Mastering Your Risk Management and Compliance Framework for CMMC
Master your risk management and compliance framework to achieve CMMC certification effectively.

Introduction
Mastering the complexities of the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) presents a significant challenge for organizations navigating the intricate landscape of risk management and compliance. As standards evolve and a tiered framework emerges to protect sensitive information, grasping the specific requirements becomes essential for achieving certification. With the compliance deadline looming, many organizations face the dual challenge of not only meeting these standards but also fostering a culture of adherence.
How can businesses effectively implement a tailored risk management framework while ensuring continuous improvement and engaging employees in their compliance efforts? By addressing these questions, organizations can not only comply with CMMC but also enhance their overall security posture.
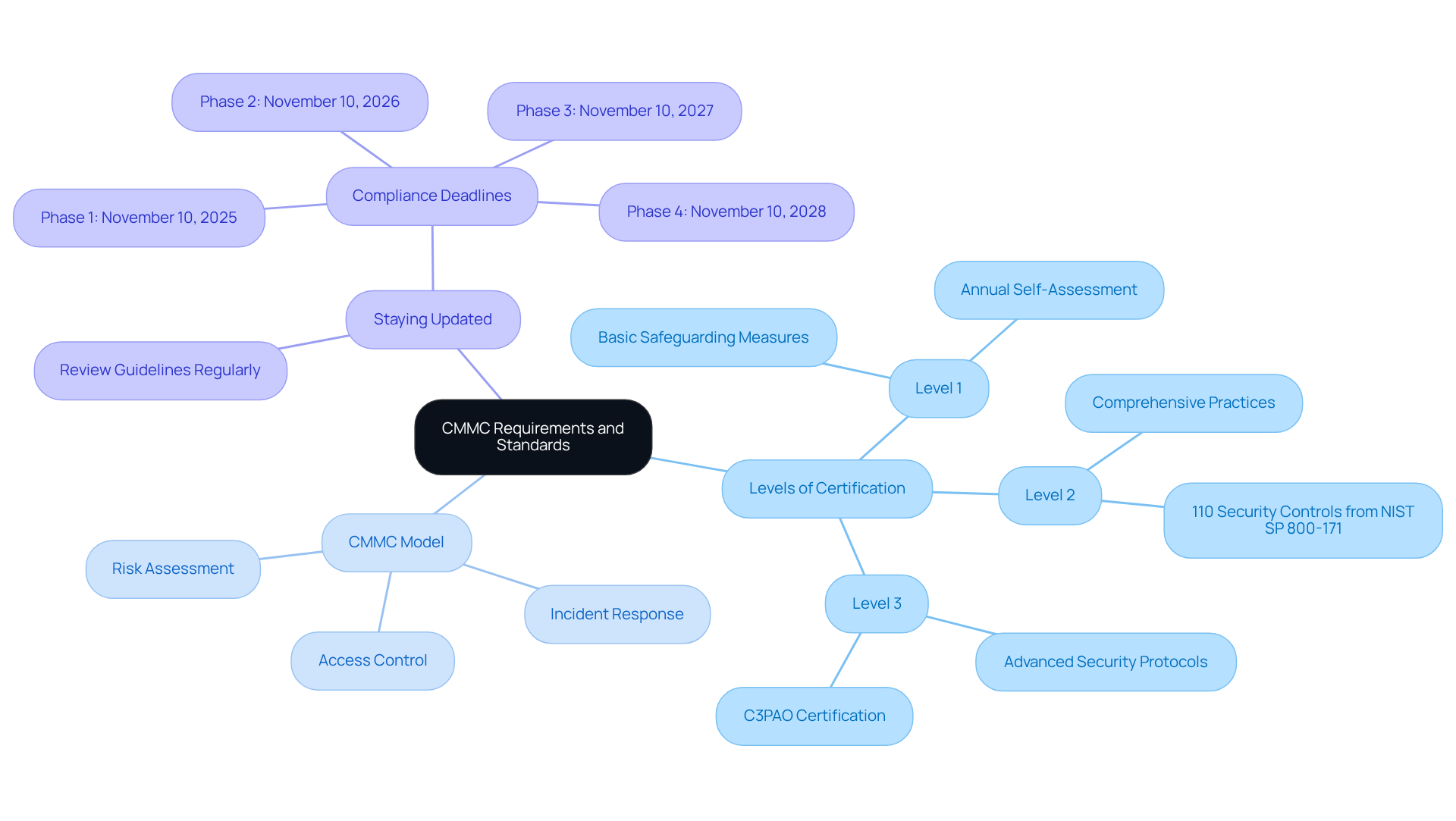
Understand CMMC Requirements and Standards
To effectively master the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification, it’s crucial to understand the specific requirements and standards of your risk management and compliance framework. This framework consists of three distinct levels, each featuring unique practices and processes aimed at safeguarding Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) and Federal Contract Information (FCI). By leveraging practical strategies and insights from peers, organizations can navigate these complexities with confidence.
