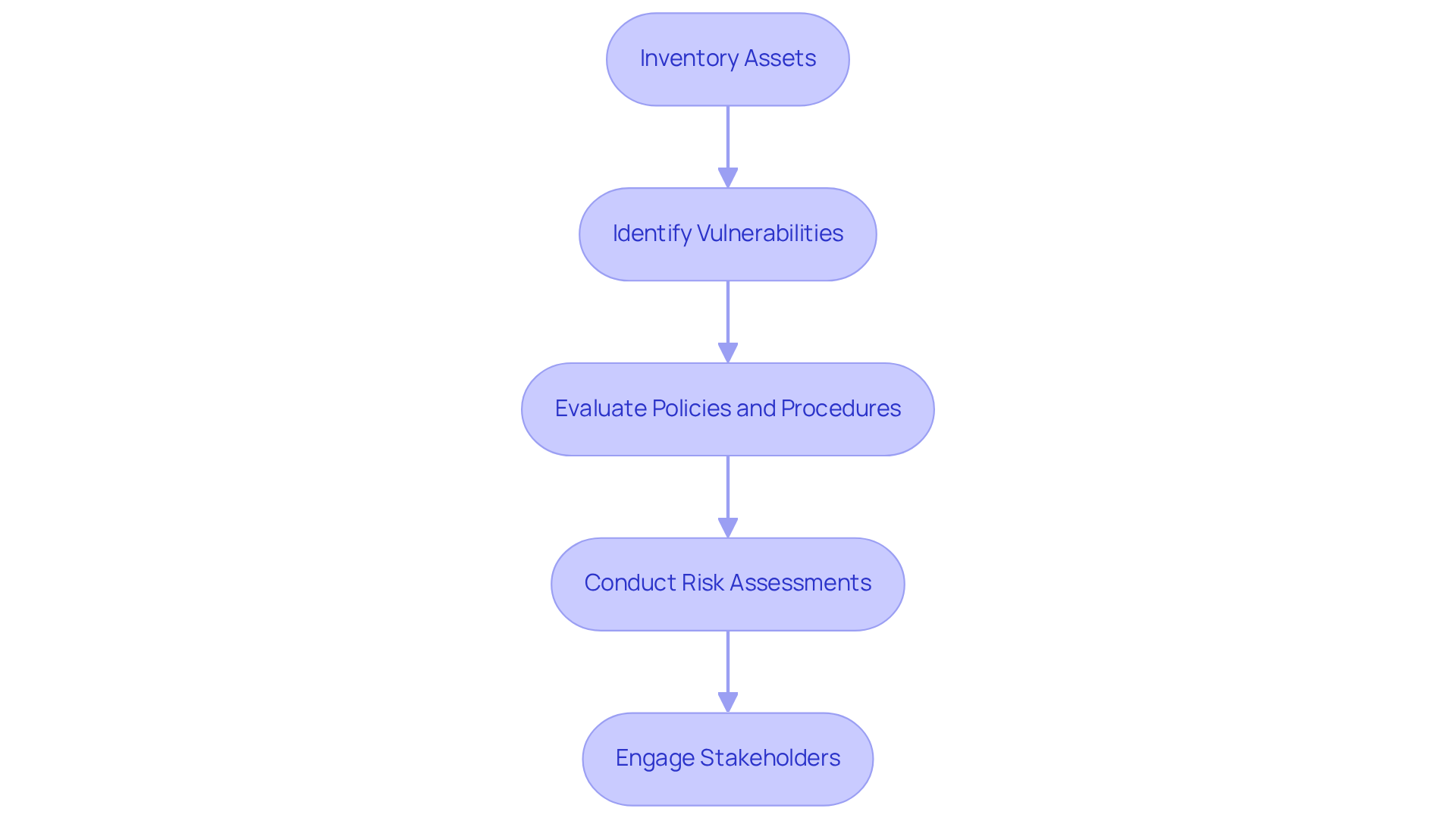
- Inventory Assets: Start by cataloging all hardware, software, and data assets that require protection. This foundational step ensures you understand what needs safeguarding.
- Identify Vulnerabilities: Utilize advanced vulnerability scanners, such as Nessus or Qualys, to uncover weaknesses within your systems. Regular scanning is crucial; it helps detect potential security gaps before they can be exploited.
