Master Security Risk and Compliance in Defense Contracting
Master security risk and compliance in defense contracting to safeguard sensitive information effectively.

Introduction
Security risk and compliance in defense contracting have become critical focal points for organizations navigating an increasingly complex regulatory landscape. As threats to sensitive information escalate and compliance requirements tighten, understanding the nuances of frameworks like the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) and the Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement (DFARS) is essential.
How can defense contractors not only meet these stringent standards but also fortify their operations against a backdrop of rising cyberattacks and financial repercussions? This article delves into effective strategies and best practices that empower defense firms to master security risk and compliance, ensuring both operational integrity and competitive advantage.
To illustrate the stakes, consider this: organizations that fail to comply with CMMC and DFARS face not only potential financial penalties but also reputational damage that can hinder future contracts. Therefore, it’s imperative for defense contractors to proactively engage with these frameworks.
In the following sections, we will explore actionable insights and recommendations that can help defense firms navigate this challenging landscape. By implementing robust compliance strategies, organizations can not only safeguard their sensitive information but also enhance their overall operational resilience.
Define Security Risk and Compliance in Defense Contracting
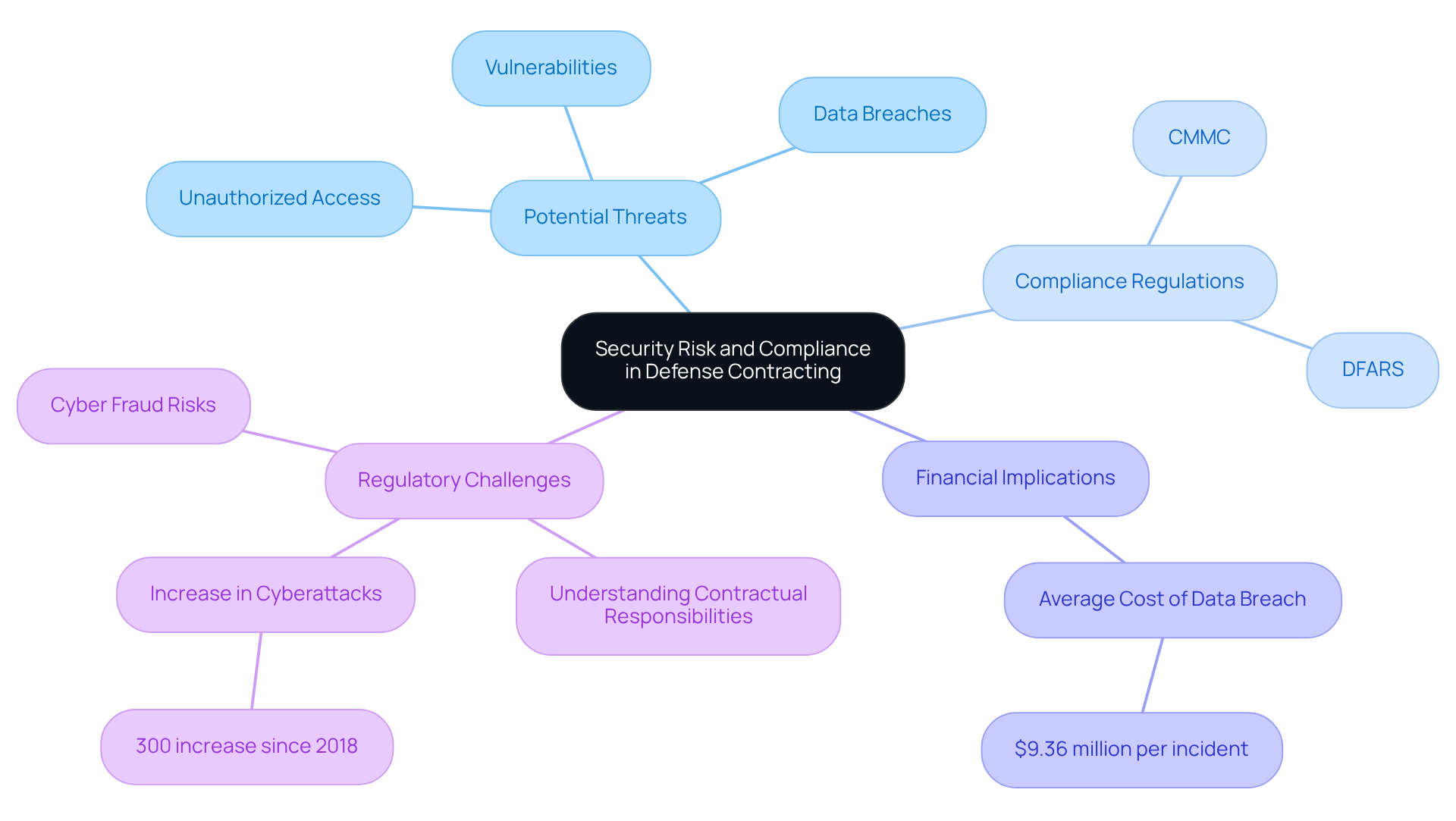
Security risk and compliance in military contracting represents a significant concern, encompassing potential threats that could compromise sensitive information or disrupt operations. This includes unauthorized access, data breaches, and various vulnerabilities that malicious actors may exploit. Compliance is crucial, as it involves adhering to established regulations and standards related to security risk and compliance, such as the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) and the Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement (DFARS). For defense firms, grasping these concepts is vital for navigating the regulatory landscape and achieving security risk and compliance while implementing necessary security measures effectively.
