Understanding the Cybersecurity CISO: Role, Skills, and Evolution
Explore the evolving role and essential skills of the cybersecurity CISO in modern organizations.

Introduction
The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) has emerged as a critical figure in today’s organizations, especially as they face an ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. This role transcends traditional technical oversight, positioning the CISO as a key architect of comprehensive security strategies that not only align with business objectives but also meet regulatory requirements. As the demand for effective cybersecurity leadership intensifies, the complexity of the CISO's responsibilities grows, prompting essential questions:
- How can these leaders adeptly navigate the intricate challenges of compliance, risk management, and organizational culture?
- What skills and insights are vital for a CISO to excel in this dynamic environment?
Understanding the multifaceted nature of the CISO role is crucial. It requires a blend of technical expertise, strategic vision, and strong leadership capabilities. The CISO must not only protect the organization from cyber threats but also foster a culture of security awareness among employees. This dual focus is essential for building a resilient organization that can withstand the pressures of today’s cyber landscape.
To thrive, a CISO must cultivate a deep understanding of both the technical and business aspects of their organization. This includes staying informed about the latest cybersecurity trends and threats, as well as understanding how security initiatives can drive business value. By doing so, the CISO can effectively advocate for necessary resources and support from executive leadership.
In conclusion, the role of the CISO is more critical than ever. As organizations continue to grapple with complex cybersecurity challenges, the insights and skills of a CISO will be paramount in shaping a secure future. Are you ready to explore the essential competencies that will empower CISOs to lead effectively in this evolving landscape?
Define the Cybersecurity CISO: Role and Importance
The Chief Information Protection Officer (CISO) plays a pivotal role in shaping an organization's information protection strategy and its execution. As cyber threats grow more sophisticated and regulatory demands become more stringent, the responsibilities of the CISO have expanded dramatically. This senior executive is tasked with safeguarding sensitive data, ensuring compliance with applicable laws, and aligning protective initiatives with broader business objectives. In fact, by 2025, a striking 84% of CISOs are expected to prioritize operational measures, reflecting a strategic focus on both immediate threat response and long-term planning.
The CISO serves as the guardian of an organization’s information assets, making critical decisions that influence the overall security posture. Consider this: organizations where the CISO reports directly to the Chief Executive Officer experience 20% fewer incidents. This statistic underscores the importance of leadership alignment in effective protective measures. Moreover, with 66% of CISOs identifying human error as the primary vulnerability, their role extends to cultivating a culture of cybersecurity awareness among employees.
Case studies reveal that a staggering 90% of successful cyber attacks originate from human error, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive training and a proactive approach to risk management. As organizations grapple with the complexities of compliance and security, the influence of the CISO is vital in mitigating risks and bolstering resilience against cyber incidents. In this evolving landscape, the CISO not only protects sensitive data but also ensures that the organization is well-equipped to meet regulatory standards and respond effectively to emerging threats.