- Evaluate Policies and Procedures: Review your existing cybersecurity policies to ensure they meet regulatory requirements and industry standards. This evaluation should align with the latest regulatory frameworks for cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector, which are becoming increasingly stringent. Policies should be reviewed at least annually, with a formal process for proposing and approving changes. Maintain version control of policies and store prior versions to guarantee clarity and adherence. Additionally, communicate any policy changes to all affected personnel to foster awareness and adherence.
- Conduct Risk Assessments: Identify potential threats and assess their impact on your organization. This proactive approach allows you to prioritize vulnerabilities based on their severity and potential consequences.
- Engage Stakeholders: Involve key personnel from IT, regulatory affairs, and management to gather insights and provide a comprehensive view of your security stance. Collaboration across departments fosters a culture of security awareness and accountability.
Documenting your findings is crucial for internal assessments and aligns with the requirements of cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector. By doing so, you can implement effective strategies that improve your security resilience against evolving threats.
Implement Required Cybersecurity Controls
To ensure robust security compliance, companies must implement essential controls. Here’s how:
-
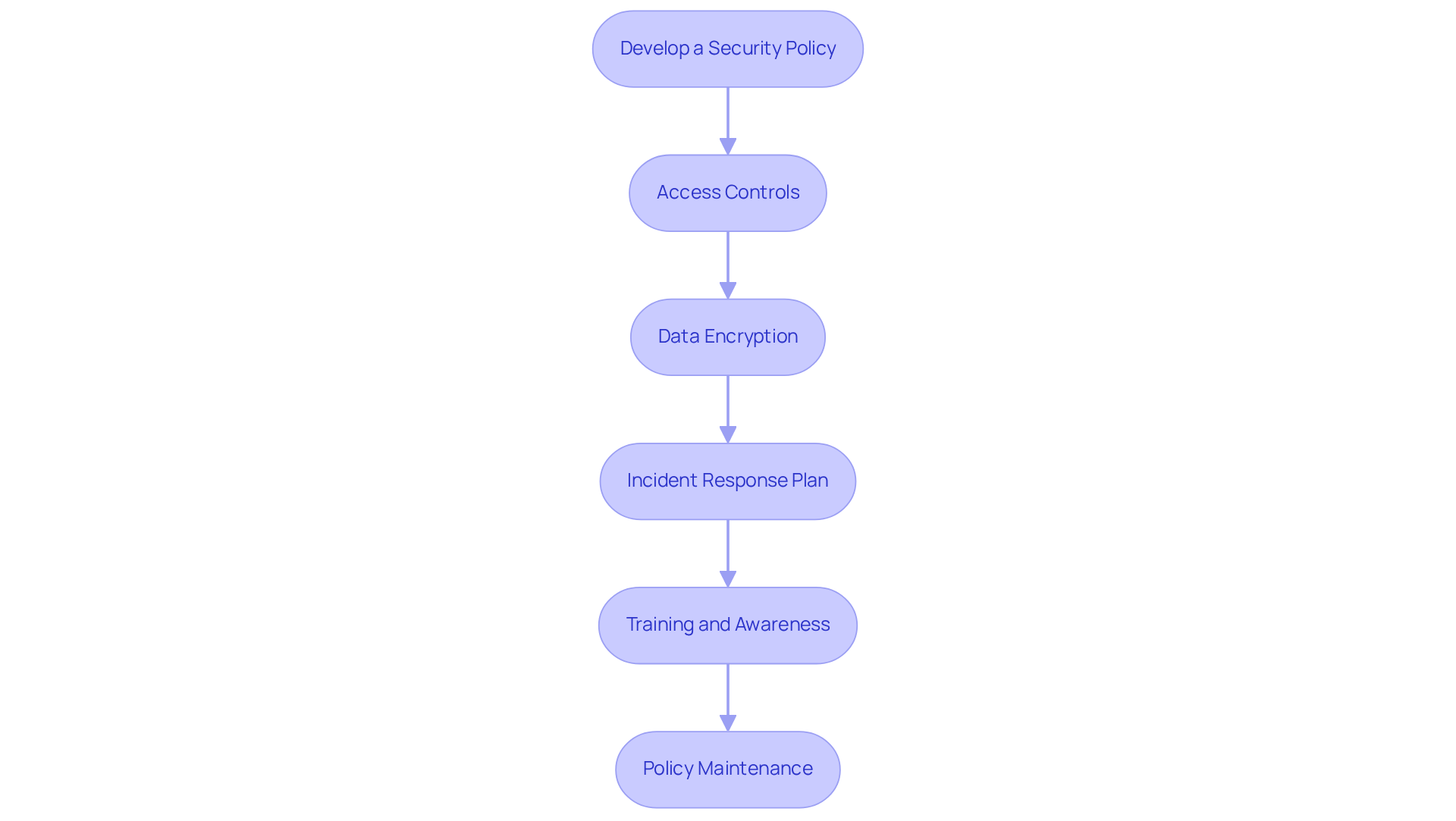
Develop a Security Policy: Start by formulating a comprehensive security policy that clearly defines your organization's digital security strategy. This should include procedures for data protection and incident management.