-
Familiarize with the Levels: The certification is tiered into three levels. Level 1 focuses on basic safeguarding measures, while Level 2 introduces more comprehensive practices, and Level 3 emphasizes advanced security protocols. Understanding these levels is essential for organizations to identify their regulatory requirements based on the agreements they aim to secure. Starting January 2026, it’s important to note that most agreements will require at least a self-evaluation and annual confirmation of compliance, especially since Phase 1 of the cybersecurity maturity model rollout is currently underway.
-
Review the CMMC Model: The CMMC model outlines specific practices and capabilities that organizations must demonstrate. Key domains include Access Control, Incident Response, and Risk Assessment, which are vital for achieving compliance. For example, organizations are required to implement 110 security controls from NIST SP 800-171 to effectively protect CUI. This structured approach not only enhances cybersecurity posture but also aligns with the Department of Defense's expectations.
-
Stay Updated: The cybersecurity maturity model framework is dynamic, with updates and changes occurring regularly. Organizations must consistently review the latest guidelines from the Department of Defense (DoD) to ensure adherence to evolving standards. The gradual execution of the framework, leading to complete compliance by November 2028, necessitates that organizations remain proactive in their efforts to meet these standards.
By developing a thorough understanding of the cybersecurity maturity model criteria and utilizing practical approaches along with peer perspectives, companies can efficiently align their strategies with the risk management and compliance framework to meet regulatory goals. This alignment not only enhances their preparedness for defense contracts but also strengthens the protection of sensitive data.