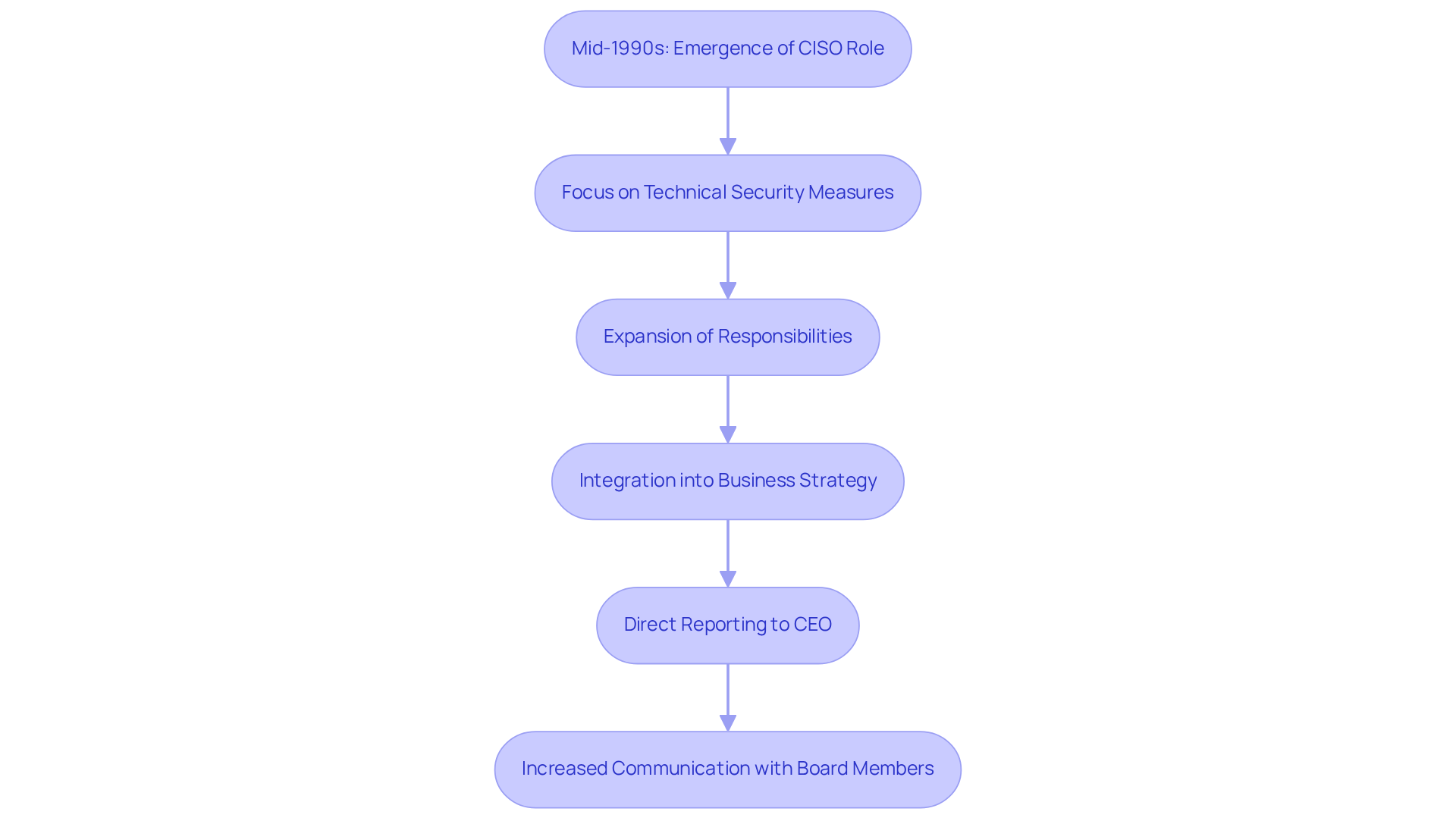
Trace the Evolution of the CISO Role in Cybersecurity
The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) role emerged in the mid-1990s, primarily as a response to the increasing need for a cybersecurity CISO to protect organizations' digital assets. Initially, CISOs concentrated on technical security measures, such as deploying firewalls and intrusion detection systems. However, as cyber threats have grown in complexity and frequency, the responsibilities of the cybersecurity CISO have significantly expanded. Today, the cybersecurity CISO is not only responsible for technical oversight but also for integrating digital security into the broader business strategy of their organizations.
This transformation marks a critical shift in perspective: digital security is now recognized as a vital component of business risk management and organizational resilience. Consider this: organizations where the chief information security officer reports directly to the CEO experience 20% fewer security incidents. This statistic underscores the importance of strategic alignment between cybersecurity CISO leadership and executive management. Yet, it’s noteworthy that 90% of cybersecurity CISO professionals are at least two organizational levels removed from the CEO, which presents challenges in influencing strategic decisions.