As we approach 2025, updates to compliance requirements are becoming increasingly significant. The CMMC program, designed to enhance cybersecurity standards, mandates that vendors achieve certification at the appropriate level to qualify for Department of Defense (DoD) contracts. Beginning November 10, 2028, CMMC clauses will be required in all relevant agreements, underscoring the urgency for providers to comply with these standards. Notably, the average cost of a data breach for American businesses has soared to $9.36 million per incident, highlighting the financial implications of security risk and compliance failures.
Defense suppliers face various regulatory challenges, particularly in understanding and fulfilling their contractual responsibilities. For example, the Department of Justice has emphasized that cyber fraud can occur even without a cyber breach, indicating that contractors must uphold robust cybersecurity practices throughout their operations. Furthermore, the aerospace and defense industry has experienced a staggering 300% increase in cyberattacks since 2018, complicating regulatory efforts even further.
Industry experts reinforce the importance of these compliance measures. One expert noted that federal suppliers must ensure they fully comprehend and implement their contractual obligations, especially concerning new DFARS requirements. This proactive approach is essential for addressing security risk and compliance while safeguarding sensitive information.
In 2025, data breaches in defense contracting remain a pressing concern, with hacking and IT incidents accounting for 73% of breaches in the healthcare sector-a trend mirrored in defense. As contractors navigate this complex environment, understanding security risk and compliance is not just a legal obligation; it is a fundamental aspect of their operational integrity.
Explore Regulatory Frameworks and Compliance Standards
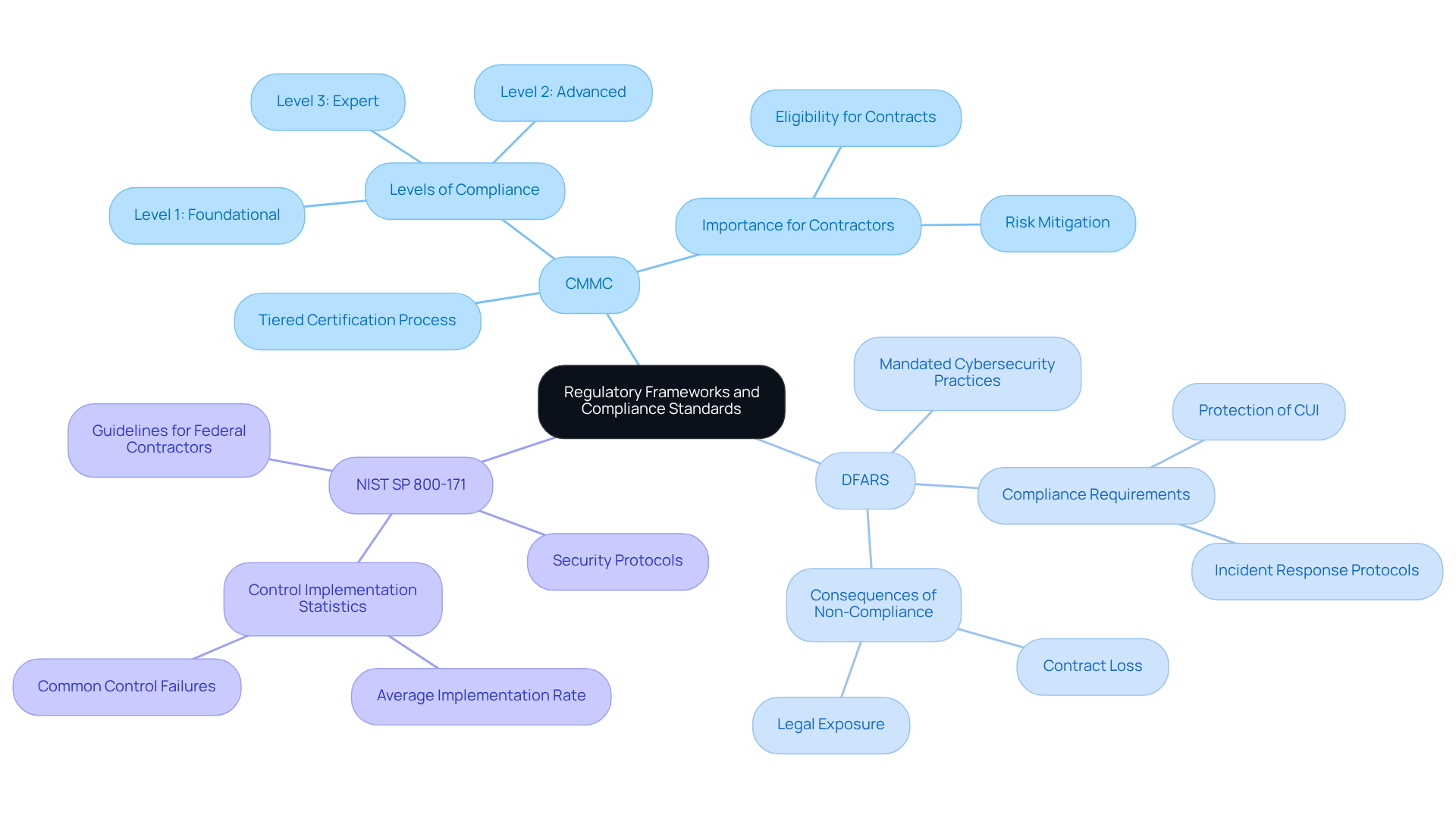
Defense providers face a complex landscape of regulatory frameworks, including the CMMC, DFARS, and NIST SP 800-171. These standards are not just bureaucratic hurdles; they outline essential requirements for safeguarding Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) and bolstering cybersecurity resilience.
For instance, the CMMC establishes a tiered certification process that assesses an organization’s cybersecurity maturity. Meanwhile, DFARS mandates adherence to specific cybersecurity practices. Understanding these frameworks is not merely beneficial; it’s crucial for builders aiming to develop effective strategies for security risk and compliance while mitigating risks associated with non-compliance.
Are you prepared to navigate this intricate web? By understanding these regulations, you can ensure security risk and compliance while also enhancing your organization’s overall security posture. Take action now to leverage the resources available for mastering these standards.