Implement a Tailored Risk Management Framework
A customized management structure is essential for organizations aiming to achieve cybersecurity maturity model certification. Here’s how to implement an effective framework:
-
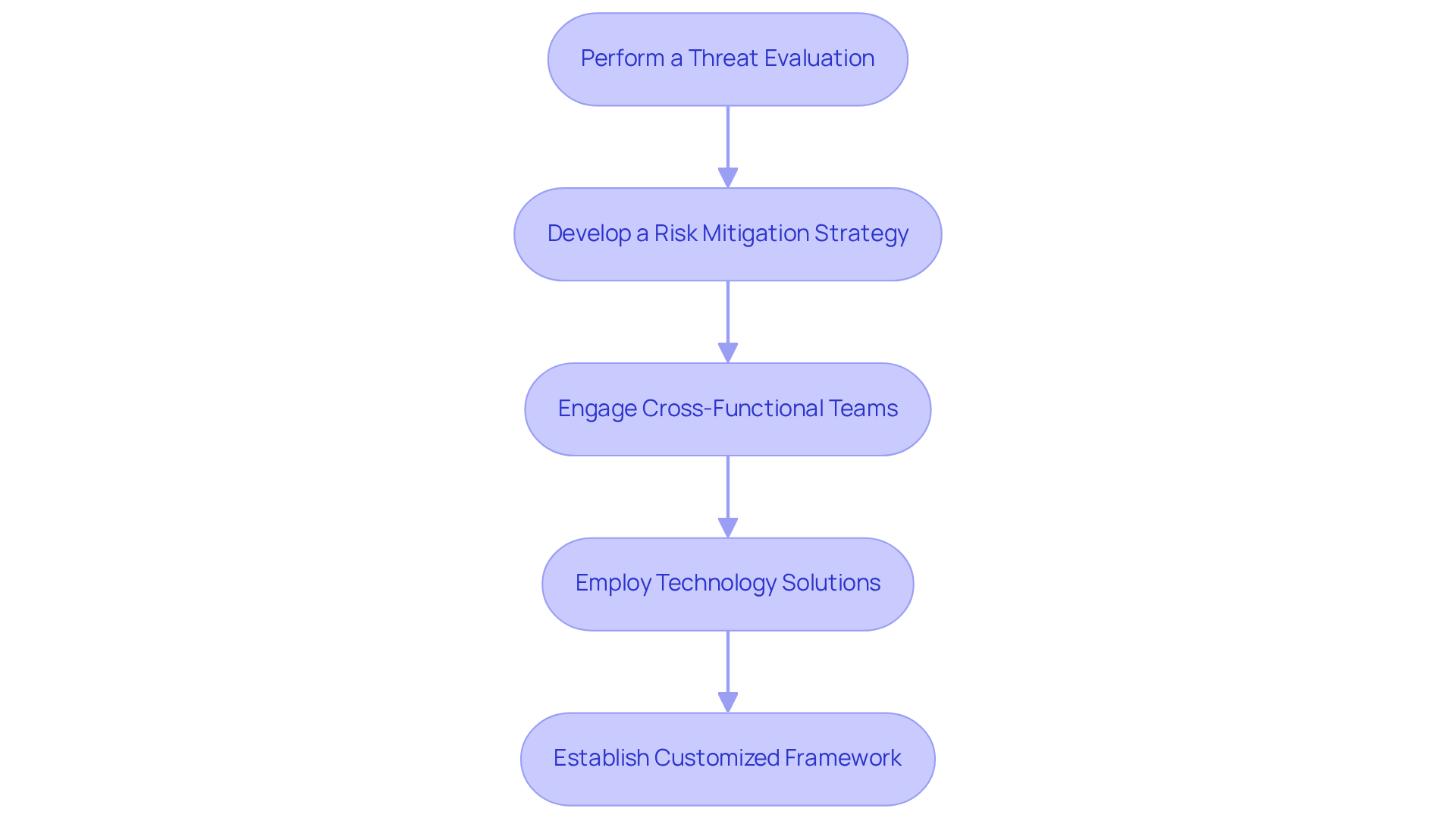
Perform a Threat Evaluation: Start by identifying potential threats to your organization’s information systems. Utilize established frameworks like NIST SP 800-30 to systematically assess vulnerabilities and threats. Did you know that only 30% of organizations had tailored management strategies for cybersecurity maturity model certification in 2026? This statistic underscores the importance of thorough evaluations.
-
Develop a Risk Mitigation Strategy: After your evaluation, craft a comprehensive management plan that details strategies to mitigate identified threats. This plan should specify controls and measures that align with CMMC requirements, ensuring your organization is prepared for compliance.
-
Engage Cross-Functional Teams: Involve various departments - IT, legal, and regulatory - to foster a holistic approach to managing uncertainties. Collaboration among teams cultivates a culture of safety and compliance, which is vital for effective risk management.
-
Employ Technology Solutions: Implement technology solutions that enhance management processes, such as automated monitoring tools and incident response systems. These technologies streamline regulatory efforts and bolster security measures, making it easier to maintain compliance with standards.
By establishing a customized risk management framework, organizations can proactively address cybersecurity threats while ensuring adherence to CMMC standards. As industry experts emphasize, "Being able to show documented progress, even if not fully certified, can open doors" for future opportunities.