Moreover, the role of the cybersecurity CISO has become increasingly multifaceted. In 2024, 84% of Chief Information Security Officers reported agreement with board members on security matters, a significant increase from previous years. This enhanced communication fosters better decision-making and resource allocation for cybersecurity initiatives. As the landscape of cyber threats continues to evolve, cybersecurity CISOs are prioritizing investments in new technologies, employee training, and compliance tools to strengthen defenses against emerging risks. Notably, 76% of Chief Information Security Officers come from a predominantly technical background, reflecting the traditional pathway into this role.
The evolution of the chief information security officer role is further illustrated by the fact that the number of such positions in Fortune 500 companies has surged by over 300% since the role's inception. This growth emphasizes the increasing significance of cybersecurity CISO leadership in large organizations, where the role of Chief Information Security Officers is now seen as that of strategic leaders rather than merely technical specialists. As they navigate the complexities of contemporary security challenges, cybersecurity CISOs must balance immediate threat responses with long-term strategic planning, ensuring that security remains a foundational aspect of organizational success. Furthermore, the average job tenure for a Chief Information Security Officer is only 26 months, reflecting the intense pressures and demands of the role. The need for cybersecurity leadership has nearly doubled in just over a decade, highlighting its growing recognition.
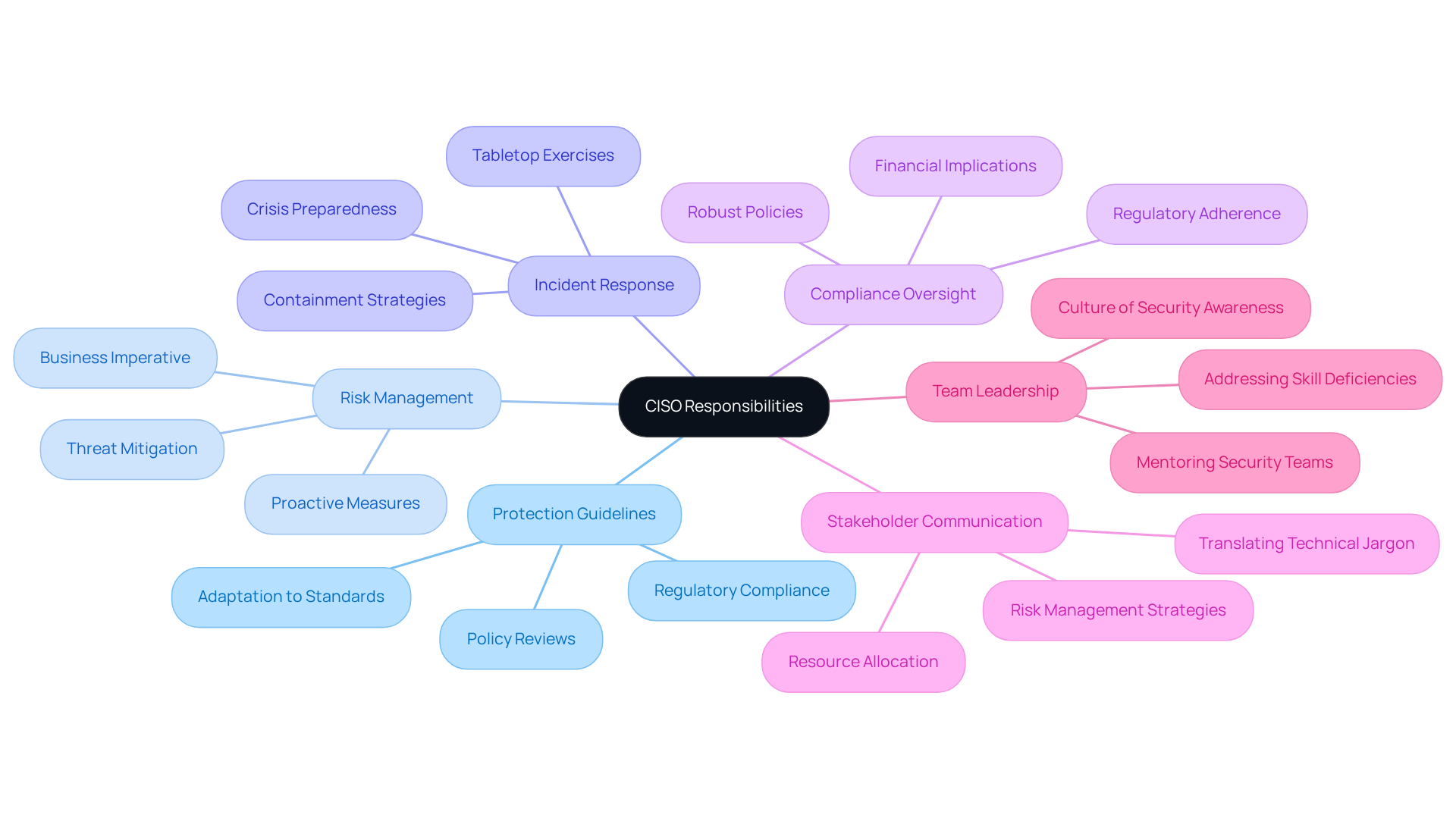
Outline Key Responsibilities of a Cybersecurity CISO
The responsibilities of a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) are diverse and encompass several key areas:
-
Formulating Protection Guidelines: The cybersecurity CISO plays a crucial role in establishing and implementing protective policies that align with organizational objectives and regulatory standards. This responsibility includes adapting policies to meet evolving standards, such as those outlined in the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC). To achieve compliance, organizations should conduct regular policy reviews and updates that reflect changes in regulations and emerging threats.