Implement Effective Strategies for Achieving Compliance
To achieve compliance, defense contractors must adopt a multi-faceted approach that encompasses several critical strategies:
-
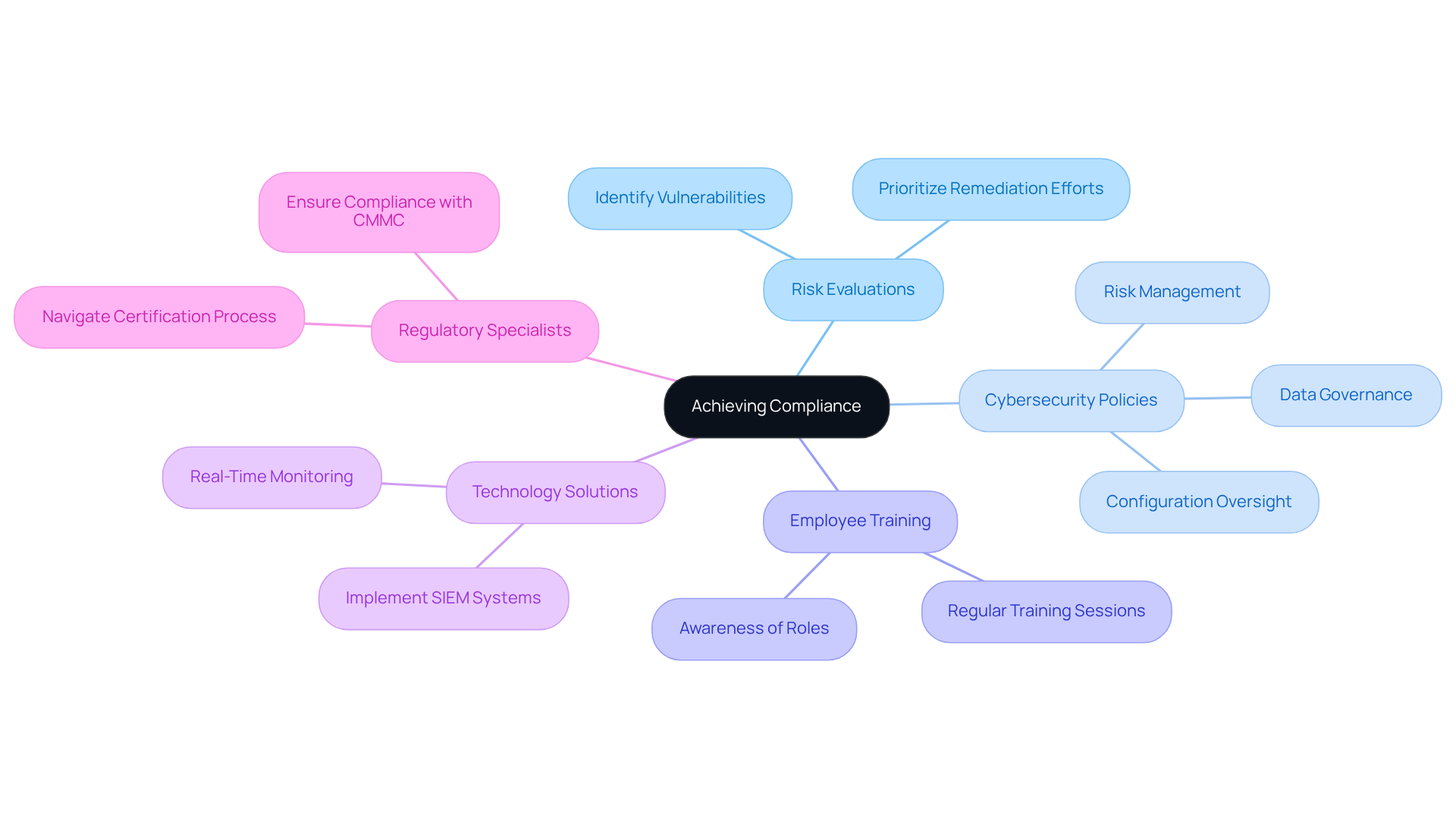
Conduct Comprehensive Risk Evaluations: Identifying vulnerabilities and gaps in current protective practices is essential. This proactive measure allows organizations to understand their security risk and compliance landscape and effectively prioritize remediation efforts.
-
Develop Robust Cybersecurity Policies: Crafting policies that ensure security risk and compliance with CMMC and DFARS requirements is crucial. These policies should address data governance, risk management, and configuration oversight to ensure a structured response to potential security risk and compliance issues.
-
Provide Regular Employee Training: Continuous training ensures that employees are aware of their roles in maintaining compliance. This is vital, as human error remains a significant factor in data breaches, with 60% of small businesses experiencing a breach in the last year.
Utilizing advanced technology solutions, such as Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, can significantly improve the monitoring and management of security risk and compliance incidents. These technologies provide real-time visibility into security events, which is crucial for managing security risk and compliance by enabling swift responses to potential threats.
- Engage Regulatory Specialists: Working with regulatory advisors can assist organizations in navigating the certification process, ensuring that all requirements are fulfilled efficiently. This support is especially advantageous as the final CMMC 2.0 rule becomes effective on November 10, 2025, making adherence a requirement for contract awards.