Establish Continuous Monitoring and Improvement Processes
Ongoing monitoring and enhancement are crucial components of a robust risk management and compliance framework. Here’s how organizations can effectively implement these processes:
-
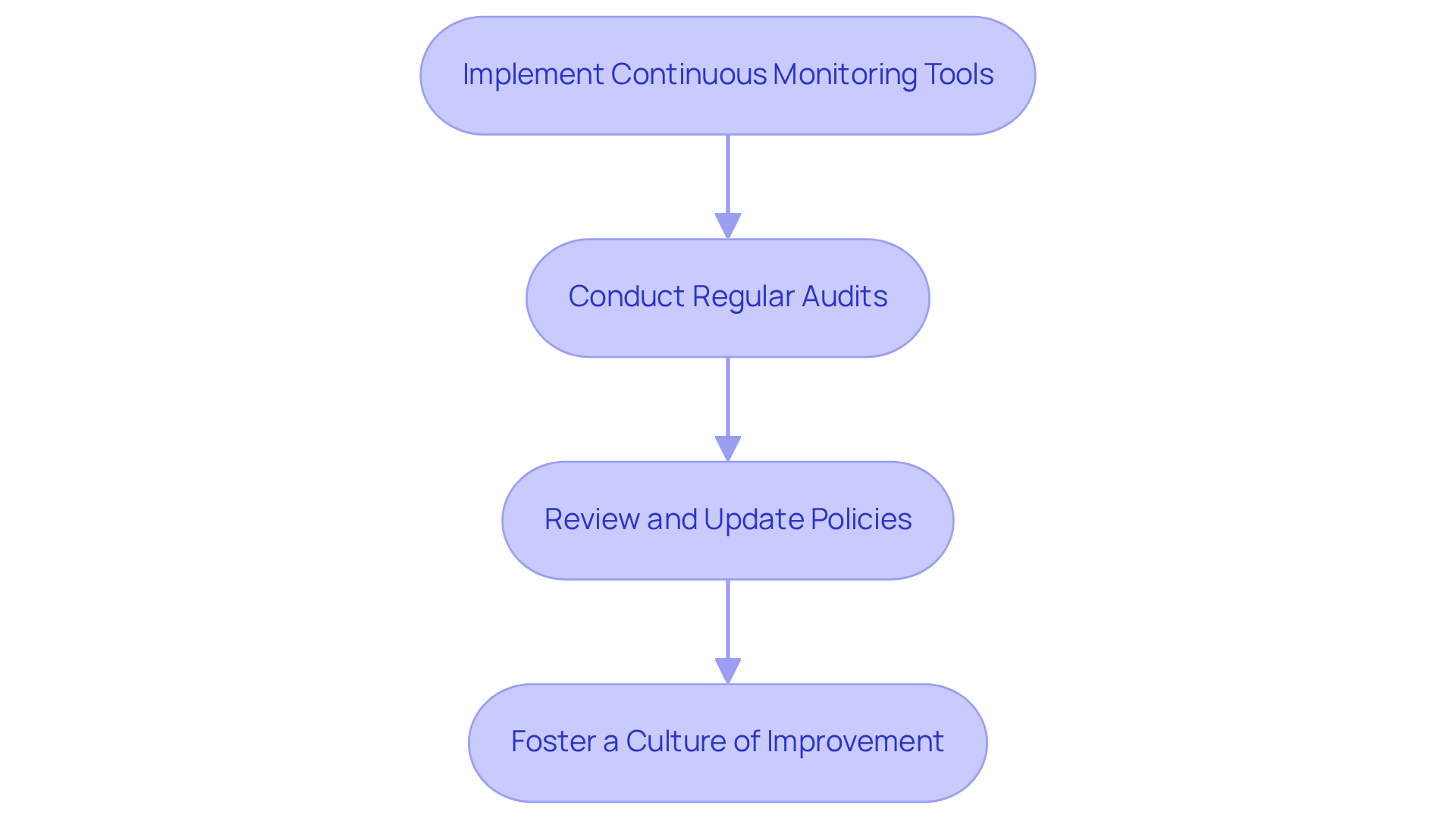
Implement Continuous Monitoring Tools: Leverage automated tools to continuously monitor your systems for vulnerabilities and compliance status. This proactive approach enables real-time detection of potential issues, ensuring that you stay ahead of threats.
-
Conduct Regular Audits: Schedule periodic audits to assess adherence to security standards. These audits should not only evaluate the effectiveness of implemented controls but also identify areas ripe for improvement. Are your current measures truly safeguarding your organization?
-
Review and Update Policies: Regularly revisit and update your cybersecurity policies and procedures to reflect changes in the CMMC framework and emerging threats. This practice guarantees that your entity remains compliant and secure in an ever-evolving landscape.