-
Risk Management: Evaluating and managing risks related to information protection is essential. CISOs must ensure that appropriate measures are in place to mitigate potential threats. A proactive approach is vital, as the cybersecurity CISO increasingly recognizes cyber risk as a business imperative rather than just a technical issue.
-
Incident Response: CISOs direct the organization's response to incidents, coordinating efforts to contain breaches and minimize damage. Effective incident response plans are critical, and conducting regular tabletop exercises can help identify gaps in preparedness, ensuring that key decision-makers are ready during crises.
-
Compliance Oversight: Ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations, such as GDPR and CMMC, is a significant responsibility. A large percentage of cybersecurity CISOs are directly involved in compliance oversight, reflecting the growing importance of adhering to these standards, especially for defense contractors. Organizations must maintain robust policies and procedures to avoid the financial implications of non-compliance.
-
Stakeholder Communication: Cybersecurity CISOs must effectively communicate risk management strategies and challenges to executive leadership and the board, translating technical jargon into business terms. This communication is vital for securing necessary resources and fostering strong partnerships with business leaders.
-
Team Leadership: Managing and mentoring security teams is another key responsibility. The cybersecurity CISO fosters a culture of security awareness throughout the organization. Given the current talent scarcity in digital security, developing internal capabilities and utilizing external resources are strategies leaders in information security are implementing to address skill deficiencies and enhance team performance.
FAQs:
- What are the key responsibilities of a CISO in relation to CMMC compliance?
- How can Chief Information Security Officers ensure their organizations are prepared for cybersecurity incidents?
- What strategies can be implemented to foster a culture of security awareness within an organization?