By incorporating these tactics, as described in the 'Ultimate Guide to Achieving CMMC Compliance,' military contractors can not only meet security risk and compliance requirements but also greatly bolster their overall protection stance. This proactive approach not only improves their preparedness for military contracts but also safeguards sensitive information efficiently.
Establish Continuous Monitoring and Improvement Practices
Ongoing monitoring is essential for ensuring security risk and compliance in military contracting. Organizations must adopt effective practices to navigate this complex landscape:
-
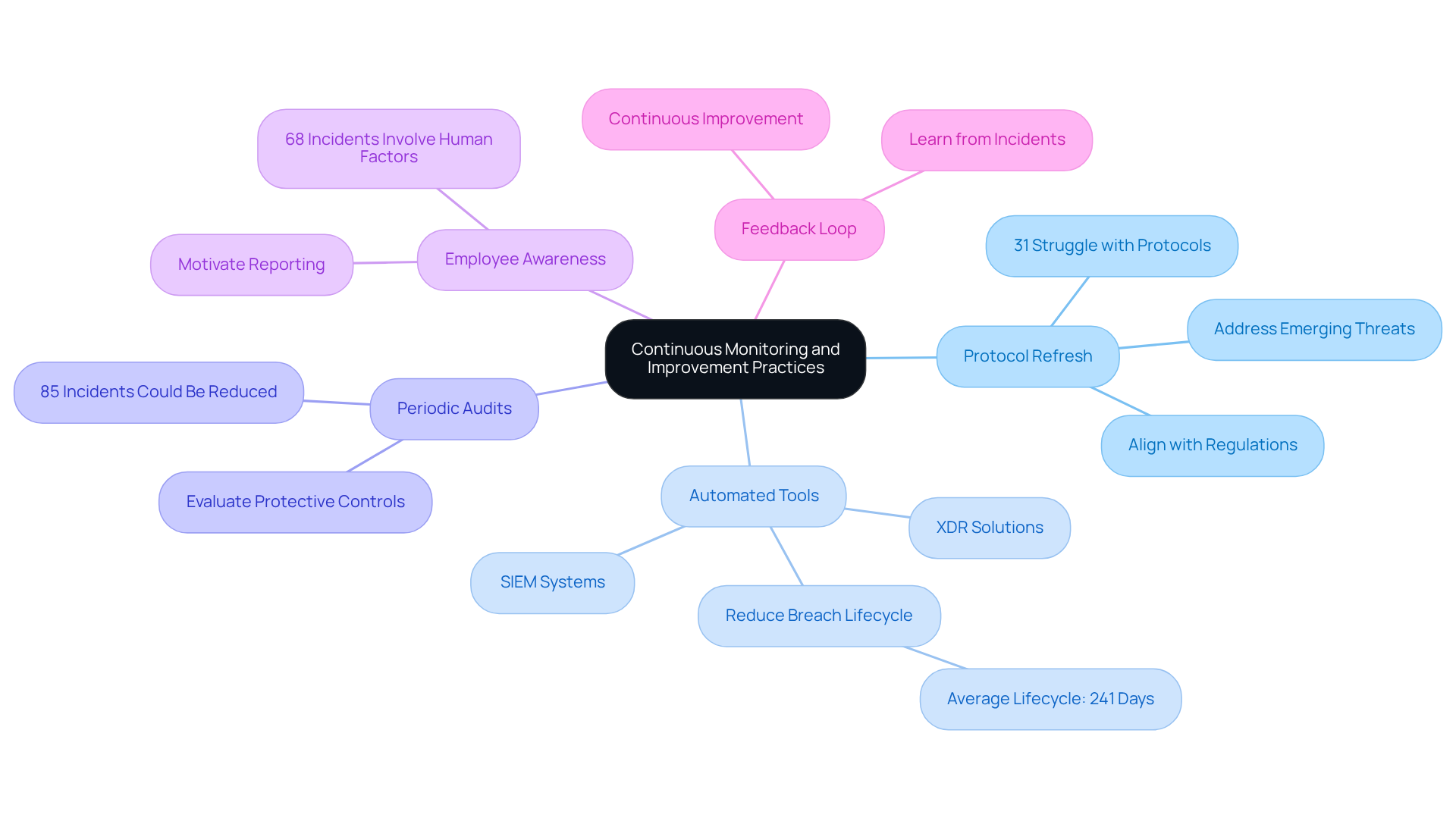
Consistently examine and refresh protocols to align with evolving regulations and emerging threats. Did you know that 31% of defense contractors struggle to create effective protocols for data breach protection? This statistic underscores the urgent need for proactive policy management.