-
Foster a Culture of Improvement: Encourage employees to report security incidents and suggest enhancements. A culture that prioritizes continuous improvement can significantly bolster a company’s cybersecurity posture.
By implementing these continuous monitoring and enhancement procedures as part of a risk management and compliance framework, organizations can ensure ongoing adherence to standards while adapting to the dynamic cybersecurity environment. Additionally, consider integrating relevant FAQs or external links to provide further resources and insights for your audience.
Cultivate a Strong Compliance Culture Through Training and Communication
Establishing a robust adherence culture is essential for effectively executing cybersecurity maturity model certification (CMMC) requirements. How can organizations cultivate this culture? Here are key strategies:
-
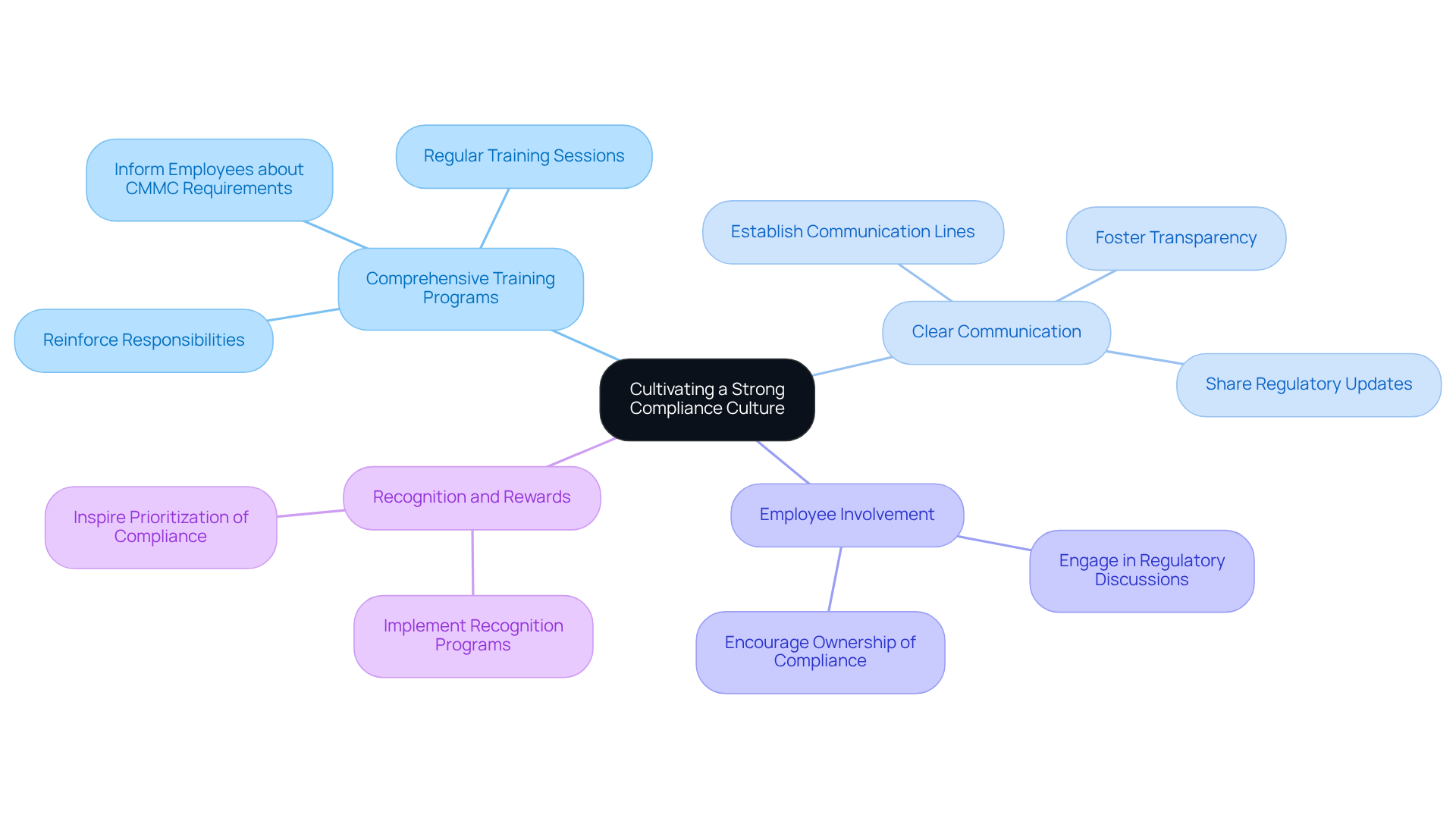
Develop Comprehensive Training Programs: Create training initiatives that inform employees about CMMC requirements, cybersecurity best practices, and their specific roles in upholding these standards. Regular training sessions reinforce the significance of adherence, ensuring everyone understands their responsibilities.