-
Access Controls: Enforce stringent access controls. This guarantees that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information, significantly minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
-
Data Encryption: Employ encryption techniques to safeguard data both at rest and in transit. This ensures its confidentiality and integrity against potential breaches.
-
Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response strategy. Clearly specify roles and responsibilities for a swift reaction to security incidents. Regular updates to this plan are essential to maintain its effectiveness.
-
Training and Awareness: Implement regular training programs for employees. This enhances their understanding of security threats and promotes best practices. Collaborating with outside security providers can further bolster these efforts.
-
Policy Maintenance: Regularly review and update your policies and procedures to ensure they remain current and effective. Establish a formal review frequency—at least annually. Implement a change process for proposing and approving updates, maintain version control of policies, archive previous versions, and effectively communicate any changes to all affected personnel.
By incorporating these practices, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture and ensure cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector. Are you ready to take action and fortify your security compliance?
Establish Continuous Monitoring and Improvement Processes
To ensure ongoing cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector and security, it’s crucial to establish processes for continuous monitoring and improvement. Here’s how you can do it:
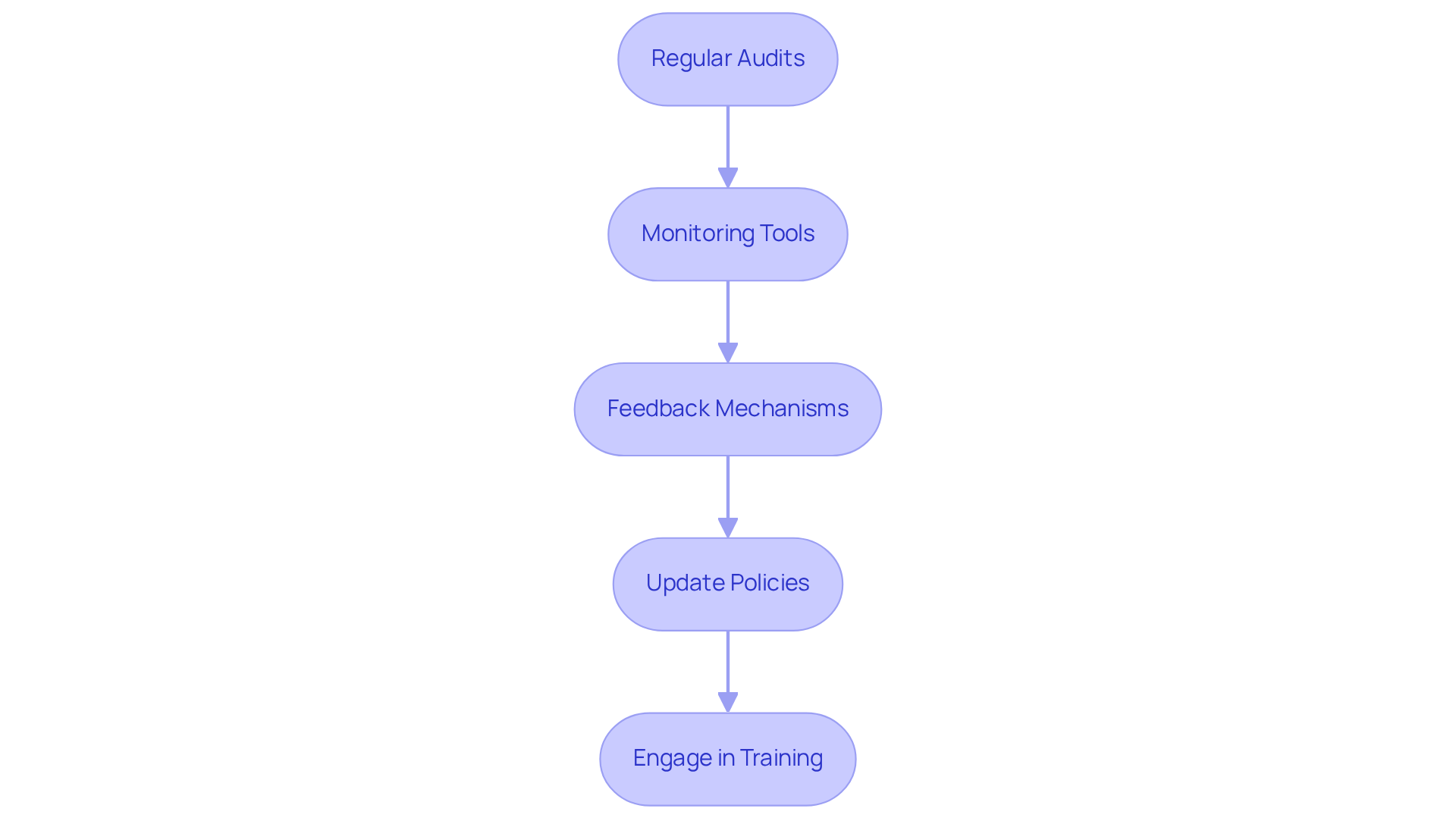
- Regular Audits: Arrange recurring evaluations to gauge adherence to security policies and regulations. These audits not only identify gaps but also reinforce a culture of accountability.