-
Utilize automated tools like Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems and Extended Detection and Response (XDR) solutions. These tools monitor network activity and detect anomalies in real-time, significantly reducing the average breach lifecycle, which currently stands at 241 days.
-
Conduct periodic audits and assessments to evaluate the effectiveness of protective controls and compliance measures. Routine evaluations are crucial; they help identify deficiencies in protective measures and ensure compliance with standards. In fact, 85% of incidents in critical infrastructure organizations could potentially be reduced through improved protective practices.
-
Cultivate a culture of awareness regarding safety among employees. Motivating them to report unusual activities is vital, as human error remains a leading cause of breaches. With 68% of incidents involving human factors, training and awareness are paramount.
-
Establish a feedback loop for continuous improvement. Lessons learned from incidents should be used to enhance security practices. This iterative method not only strengthens security but also prepares organizations for future challenges.
By prioritizing continuous monitoring and improvement, organizations can ensure ongoing security risk and compliance while also enhancing their resilience against cyber threats. This commitment ultimately safeguards sensitive information and maintains eligibility for defense contracts.
Conclusion
Understanding security risk and compliance in defense contracting is essential for organizations aiming to protect sensitive information and maintain operational integrity. As the landscape evolves with new regulations and increasing cyber threats, it becomes imperative for defense contractors to prioritize these aspects to navigate the complexities of military contracting successfully.
This article has explored the critical importance of compliance frameworks like the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) and the Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement (DFARS). It highlighted the necessity for comprehensive risk evaluations, robust cybersecurity policies, regular employee training, and the use of advanced technology solutions. By implementing these strategies, defense contractors can not only meet regulatory requirements but also enhance their overall security posture against potential breaches.
Ultimately, the call to action is clear: organizations must adopt a proactive approach to security risk and compliance. Continuous monitoring, regular assessments, and an ingrained culture of cybersecurity awareness can significantly bolster defenses against the rising tide of cyber threats. By taking these steps, defense contractors can safeguard sensitive information, ensure compliance, and maintain their eligibility for vital defense contracts in an increasingly competitive and regulated environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is security risk and compliance in defense contracting?
Security risk and compliance in defense contracting refers to the potential threats that could compromise sensitive information or disrupt operations, including unauthorized access, data breaches, and vulnerabilities that malicious actors may exploit. Compliance involves adhering to regulations and standards like the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) and the Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement (DFARS).
Why is compliance important for defense firms?
Compliance is crucial for defense firms as it helps them navigate the regulatory landscape, achieve security risk and compliance, and implement necessary security measures effectively to protect sensitive information.
What updates to compliance requirements are expected by 2025?
By 2025, updates to compliance requirements are becoming increasingly significant, particularly with the CMMC program, which mandates that vendors achieve certification at the appropriate level to qualify for Department of Defense (DoD) contracts. CMMC clauses will be required in all relevant agreements starting November 10, 2028.
What are the financial implications of security risk and compliance failures?
The average cost of a data breach for American businesses has increased to $9.36 million per incident, highlighting the significant financial risks associated with failures in security risk and compliance.
What regulatory challenges do defense suppliers face?
Defense suppliers face challenges in understanding and fulfilling their contractual responsibilities, especially with the emphasis from the Department of Justice on robust cybersecurity practices, indicating that cyber fraud can occur even without a cyber breach.
How has the aerospace and defense industry been affected by cyberattacks?
The aerospace and defense industry has experienced a 300% increase in cyberattacks since 2018, complicating efforts to maintain regulatory compliance and security.
What is the significance of understanding contractual obligations for federal suppliers?
Federal suppliers must fully comprehend and implement their contractual obligations, particularly concerning new DFARS requirements, to effectively address security risk and compliance and safeguard sensitive information.
What trends are observed in data breaches within defense contracting?
In 2025, data breaches in defense contracting are a pressing concern, with hacking and IT incidents accounting for 73% of breaches in the healthcare sector, a trend that is also reflected in the defense sector. Understanding security risk and compliance is essential for operational integrity.