-
Communicate Clearly and Frequently: Establish clear lines of communication regarding adherence expectations and updates. Consistently share details about regulatory initiatives and achievements to keep employees engaged and informed. This transparency fosters a culture of compliance.
-
Encourage Employee Involvement: Engage employees in regulatory discussions and decision-making processes. By involving them, you cultivate a sense of ownership and responsibility for adherence efforts, making compliance a collective goal.
-
Acknowledge and Reward Adherence Efforts: Implement recognition programs that reward employees for their contributions to adherence initiatives. Recognizing efforts can inspire employees to prioritize compliance in their daily activities, reinforcing a culture of adherence.
By cultivating a strong compliance culture through training and communication, organizations can significantly enhance their overall cybersecurity posture and ensure sustained adherence to the risk management and compliance framework associated with CMMC requirements. Are you ready to take action and implement these strategies?
Conclusion
Mastering the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) is essential for organizations aiming to enhance their cybersecurity posture. It requires a comprehensive understanding of its requirements and the implementation of a tailored risk management and compliance framework. Are you prepared to navigate the intricacies of the CMMC levels? From basic safeguarding measures to advanced security protocols, organizations must ensure they meet the evolving standards set by the Department of Defense. By prioritizing compliance and developing robust frameworks, companies can significantly bolster their defenses while safeguarding sensitive information.
Key strategies include:
- Performing thorough threat evaluations
- Engaging cross-functional teams
- Establishing continuous monitoring processes
Regular audits and updates to cybersecurity policies are crucial for adapting to the dynamic landscape of compliance. Moreover, fostering a strong culture of compliance through comprehensive training and clear communication empowers employees to take ownership of adherence efforts. This not only reinforces the organization's commitment to security but also cultivates a proactive approach to risk management.
As organizations gear up for the upcoming CMMC requirements, adopting a proactive and informed approach is vital. Implementing best practices and cultivating a culture of compliance positions companies for successful certification and enhances their overall resilience against cybersecurity threats. Taking these steps today will pave the way for a secure and compliant future in the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape. Are you ready to take action?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC)?
The CMMC is a certification framework designed to enhance cybersecurity practices within organizations that handle Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) and Federal Contract Information (FCI).
How many levels are there in the CMMC framework, and what do they represent?
The CMMC framework consists of three levels. Level 1 focuses on basic safeguarding measures, Level 2 introduces more comprehensive practices, and Level 3 emphasizes advanced security protocols.
What is required for organizations to achieve CMMC compliance?
Organizations must demonstrate specific practices and capabilities outlined in the CMMC model, including implementing 110 security controls from NIST SP 800-171 to protect CUI.
When will most agreements require a self-evaluation and annual confirmation of compliance?
Starting January 2026, most agreements will require at least a self-evaluation and annual confirmation of compliance.
What are some key domains included in the CMMC model?
Key domains include Access Control, Incident Response, and Risk Assessment, which are essential for achieving compliance.
How can organizations stay updated on CMMC requirements?
Organizations must consistently review the latest guidelines from the Department of Defense (DoD) to ensure adherence to evolving standards.
What is the timeline for achieving complete compliance with the CMMC framework?
Organizations are expected to achieve complete compliance with the CMMC framework by November 2028.
How does understanding the CMMC framework benefit organizations?
A thorough understanding of the CMMC criteria helps organizations align their strategies with risk management and compliance goals, enhancing their preparedness for defense contracts and strengthening the protection of sensitive data.