- Monitoring Tools: Utilize security information and event management (SIEM) tools to monitor network activity and detect anomalies. This proactive approach allows for immediate response to potential threats.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Create channels for employees to report security concerns or incidents. Encouraging open communication fosters a vigilant workforce.
- Update Policies: Regularly review and revise your security policies to reflect changes in regulations and emerging threats. Staying current is essential in the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape.
- Engage in Training: Continuously train staff on new threats and regulatory requirements to maintain a high level of awareness. An informed team is your first line of defense.
By implementing these processes, your organization can effectively adapt to the dynamic cybersecurity landscape and ensure sustained cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector. Are you ready to take action and fortify your security measures?
Conclusion
To master cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector, organizations must first recognize the critical importance of understanding and adhering to various regulatory requirements. This isn’t just about fulfilling legal obligations; it’s about fostering a culture of security that prioritizes the protection of sensitive data and customer trust.
Essential regulations like the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard play a pivotal role in this landscape. Organizations should assess their current cybersecurity measures and implement necessary controls. By conducting thorough risk assessments, engaging stakeholders, and establishing continuous monitoring processes, financial institutions can significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture and ensure compliance with evolving standards.
The journey toward robust cybersecurity compliance is ongoing and requires a proactive approach. Organizations are encouraged to embrace best practices, remain adaptable to new threats, and engage in continuous improvement efforts. By doing so, they not only safeguard their assets but also contribute to the overall integrity and stability of the financial sector. Taking decisive action today will pave the way for a more secure tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) and its significance in cybersecurity compliance?
The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) requires financial institutions to disclose their information-sharing practices to customers and implement measures to protect sensitive data. Compliance with GLBA is essential for achieving cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector, helping to maintain customer trust and safeguard personal information.
What are the requirements of the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)?
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) mandates that organizations processing credit card transactions protect cardholder data. The latest version, PCI DSS v4.0, introduces 64 new requirements that emphasize continuous monitoring and risk-based security management, with full adherence required by March 2025.
What challenges do organizations face in achieving cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector?
Organizations face significant challenges in achieving cybersecurity compliance, including increasing complexity in regulations. As of now, only 32% of entities feel entirely ready for the requirements of PCI DSS v4.0, and 64% cite complexity as a major obstacle.
What role do the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC) guidelines play in cybersecurity compliance?
The FFIEC guidelines provide a comprehensive framework for managing cybersecurity compliance in the financial sector. They emphasize the importance of conducting robust risk assessments and implementing effective controls to mitigate potential cybersecurity threats.
How can organizations foster a culture of security beyond mere compliance?
Organizations can foster a culture of security by implementing proactive measures and developing consultative risk reduction programs, such as a BSA/AML-oriented program that aligns with FDIC guidelines. This approach enhances regulatory compliance and minimizes risks while strengthening the overall security framework.
Why is transitioning from checklist conformity to continuous, risk-oriented security management important?
Transitioning to continuous, risk-oriented security management is vital for addressing operational challenges and ensuring a robust defense against emerging digital security threats. This approach focuses on proactive measures rather than just meeting compliance checklists.
How can organizations develop a strategic approach to cybersecurity compliance?
Organizations can develop a strategic approach by thoroughly investigating each regulation and its implications, allowing them to fulfill statutory obligations while also strengthening their overall security framework.