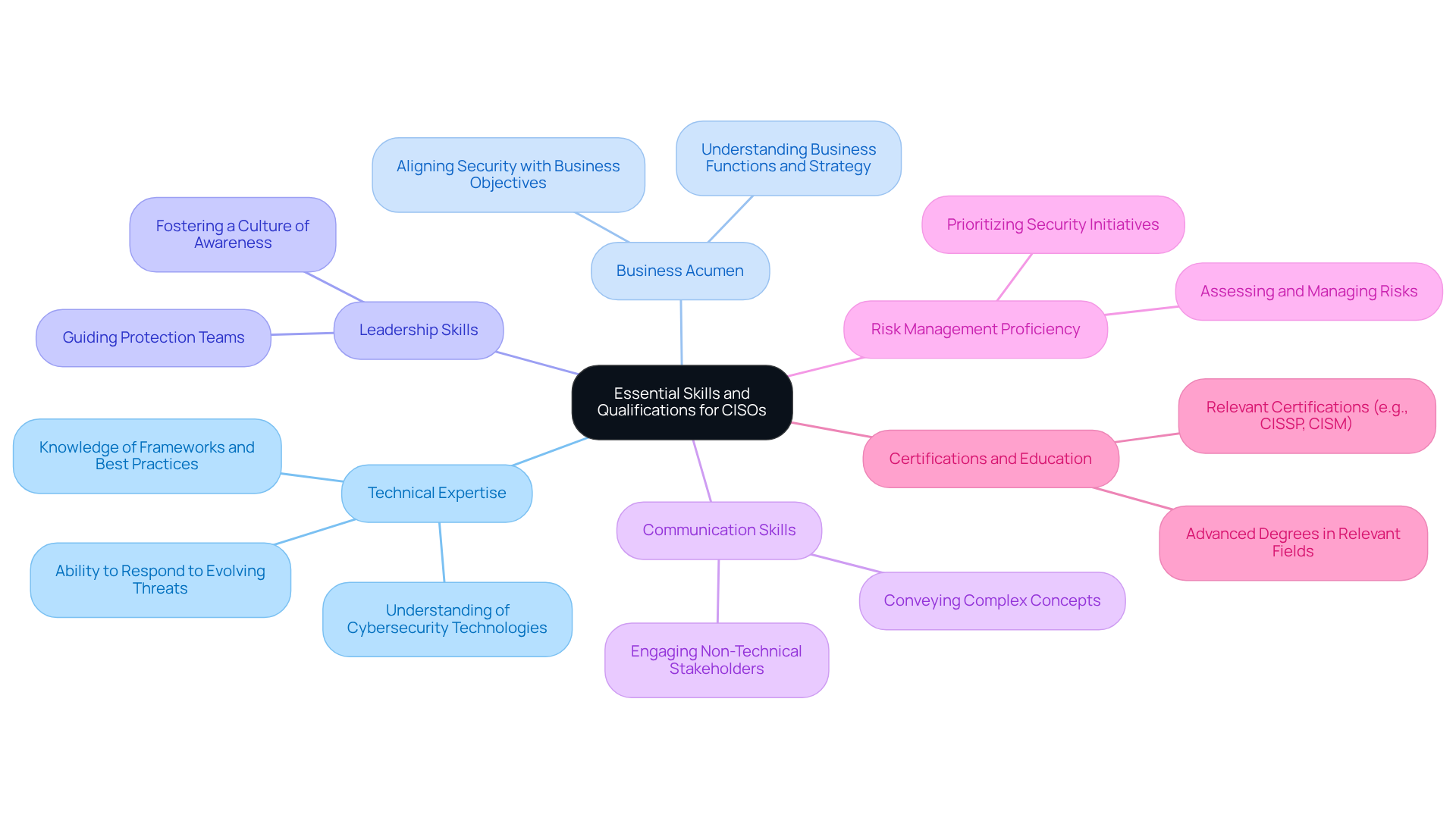
Identify Essential Skills and Qualifications for CISOs
To be effective, a cybersecurity CISO must possess a unique combination of skills and qualifications. Here’s a closer look at what makes a successful CISO:
-
Technical Expertise: A robust understanding of cybersecurity technologies, frameworks, and best practices is essential. This expertise enables the cybersecurity CISO to implement effective protective measures and respond to evolving threats.
-
Business Acumen: Aligning protection initiatives with business objectives is crucial. To ensure that security initiatives align with overall organizational goals, a cybersecurity CISO must have a strong grasp of business functions and strategy.
-
Leadership Skills: Effective guidance is vital for managing protection teams and fostering a culture of awareness throughout the organization. Cybersecurity CISOs must inspire and lead their teams to prioritize cybersecurity.
-
Communication Skills: The ability to convey complex protection concepts to non-technical stakeholders is essential. Cybersecurity CISOs must ensure that security is understood at every level of the organization, enabling informed decision-making.
-
Risk Management Proficiency: Assessing and managing risks is a critical responsibility. Cybersecurity CISOs must prioritize security initiatives based on their potential impact, ensuring effective allocation of resources.
-
Certifications and Education: Many CISOs hold advanced degrees in information security, information technology, or business administration, complemented by relevant certifications such as CISSP, CISM, or specialized credentials for CISOs. This educational background equips them with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of cybersecurity management as a cybersecurity CISO.
Statistics reveal that as of 2020, 56% of U.S. healthcare organizations employed a CISO, reflecting the growing recognition of this role's importance across industries. Moreover, the number of cybersecurity CISOs in Fortune 500 companies has surged by over 300% since 1995, underscoring the rising demand for cybersecurity CISOs.
However, challenges abound. The average tenure for a cybersecurity CISO is only 26 months, with 88% of these professionals operating in moderate to high-stress conditions. Additionally, 80% of cybersecurity CISOs feel they function with an inadequate budget for security measures, highlighting the financial strains that accompany their responsibilities as cybersecurity CISOs.
Continuous professional development and adaptation to the rapidly changing cybersecurity landscape are essential for success in this role. Are you ready to ensure your organization is equipped with the right leadership in cybersecurity?
Conclusion
The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) has become an indispensable leader within organizations, tasked with steering comprehensive cybersecurity strategies that align seamlessly with business objectives. This role has evolved from a primarily technical focus to encompass a broader mandate, including risk management, compliance, and cultivating a culture of awareness throughout the organization. As cyber threats grow increasingly sophisticated, the CISO's influence on organizational resilience and security posture is more critical than ever.
Key insights throughout this article underscore the significant responsibilities of the CISO, such as:
- Formulating protection guidelines
- Managing risks
- Ensuring effective incident response
The evolution of the CISO role highlights a shift towards strategic leadership, with an increasing emphasis on communication and collaboration with executive management. Notably, statistics reveal that organizations with a CISO reporting directly to the CEO experience fewer security incidents, underscoring the importance of leadership alignment in cybersecurity efforts.
In a landscape where the demands on cybersecurity leaders are intensifying, the need for effective CISOs is paramount. Organizations must prioritize investing in skilled professionals who possess a unique blend of technical expertise, business acumen, and leadership capabilities. As the cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve, ensuring that the CISO role is filled with qualified individuals will be essential in safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining compliance. Embracing this leadership role not only protects assets but also fortifies the organization’s overall strategic framework against emerging threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)?
The CISO is responsible for shaping and executing an organization's information protection strategy, safeguarding sensitive data, ensuring compliance with laws, and aligning security initiatives with business objectives.
Why is the role of the CISO becoming more important?
As cyber threats become more sophisticated and regulatory demands increase, the responsibilities of the CISO have expanded significantly, making their role crucial in mitigating risks and enhancing organizational resilience against cyber incidents.
What is the expected trend for CISOs by 2025?
By 2025, it is expected that 84% of CISOs will prioritize operational measures, focusing on immediate threat response as well as long-term strategic planning.
How does the reporting structure of a CISO affect cybersecurity incidents?
Organizations where the CISO reports directly to the Chief Executive Officer experience 20% fewer incidents, highlighting the importance of leadership alignment in effective cybersecurity measures.
What is the primary vulnerability identified by CISOs?
66% of CISOs identify human error as the primary vulnerability, indicating the need for a strong focus on employee training and cybersecurity awareness.
What percentage of successful cyber attacks are attributed to human error?
Case studies show that 90% of successful cyber attacks originate from human error, emphasizing the need for comprehensive training and a proactive risk management approach.
How does the CISO contribute to compliance and security?
The CISO plays a vital role in ensuring that the organization meets regulatory standards and is prepared to respond effectively to emerging threats, thereby bolstering overall security and compliance efforts.




